
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The full name of dUMP, UMP, CDP, AMP, and ATP has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Composition of
Sugar: In both DNA and RNA, sugar portion is found. In DNA, the sugar is D-ribose, where at 2’hydroxyl group is absent and in RNA, the hydroxyl group is present at 2’.
Nitrogenous bases: Five types of nitrogenous bases (has unique one-letter code A, G, T, U, and C) are derived from two parent compounds called purine and pyrimidine. The purine derivatives are Adenine and Guanine are two fused nitrogen containing rings. The pyrimidine derivatives are Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil are only one nitrogen containing six-membered ring. Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine are the nitrogenous bases present in DNA. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil are the nitrogenous bases present in RNA.
Nucleotide: (Nucleoside + phosphate)
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nuclei acids; monomers of DNA and RNA
Nucleoside and its naming: The combination of monosaccharide (sugar) and nitrogenous base is known as nucleoside. The nucleoside names are the nitrogenous base name modified with criteria. While naming nucleoside of purine derivatives the suffix ‘-osine’ is included and for pyrimidine derivatives the suffix ‘-idine’ is used. No prefix used for the nucleosides containing ribose and the prefix ‘deoxy-’ is used for deoxyribose.
Naming nucleotide: At the end of the nucleoside, phosphate group is added. For example, 5’-monophosphate means adding one phosphate group at 5’carbon in the sugar ring. Uridine monophosphate can be written as UMP.
Numbering the atoms in sugar and base rings:
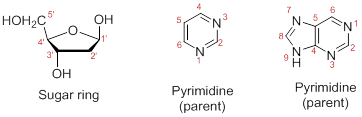
In order to distinguish the atoms in the sugar of a nucleoside and atoms of a base ring, numbers without prime is used for atoms in the base ring and numbers with prime used for the atoms in the sugar ring.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- Background Freezing isn't the only challenge in cryopreservation - thawing can be just as difficult. A microwave oven seems like a nice solution, since it deposits energy quickly and microwaves are non-ionizing radiation (they do not cause DNA mutation). However, water absorbs microwaves more effectively than ice does, meaning that the portion of an organ that has already melted will get warmer at a higher rate than the remaining ice – the opposite of what we want! - The transmission of radiation through a weakly absorbing material such as ice or water can be modeled by Beer's law, which assumes that the rate of absorption at a depth x is proportional to the local radiation intensity I(x) times an absorption coefficient, which is often written as μ or a or just µ). Noting that absorption decreases the intensity, we can write a differential equation a Solving the differential equation with the boundary condition on the surface being gives the relationship For a standard microwave oven…arrow_forward3. Dry air is inhaled at a rate of 10 liter/min through a trachea with a diameter of 20 mm and a length of 125 mm. The inner surface of the trachea is at a normal body temperature of 37°C and may be assumed to be saturated with water. a. Assuming steady, fully developed flow in the trachea, estimate the mass transfer convection coefficient. b. Estimate the daily water loss (liter/day) associated with evaporation in the trachea.arrow_forward1. Conceptual questions a. What dimensionless group describes the relative importance of convection versus diffusion. Explain the physical basis of this group. b. For mass transfer from a flowing fluid to a reactive surface, explain how convection increases the flux of solute to the surface.arrow_forward
- Assessment +1501 pts /1600 Resources Solution ? Hint Sub bo Each pictured Lewis structure is invalid. Identify the error in each case. O Macmillan Learning :0▬▬0: Answer Bank wrong electron total :0- :F======F: octet-rule violation N :0:arrow_forward[s] mM V (M/s) Uninhibited 0.333 1.65 x 107 1.05 x 107 V (M/s) x 10' Inhibitor A V (M/s) x 107 Inhibitor B 0.794 x 107 0.40 1.86 x 107 1.21 x 107 0.893 x 107 0.50 2.13 x 107 1.43 x 107 1.02 x 107 0.666 2.49 x 107 1.74 x 107 1.19 x 107 1.0 2.99 x 107 2.22 x 107 1.43 x 107 2.0 3.72 x 107 3.08 x 107 1.79 x 107arrow_forwardFor a Michaelis-Menten reaction, k₁-5 x 10'/M-s, k.-2 x 10%/s, and k₂-4 x 10²/s. a) Calculate the Ks and KM for this reaction. b) Does substrate binding achieve equilibrium or steady state?arrow_forward
- Assume that an enzyme-catalyzed reaction follows the scheme shown: E+S SES →E + P k₁ = 1 x 109/M-s k-1=2.5 x 10%/s k₂ = 3.4 x 107/s What is the dissociation constant for the enzyme-substrate, K,? What is the Michaelis constant, Km, for this enzyme? What is the turnover number, Keat, for this enzyme? What is the catalytic efficiency for the enzyme? If the initial Et concentration is 0.25mM, what is Vmax?arrow_forwardAn enzyme lowers the activation energy, (AG) of a reaction from 50.0 kcal/mol to 40.0 kcal/mol. Calulate the catalytic power at 310K. (R-1.987x10 kcal/mol)arrow_forwardDraw a typical axodendritic synapse, including a specific neurotransmitter of your choice, its associated postsynaptic receptors (indicating whether they are ionotropic or metabotropic), and any associated reuptake transporters or degradation enzymes. Please include a description of what specific steps would occur as an action potential reaches the axonal terminal.arrow_forward
- Give a full arrow pushing mechanism of the spontaneous redox reaction between NAD+/NADH and oxaloacetate/malate. Please include diagram drawing of the mechanism! (Thank You!)arrow_forward18. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following series of reactions? 1. BH3 2. H2O2, NaOH H₂CrO4 CH2N2 oro ororos A B C D Earrow_forward17. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following series of reactions? CI benzyl alcohol OH PBr3 Mg 1. CO2 SOCl2 ? ether 2. H+, H₂O CI Cl HO OH CI Cl A B C D Earrow_forward
- Essentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:Cengage
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning  Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





