
FIGURE 26.9 Using the terms provided, label the surface features of the (a) anterior view of the body and (b) posterior view of the body (Boldface indicates bony features: not boldface indicates soft tissue features.)
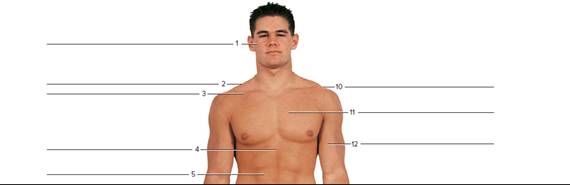
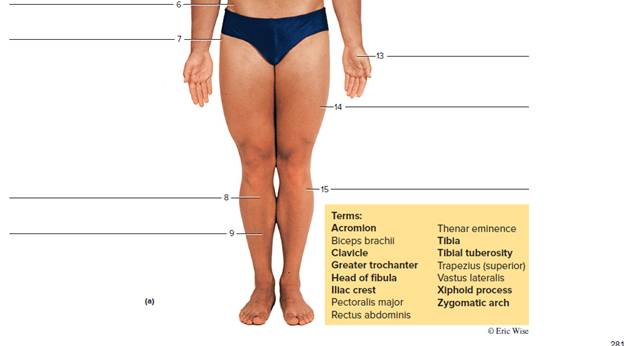
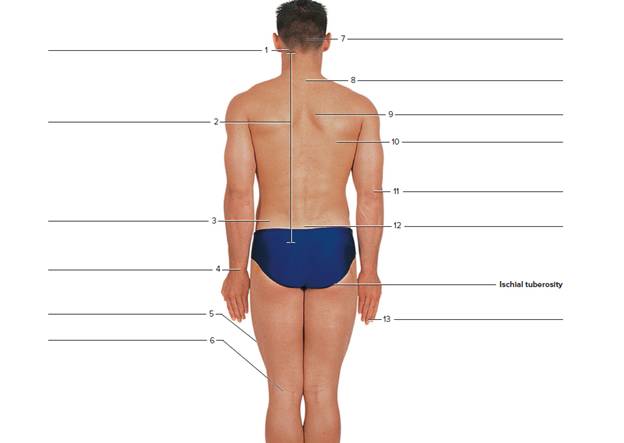
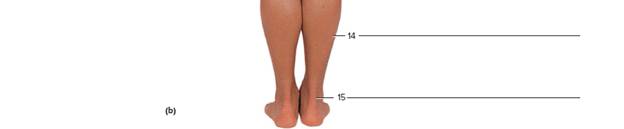
Terms: C7 lliac crest Olecranon process Calcaneal tendon lliotibiai tract PopiteaI fossa Distal Interphalangeal Joint (DIP) Inferior angle of scapula Sacrum Erector spinae Mastoid process Soleus External occipItal protuberance Medial border of scapula Stylold process of ulna
To label:
The given image in anterior and posterior view of the human body.
Introduction:
Skeleton is a rigid bony or cartilaginous protective framework in an organism. It generally protects the soft tissues and internal organs of a vertebrate.The human skeleton plays six main roles that include the movement, protection, support, storage of minerals, production of blood cells, and endocrine regulation.
Explanation of Solution
Muscle is a bundle or band of fibrous tissue present in a human or animal body. It can contract and move in preserving the position of body parts. Muscles play a role in the production of force and motion. They are mainly responsible for sustaining and shifting posture, locomotion.
The anterior view:
1. Zygomatic arch:
Zygomatic arch is a bridge of bone that extends from the temporal bone at around the head side to the upper jawbone in front and has the cheek or zygomatic bone as its main region.
2. Trapezius:
A large paired surface muscle is the trapezius. It spreads longitudinally from the region of occipital bone to the area of lower thoracic vertebrae and across the spine of the scapula. It is a flat, broad, and superficial muscle.
It is responsible for rotating, moving, and stabilizing the shoulder blade or scapula.
3. Clavicle:
The pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle is a set of bones located in the appendicular skeleton. It joins to the arm on each side. Pectoral girdle consists of the scapula, coracoid and clavicle.
Clavicle is a bone of the pectoral girdle usually helps to join the scapula and sternum is known as the collarbone.
4. Xiphoid process:
It is a cartilaginous section located at the inferior end of the sternum. It is not associated to any ribs, steadily ossifies through the adult life.
5. Rectus abdominis:
It is also known as abdominal muscle. It is a paired muscle. It runs vertically on both the sides of the anterior wall of the abdomen (in human) in addition to some other mammals. It flexes trunk of the body or the spinal column.
6. Iliac crest: It is a curved superior boundary of the ilium. It is the biggest of the three bones. It merges to shape the hip bone or os coxa.
7. Greater trochanter:
A trochanter is a type of tubercle of the femur. It is close to the joint with the hip bone. These trochanters play a great role as a muscle attachment site in most of the mammals and humans. Humans have three trochanters. Though the normal anatomic has only the greater and lesser trochanters. A trochanter is a very huge projection on a bone.
8. Tibial tuberosity:
Tuberosity is a moderate distinction where the connective tissues and muscles join. Its role is similar to the trochanter. For example the tibial tuberosity. The tuberosity of the tibia or tibial tuberosity or tibial tubercle is a large oblong elevation on the proximal, anterior aspect of the tibia, just below where the anterior surfaces of the lateral and medial tibial condyles end.
9. Tibia:
It is the inner and characteristically larger of the two bones located between the knee and the ankle. It is parallel with the fibula.
10. Acromion:
It is a bony process located on the scapula or shoulder blade. It expands laterally over the shoulder joint along with the coracoid process. It is an extension of the scapular spine that hooks over anteriorly.
11. Pectoralis major:
The pectoralis major is a thick and fan-shaped muscle. It is situated at the human body chest. It forms up the bulkiness of the muscles of the chest. It is located under the breast.
12. The biceps:
The brachialis anticus or the brachialis is a muscle located in the upper arm. It flexes the elbow joint. It is located deeper than the biceps brachii. It makes up the region of the floor of the location that is known as the cubital fossa. The brachialis functions as the major mover of elbow flexion. The flexor group includes the biceps brachii, brachialis, and the brachioradialis. It helps in the bending of the arm by declining the angle present between the upper arm and the forearm.
13. Thenar eminence:
It is classified as the group of muscles located on the human hand palm. It is present at the thumb base.
14. Vastus lateralis:
The vastus lateralis is also known as the vastus externus. It is the largest and powerful region of the quadriceps femoris. It is a muscle of the thigh or lower limb. Along with the other muscles of quadriceps group. It helps to enlarge the knee joint and moves the lower leg forward.
15. Head of fibula:
The fibula (or calf bone) is a leg bone found on the lateral side of the tibia. It is joined above and below to tibia. It is the smaller than tibia in proportion to its length. Fibula is also the slenderest of all the long bones. The head region is the uppermost region of fibula.
The posterior view:
1. Mastoid process:
It is a conical eminence of the temporal bone. It is present behind the ear. It is attached with the help of neck muscles. It contains air spaces connected to the middle ear.
2. Medial border of scapula:
The shoulder blade or scapula or wing bone is the well-known flat triangular bone located at the back of the shoulder. The pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle is a set of bones located in the appendicular skeleton. It joins to the arm on each side. Pectoral girdle consists of the scapula, coracoid and clavicle. It has a medial border.
3. Iliac crest: It is a curved superior boundary of the ilium. It is the biggest of the three bones. It merges to shape the hip bone or os coxa.
4. Styloid process of ulna:
The ulna bone is a long bone located in the forearm. It stretches from the region of elbow to the smallest finger. In a normal anatomical location it lies on the medial side of the forearm. It extends parallel to the radius (the other long bone of the forearm). Thus, ulna is a bone located in the upper limb. At the distal end of the forearm, the styloid process of the ulna is present. This process projects from the medial portion and back portion of the bone;
5. Iliotibial tract:
It is a longitudinal fibrous support associated with the fascia lata (deep fascia of the thigh). The function of this tract is to abduct, extend, and laterally turn around the hip.
6. Popliteal fossa:
The popliteal fossa is also known as the kneepit. It is a superficial depression. It is situated at the backside of the knee joint.
7. External occipital protuberance:
The external occipital protuberance is the nearest the middle of the squamous portion of the occipital bone. It has a highest point that is known as the inion.
8. Vertebra prominens (C7):
It has a distinct long and well-known spinous process. It is palpable from the surface of the skin.Its provides the support to the skull and helps in the head movements back and forth. It also possesses the side to side head movements and also protects the spinal cord.
9. Erector spinae:
These are a group of long muscles which arise near the sacrum and expand vertically up to the length of the back.
10. Inferior angle of scapula:
It is formed by the combination of the lateral and medial borders of the scapula. It is a thick and rough surface. Its posterior side surface affords the link to the teres major and often to a small number of latissimus dorsi fibers.
11. Olecranon process:
It is a process of the ulna. It makes the elbow outer bump. It fits into the fossa of the humerus bone during the extension of arm.
12. Sacrum:
It is a triangular bone located in the lower part of the back. It is formed from the fused vertebrae. It is located between the two hip bones of the pelvis region.
13. Distal interphalangeal joints (DIP):
The articulations present between the hand or foot phalanges are the distal interphalangeal joints.These are in fact the most common position for osteoarthritis (OA) on the body.
14. Soleus:
It is a strong muscle located in the back portion of the lower leg. It extends from just inferior the knee to the heel. It helps in standing and walking.
15. The calcaneal tendon:
It is also known as an Achilles tendon. It is a hard band of the fibrous tissue. It attaches the calf muscles to the calcaneus or heel bone. The soleus and gastrocnemius muscles combine into a single band of tissue that forms the Achilles tendon at the inferior end of the calf.
Skeleton is a rigid bony or cartilaginous protective framework in an organism. It generally protects the soft tissues and internal organs of a vertebrate.Muscle is a bundle or band of fibrous tissue present in a human or animal body. It can contract and move in preserving the position of body parts.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
LABORATORY MANUAL FOR HUMAN ANATOMY & PH
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
HUMAN ANATOMY
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- One of the ways for a cell to generate ATP is through the oxidative phosphorylation. In oxidative phosphorylation 3 ATP are produced from every one NADH molecule. In respiration, every glucose molecule produces 10 NADH molecules. If a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forwardIf a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forwardHow do i know which way the arrows go?arrow_forward
- Identify the indicated structure (Saprolegnia). a. antheridium O b. oospore c.sperm d. auxospore e. tetraspore Of. zygosporearrow_forwardUsing information from the primary literature (several references have been provided as a starting point below) please answer the following question: Based on your review of the literature on rewilding, what are the major scientific pros and cons for rewilding? Please note that the focus of this assignment are the (biological) scientific issues associated with rewilding. As will be discussed in class, there are a number of non-scientific issues involved or implicated in rewilding, all ultimately affecting the public acceptability of rewilding. Although these issues are important – indeed, critical – in this assignment you should focus on the biological science issues and questions. Details: You must enumerate at least two pros and at least two cons. Your answer should be no more than 500 well-chosen words, excluding references. Think carefully about how best to organize and structure your answer. Aim for high information density: say a lot, but say it succinctly. Recall Nietzche’s…arrow_forwardUsing information from the primary literature (several references have been provided as a starting point below) please answer the following question: Based on your review of the literature on rewilding, what are the major scientific pros and cons for rewilding? Please note that the focus of this assignment are the (biological) scientific issues associated with rewilding. As will be discussed in class, there are a number of non-scientific issues involved or implicated in rewilding, all ultimately affecting the public acceptability of rewilding. Although these issues are important – indeed, critical – in this assignment you should focus on the biological science issues and questions. Details: You must enumerate at least two pros and at least two cons. Your answer should be no more than 500 well-chosen words, excluding references. Think carefully about how best to organize and structure your answer. Aim for high information density: say a lot, but say it succinctly. Recall Nietzche’s…arrow_forward
- Now draw a rough sketch of what the control data might look like if in addition to the specific binding, there was also a considerable amount of nonspecific binding (again using a normal dose/response curve) (do % total bound ligand vs concentration)arrow_forwardWhat are functions of cuboidal cells in the kidney? Select all that apply. Concentration of gases Dilution of chemicals Secretion of molecules Nutrition to tissues Support of tissues Absorption of moleculesarrow_forwardquestion1 In plants, epithelial tissue is only found as the outermost cell layer and acts as a barrier. In humans, epithelial tissue is found inside the body as well as on the surface. What function(s) does/do epithelial tissue carry out in humans? Select all that apply. Waste storage Filtration Oxygen transport Protection Diffusion Osmosis Absorptionarrow_forward
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Sectional Anatomy: An Imaging App...BiologyISBN:9781133960867Author:Denise L. LazoPublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Fundamentals of Sectional Anatomy: An Imaging App...BiologyISBN:9781133960867Author:Denise L. LazoPublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





