
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of carbon atom, total C-C σ bonds and π bonds with 1â—¦,2â—¦,3â—¦ and 4â—¦ carbon atoms should be determined.
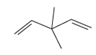
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form same energy and same shape hybrid orbitals which form covalent bond with overlapping of atomic orbitals of other atoms. The number of
1â—¦ orPrimary C atom = C atom which is bonded with one another C atom
2â—¦ orSecondary C atom= C atom which is bonded with two other C atoms
3â—¦ orTertiary C atom= C atom which is bonded with three other C atoms
4â—¦ or Quaternary C atom= C atom which is bonded with four other C atoms
(b)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of carbon atom, total C-C σ bonds and π bonds with 1â—¦, 2â—¦,3â—¦ and 4â—¦ carbon atoms should be determined.
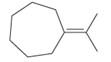
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form same energy and same shape hybrid orbitals which form covalent bond with overlapping of atomic orbitals of other atoms. The number of chemical bonds formed by the atom always determine type of hybridization. Sigma bonds could only form by hybrid orbitals whereas pi bonds are always formed by overlapping of un-hybrid orbitals hence hybridization is not part of pi bond formation.
1â—¦ or Primary C atom = C atom which is bonded with one another C atom
2â—¦ or Secondary C atom= C atom which is bonded with two other C atoms
3â—¦ or Tertiary C atom= C atom which is bonded with three other C atoms
4â—¦ or Quaternary C atom= C atom which is bonded with four other C atoms
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of carbon atom, total C-C σ bonds and π bonds with 1â—¦, 2â—¦,3â—¦ and 4â—¦ carbon atoms should be determined.
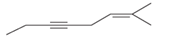
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form same energy and same shape hybrid orbitals which form covalent bond with overlapping of atomic orbitals of other atoms. The number of chemical bonds formed by the atom always determine type of hybridization. Sigma bonds could only form by hybrid orbitals whereas pi bonds are always formed by overlapping of un-hybrid orbitals hence hybridization is not part of pi bond formation.
1â—¦ or Primary C atom = C atom which is bonded with one another C atom
2â—¦ or Secondary C atom= C atom which is bonded with two other C atoms
3â—¦ or Tertiary C atom= C atom which is bonded with three other C atoms
4â—¦ or Quaternary C atom= C atom which is bonded with four other C atoms
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
Selected Solutions Manual For General Chemistry: Principles And Modern Applications
- Problem 54, could you please explain it in detail? Thank you! Step by step, I'm really confused, so please don't make it overly complex. My question is to visually draw it out and demonstrate it to me; I'm confused about that problem, please (not just in words) but demonstrate it to me in all due essence (visually) with descriptions.arrow_forwardExplain the types of electromeric effects +E and -E.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the electromeric effect (Organic Chemistry)arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. (CH3)2NH, TSOH Drawingarrow_forwardSo, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forward
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





