
Concept explainers
a.
To use the given information to conclude that two
a.
Answer to Problem 6CE
Explanation of Solution
Given:
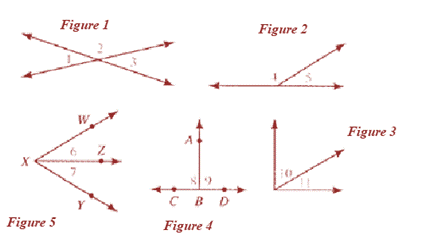
In Figure 1:
In Figure 2:
No pair of angles are congruent. Instead
In Figure 3:
No pair of angles are congruent.
In Figure 4:
In Figure 5:
Conclusion:
So, the conclusion is
b.
To name or state the definition or theorem that justifies the conclusions in part ( a ).
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
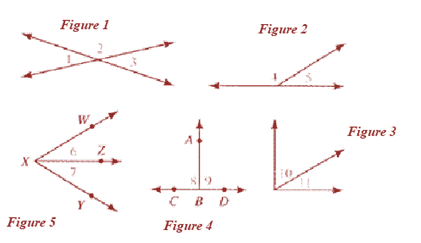
In Figure 1:
Vertically opposite angles: The angles formed opposite each other on intersection of two lines. They are always equal.
In Figure 4:
But
Linear Pair: Two angles are said to be linear pair if they are adjacent angles produced by two intersecting lines. The measure of a straight angle is
In Figure 5:
Angle Bisector: It is a line segment that divides the given angle into two halves.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the concepts used are Vertically Opposite Angles, Linear Pair and Angle Bisector.
Chapter 2 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Can you cut the 12 glass triangles from a sheet of glass that is 4 feet by 8 feet? If so, how can it be done?arrow_forwardCan you cut 12 glass triangles from a sheet of glass that is 4 feet by 8 feet? If so, draw a diagram of how it can be done.arrow_forwardIn triangle with sides of lengths a, b and c the angle a lays opposite to a. Prove the following inequality sin a 2√bc C α b a Warrow_forward
- Find the values of x, y, and z. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 8, 23arrow_forward11 In the Pharlemina's Favorite quilt pattern below, vega-pxe-frame describe a motion that will take part (a) green to part (b) blue. Part (a) Part (b)arrow_forward5. 156 m/WXY = 59° 63 E 7. B E 101 C mFE = 6. 68° 8. C 17arrow_forward
- 1/6/25, 3:55 PM Question: 14 Similar right triangles EFG and HIJ are shown. re of 120 √65 adjacent E hypotenuse adjaca H hypotenuse Item Bank | DnA Er:nollesup .es/prist Sisupe ed 12um jerit out i al F 4 G I oppe J 18009 90 ODPO ysma brs & eaus ps sd jon yem What is the value of tan J? ed on yem O broppo 4 ○ A. √65 Qx oppoEF Adj art saused taupe ed for yem 4 ○ B. √65 29 asipnisht riod 916 zelprisht rad √65 4 O ○ C. 4 √65 O D. VIS 9 OD elimiz 916 aelonsider saused supsarrow_forwardFind all anglesarrow_forwardFind U V . 10 U V T 64° Write your answer as an integer or as a decimal rounded to the nearest tenth. U V = Entregararrow_forward
- Find the area of a square whose diagonal is 10arrow_forwardDecomposition geometry: Mary is making a decorative yard space with dimensions as shaded in green (ΔOAB).Mary would like to cover the yard space with artificial turf (plastic grass-like rug). Mary reasoned that she could draw a rectangle around the figure so that the point O was at a vertex of the rectangle and that points A and B were on sides of the rectangle. Then she reasoned that the three smaller triangles resulting could be subtracted from the area of the rectangle. Mary determined that she would need 28 square meters of artificial turf to cover the green shaded yard space pictured exactly.arrow_forward7. 11 m 12.7 m 14 m S V=B₁+ B2(h) 9.5 m 16 m h+s 2 na 62-19 = 37 +, M h² = Bu-29arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

