
Concept explainers
a.
To determine two
a.
Answer to Problem 1CT
Two angles are vertical angles, then they are congruent
Explanation of Solution
When two lines intersect to make an X, angles on opposite sides of the X are called vertical angles. These angles are equal, and here is the official theorem that tells you so.
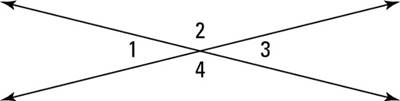
Vertical angles are congruent:
If two angles are vertical angles, then they are congruent (see the above figure).
Vertical angles are one of the most frequently used things in proofs and other types of geometry problems, and they are one of the easiest things to spot in a diagram. Do not neglect to check for them!
b.
To determine two angles are congruent if they are vertical angle (Converse).
b.
Answer to Problem 1CT
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The converse is "If two angles are congruent, they are vertical angles"
This is false. For example, two angles of an isosceles
Chapter 2 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

