
Concept explainers
Calculate the equivalent capacitance between points a and b in Figure P26.77. Notice that this system is not a simple series or parallel combination. Suggestion: Assume a potential difference Δv between [joints a and b. Write expressions for Δvab in terms of the charges and capacitances for the various possible pathways from a to b and require conservation of charge for those capacitor plates that are connected to each other.
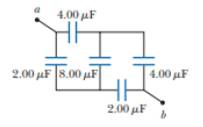
The equivalent capacitance between points
Answer to Problem 26.77CP
The equivalent capacitance between points
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The potential difference between the points
From given Figure, the capacitor
Since, capacitors
Formula to calculate the charge on the capacitor is,
Here,
The charge on the capacitor
Here,
The charge on the capacitor
Here,
The charge on the capacitor
Here,
The charge on the capacitor
Here,
Since, the charge on
Substitute
Since, the charge on
Substitute
The potential across the capacitor
Substitute
The ratio of the capacitors
Here,
Substitute
The ratio of the capacitors
Here,
Substitute
Equate the left hand side of equation (2) and equation (3).
Thus, the potential difference across the capacitor
Thus, the modified electrical circuit diagram is shown below.
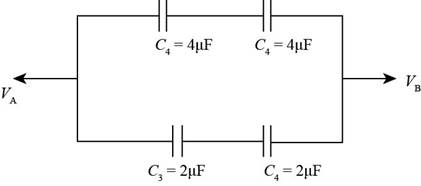
Figure (1)
The upper part of the capacitors is in series. So, the equivalent capacitance for series connection is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance for series connection is
The lower part of the capacitors is in series. So, the equivalent capacitance for series connection is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of lower part for series connection is
Now the equivalent capacitances of the upper and lower parts are in parallel. Hence, the equivalent capacitance of the system is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equivalent capacitance between points
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
PHYSICS 1250 PACKAGE >CI<
- pls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward2. Max is swimming across a river that is 42.6 m wide. He can swim at 1.6 m/s and heads 20° to the right of the vertical. There is a current pushing him more to the right and it has a speed of 0.30 m/s. Determine the time it takes him to cross the river and find out how far downstream he ends up. Draw the diagram.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





