
Concept explainers
For (he system of four capacitors shown in Figure P26.19. find (a) the total energy stored in the system and (b) the energy stored by each capacitor, (c) (Compare the sum of the answers in part (b) with your result to part (a) and explain your observation.
(a)
The energy stored in the system.
Answer to Problem 26.56AP
The energy stored in the system is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electric potential in the system is
The Figure of the circuit diagram is shown below.
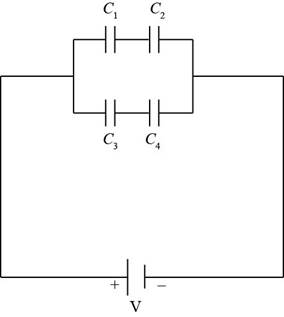
Figure (1)
Since, the capacitors
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of the first row is
Since, the capacitors
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of the second row is
Since, the first and second rows are in parallel to each other. So, the equivalent capacitance of the system is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of the system is
Formula to calculate the energy stored in the system is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the energy stored in the system is
(b)
The energy stored by each capacitor.
Answer to Problem 26.56AP
The energy stored in capacitors
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electric potential in the system is
Since, the electric potential through each capacitor is same.
Formula to calculate the charge on the first row of capacitor is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the charge on the first row of capacitor is
Formula to calculate the energy stored is,
Here,
The energy stored in capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the energy stored in capacitor
The energy stored in capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the energy stored in capacitor
Formula to calculate the charge on the first row of capacitor is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the charge on the first row of capacitor is
The energy stored in capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the energy stored in capacitor
The energy stored in capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the energy stored in capacitor
Conclusion:
Therefore, the energy stored in capacitors
(c)
The comparison of the sum of the energy in part (b) with energy of part (a) and explain it.
Answer to Problem 26.56AP
The sum of the energy of par (b) is same as the energy in part (a).
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electric potential in the system is
The sum of the energy of the part (b) is,
Substitute
The sum of the energy of par (b) is same as the energy in part (a).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the sum of the energy of par (b) is same as the energy in part (a).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
PHYSICS 1250 PACKAGE >CI<
- Two objects get pushed by the same magnitude of force. One object is 10x more massive. How does the rate of change of momentum for the more massive object compare with the less massive one? Please be able to explain why in terms of a quantitative statement found in the chapter.arrow_forwardA box is dropped on a level conveyor belt that is moving at 4.5 m/s in the +x direction in a shipping facility. The box/belt friction coefficient is 0.15. For what duration will the box slide on the belt? In which direction does the friction force act on the box? How far will the box have moved horizontally by the time it stops sliding along the belt?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA toy car speeds up at 1.0 m/s2 while rolling down a ramp, and slows down at a rate of 2.0 m/s2 while rolling up the same ramp. What is the slope of the ramp in degrees? Grade in %? The friction coefficient?arrow_forwardPlz solution should be complete No chatgpt pls will upvote .arrow_forward
- A box with friction coefficient of 0.2 rests on a 12 foot long plank of wood. How high (in feet) must one side of the plank be lifted in order for the box to begin to slide?arrow_forwardWhat is a good general rule to follow in order to find the best choice of coordinate system to solve a dynamics problem?arrow_forwardWhat is the meaning of a first order approximation?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





