
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321982582
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 26, Problem 26.70P
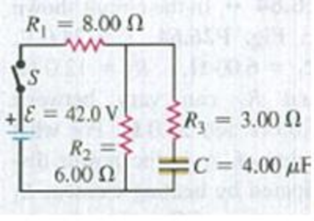
The capacitor in Fig. F26.70 is initially uncharged. The switch S is closed at t = 0. (a) Immediately after the switch is closed, what is the current through each resistor? (b) What is the final charge on the capacitor?
Figure P26.70
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule06:23
Students have asked these similar questions
In Figure P28.67, suppose the switch has been closed for a length of time sufficiently long for the capacitor to become fully charged. (E = 8.50 V, r1 = 10 kN, and r2 = 16 kN.)
10.0 µF
3.00 k2
Figure P28.67
(a) Find the steady-state current in each resistor.
I = 327
HA
I2 = 327
HA
13-kn = 0
HA
(b) Find the charge Q on the capacitor.
52
(c) The switch is opened at t = 0. Write an equation for the current IR, in R2 as a function of time.
O (327 HA)e-t/(0.190 s)
O (275 µA)et/(0.190 s)
O (275 µA)e-t/(0.190 s)
O (327 µA)et/(0.190 s)
(d) Find the time that it takes for the charge on the capacitor to fall to one-fifth its initial value.
ms
SN
10. A 11.0 μF capacitor is connected in series to a 50.0-V battery, a
is flowing through the resistor, 5.00 ms after closing the switch?
Amp
resistor, and a switch. What is the current that
550-52 resis
0 ssf60
ssf60 ss.
50 ssf60
In Figure P28.67, suppose the switch has been closed for a length of time sufficiently long for the capacitor to become fully charged. (E = 8.50 V, r1 = 10 kN, and r2 = 16 kN.)
10.0 µF
3.00 k2
Figure P28.67
(a) Find the steady-state current in each resistor.
I1 = 1.32
Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. µA
I2 = 4.32
Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. µA
I3-ko = 0
HA
(b) Find the charge Q on the capacitor.
8.83
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. µC
(c) The switch is opened at t = 0. Write an equation for the current IR, in R, as a function of time.
O (327 µA)e-t/(0.190 s)
O (275 µA)et/(0.190 s)
O (275 µA)e-t/(0.190 s)
O (327 µA)et/(0.190 s)
(d) Find the time that it takes for the charge on the capacitor to fall to one-fifth its initial…
Chapter 26 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Ch. 26.1 - Suppose all three of the resistors shown in Fig....Ch. 26.2 - Subtract Eq. (1) from Eq. (2) in Example 26.6. To...Ch. 26.3 - You want to measure the current through and the...Ch. 26.4 - The energy stored in a capacitor is equal to...Ch. 26.5 - To prevent the circuit breaker in Example 26.14...Ch. 26 - In which 120-V light bulb does the filament have...Ch. 26 - Two 120-V light bulbs, one 25-W and one 200-W,...Ch. 26 - You connect a number of identical light bulbs to a...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. Q26.4, three...Ch. 26 - If two resistors R1 and R2 (R2 R1) are connected...
Ch. 26 - If two resistors R1 and R2 (R2 R1) are connected...Ch. 26 - A battery with no internal resistance is connected...Ch. 26 - A resistor consists of three identical metal...Ch. 26 - A light bulb is connected in the circuit shown in...Ch. 26 - A real battery, having nonnegligible internal...Ch. 26 - If the battery in Discussion Question Q26.10 is...Ch. 26 - Consider the circuit shown in Fig. Q26.12. What...Ch. 26 - Is it possible to connect resistors together in a...Ch. 26 - The battery in the circuit shown in Fig. Q26.14...Ch. 26 - In a two-cell flashlight, the batteries are...Ch. 26 - Identical light bulbs A, B, and C are connected as...Ch. 26 - The emf of a flashlight battery is roughly...Ch. 26 - Will the capacitors in the circuits shown in Fig....Ch. 26 - Verify that the time constant RC has units of...Ch. 26 - For very large resistances it is easy to construct...Ch. 26 - When a capacitor, battery, and resistor are...Ch. 26 - A uniform wire of resistance R is cut into three...Ch. 26 - A machine part has a resistor X protruding from an...Ch. 26 - A resistor with R1 = 25.0 is connected to a...Ch. 26 - A 42- resistor and a 20- resistor are connected in...Ch. 26 - A triangular array of resistors is shown in Fig....Ch. 26 - For the circuit shown in Fig. E26.6 both meters...Ch. 26 - For the circuit shown in Fig. E26.7 find the...Ch. 26 - Three resistors having resistances of 1.60 , 2.40...Ch. 26 - Now the three resistors of Exercise 26.8 are...Ch. 26 - Power Rating of a Resistor. The power rating of a...Ch. 26 - In Fig. E26.11, R1, = 3.00 , R2 = 6.00 , and R3=...Ch. 26 - In Fig. E26.11 the battery has emf 35.0 V and...Ch. 26 - Compute the equivalent resistance of the network...Ch. 26 - Compute the equivalent resistance of the network...Ch. 26 - In the circuit of Fig. E26.15, each resistor...Ch. 26 - Consider the circuit shown in Fig. E26.16. The...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.17, the voltage...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.18, = 36.0 V,...Ch. 26 - CP In the circuit in Fig. E26.19, a 20.0- resistor...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.20, the rate at...Ch. 26 - Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light...Ch. 26 - Light Bulbs in Series. A 60-W, 120-V light bulb...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.23, ammeter A1...Ch. 26 - The batteries shown in the circuit in Fig. E26.24...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.25 find (a) the...Ch. 26 - Find the emfs 1 and 2 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.27, find (a) the...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.28, find (a) the...Ch. 26 - The 10.00-V battery in Fig. E26.28 is removed from...Ch. 26 - The 5.00-V battery in Fig. E26.28 is removed from...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.31 the batteries...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.32 both batteries...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.33 all meters are...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.34, the 6.0-...Ch. 26 - The resistance of a galvanometer coil is 25.0 ,...Ch. 26 - The resistance of the coil of a pivoted coil...Ch. 26 - A circuit consists of a series combination of...Ch. 26 - A galvanometer having a resistance of 25.0 has a...Ch. 26 - A capacitor is charged to a potential of 12.0 V...Ch. 26 - You connect a battery, resistor, and capacitor as...Ch. 26 - A 4.60-F capacitor that is initially uncharged is...Ch. 26 - You connect a battery, resistor, and capacitor as...Ch. 26 - CP In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.43 both...Ch. 26 - A 12.4-F capacitor is connected through a 0.895-M...Ch. 26 - An emf source with = 120 V, a resistor with R =...Ch. 26 - A resistor and a capacitor are connected in series...Ch. 26 - CP In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.47 each...Ch. 26 - A 1.50-F capacitor is charging through a 12.0-...Ch. 26 - In the circuit in Fig. E26.49 the capacitors are...Ch. 26 - A 12.0-F capacitor is charged to a potential of...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.51, C = 5.90 F, ...Ch. 26 - Prob. 26.52ECh. 26 - A 1500-W electric beater is plugged into the...Ch. 26 - In Fig. P26.54, the battery has negligible...Ch. 26 - The two identical light bulbs in Example 26.2...Ch. 26 - Each of the three resistors in Fig. P26.56 has a...Ch. 26 - (a) Find the potential of point a with respect to...Ch. 26 - CP For the circuit shown in Fig. P26.58 a 20.0-...Ch. 26 - Calculate the three currents I1, I2, and I3...Ch. 26 - What must the emf in Fig. P26.60 be in order for...Ch. 26 - Find the current through each of the three...Ch. 26 - (a) Find the current through the battery and each...Ch. 26 - Consider the circuit shown in Fig. P26.63. (a)...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. P26.64, = 24.0 V,...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. P26.65, the current...Ch. 26 - In the circuit shown in Fig. P26.66 all the...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.67 employs a convention often used in...Ch. 26 - Three identical resistors are connected in series....Ch. 26 - A resistor R1 consumes electrical power P1 when...Ch. 26 - The capacitor in Fig. F26.70 is initially...Ch. 26 - A 2.00-F capacitor that is initially uncharged is...Ch. 26 - A 6.00-F capacitor that is initially uncharged is...Ch. 26 - Point a in Fig. P26.73 is maintained at a constant...Ch. 26 - The Wheatstone Bridge. The circuit shown in Fig....Ch. 26 - (See Problem 26.67.) (a) What is the potential of...Ch. 26 - A 2.36-F capacitor that is initially uncharged is...Ch. 26 - A 224- resistor and a 589- resistor are connected...Ch. 26 - A resistor with R = 850 is connected to the...Ch. 26 - A capacitor that is initially uncharged is...Ch. 26 - DATA You set up the circuit shown in Fig. 26.22a,...Ch. 26 - DATA You set up the circuit shown in Fig. 26.20....Ch. 26 - DATA The electronics supply company where you work...Ch. 26 - An Infinite Network. As shown in Fig. P26.83, a...Ch. 26 - Suppose a resistor R lies along each edge of a...Ch. 26 - BIO Attenuator Chains and Axons. The infinite...Ch. 26 - Assume that a typical open ion channel spanning an...Ch. 26 - In a simple model of an axon conducting a nerve...Ch. 26 - Cell membranes across a wide variety of organisms...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
27. (I) A spring has a spring constant k of 88.0 N/m. How much must this spring be compressed to store 45.0 J o...
Physics: Principles with Applications
Rooms A and B are the same size, and are connected by an open door. Room A, however, is warmer (perhaps because...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Answer Problems 3 through 5 by choosing one of the eight labeled acceleration vectors or selecting option I: = ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
A thin metal rod of length ℓ rotates with angular velocity ω about an axis through one end (Fig. 29–51). The ro...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Does the acceleration change as the ball rolls up the track? Would the acceleration vector you obtain differ if...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1. When is energy most evident?
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The- pair of capacitors in Figure P28.63 are fully charged by a 12.0-V battery. The battery is disconnected, and the switch is then closed. Alter 1.00 ms has elapsed, (a) how much charge remains 011 the 3.00-F capacitor? (b) How much charge remains on the 2.00-F capacitor? (c) What is the current in the resistor at this time?arrow_forwardIn Figure P29.81, N real batteries, each with an emf and internal resistance r, are connected in a closed ring. A resistor R can be connected across any two points of this ring, causing there to be n real batteries in one branch and N n resistors in the other branch. Find an expression for the current through the resistor R in this case.arrow_forwardA student makes a homemade resistor from a graphite pencil 5.00 cm long, where the graphite is 0.05 mm indiameter. The resistivity of the graphite is =1.38102/m . The homemade resistor is place inseries with a switch, a 10.00-mF capacitor and a 0.50-V power source, (a) What is the BC time constant of the circuit? (b) What is the potential drop across the pencil 1.00 s after the switch is closed?arrow_forward
- Consider a series RC circuit as in Figure P28.38 for which R = 1.00 M, C = 5.00 F, and = 30.0 V. Find (a) the time constant of the circuit and (b) the maximum charge on the capacitor after the switch is thrown closed. (c) Find the current in the resistor 10.0 s after the switch is closed.arrow_forwardA battery is used to charge a capacitor through a resistor as shown in Figure P27.44. Show that half the energy supplied by the battery appears as internal energy in the resistor and half is stored in the capacitor. Figure P27.44arrow_forwardA 12.0-V emf automobile battery has a terminal voltage of 16.0 V when being charged by a current of 10.0 A. (a) What is the battery’s internal resistance? (b) What power is dissipated inside the battery? (c) At what rate (in °C/min ) will its temperature increase if its mass is 20.0 kg and it has a specific heat of 0.300 kcal/kg • °C, assuming no heat escapes?arrow_forward
- Figure P29.45 shows five resistors connected between terminals a and b. a. What is the equivalent resistance of this combination of resistors? b. What is the current through each resistor if a 24.0-V battery is connected across the terminals?arrow_forwardA capacitor with initial charge Q0 is connected across a resistor R at time t = 0. The separation between the plates of the capacitor changes as d = d0/(1 + t) for 0 t 1 s. Find an expression for the voltage drop across the capacitor as a function of time.arrow_forwardA lightbulb is connected to a variable power supply. As the potential across the bulb is varied, the resulting current and the filaments temperature are measured. The data are listed in Table P28.38. a. Find R for each entry in Table P28.38, and then plot R as a function of T. b. Assume that room temperature is at 293 K. Find R0 (resistance at room temperature). Comment on your result.arrow_forward
- A 20.00-V battery is used to supply current to a 10-k resistor. Assume the voltage drop across any wires used for connections is negligible, (a) What is the current through the resistor? (b) What is the power dissipated by the resistor? (c) What is the power input from the battery; assuming all the electrical power is dissipated by the resistor? (d) What happens to the energy dissipated by the resistor?arrow_forwardA potential difference of 1.00 V is maintained across a 10.0- resistor for a period of 20.0 s. What total charge passes by a point in one of the wires connected to the resistor in this time interval? (a) 200 C (b) 20.0 C (c) 2.00 C (d) 0.005 00 C (e) 0.050 0 Carrow_forwardSwitch S in in the figure is closed at time t = 0, to begin charging an initially uncharged capacitor of capacitance C = 17.9 µF through a resistor of resistance R = 22.8 2. At what time is the potential across the capacitor equal to that across the resistor? Number i 0 Units H S W m R ◄► сarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

DC Series circuits explained - The basics working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VV6tZ3Aqfuc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY