
(a)
Interpretation:
A mechanism for the initiation step for the
Concept introduction:
The
The polymerizations can be initiated by anions or cations, resulting in anionic polymerization or cationic polymerization, respectively. The polymerization involves, 1) initiation, 2) propagation, and 3) termination.
Initiation is the first step of the polymerization process. An active center is created during initiation, from which a polymer chain is generated. Not all monomers are susceptible to all types of initiators.
In propogation a reactive intermediate is repetitively redeveloped throughout the sequence of a chemical chain reaction. Then it is terminated by adding mono
Answer to Problem 26.42P
The initiation step for the polymerization reaction of the given compound is as follows.
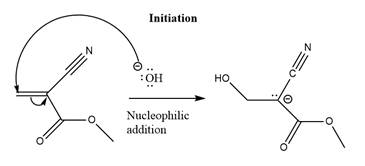
Explanation of Solution
The
The given explanation is obtained by applying the concept polymerization mechanism.
(b)
Interpretation:
A mechanism for the propagation step for the polymerization reaction of the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The chemical reaction in which the monomer molecules reacts together to form polymer chains or three dimentional networks is termed as polymerization. This are classified by different syatem avaible for the different types if polymerization.
The polymerizations can be initiated by anions or cations, resulting in anionic polymerization or cationic polymerization, respectively. The polymerization involves, 1) initiation, 2) propagation, and 3) termination.
Initiation is the first step of the polymerization process. An active center is created during initiation, from which a polymer chain is generated. Not all monomers are susceptible to all types of initiators.
In propogation a reactive intermediate is repetitively redeveloped throughout the sequence of a chemical chain reaction. Then it is terminated by adding mono functional groups that having equal of different types of monomer.
Answer to Problem 26.42P
The propagation step for the polymerization reaction of the given compound is as follows.
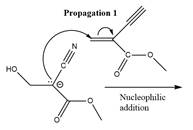
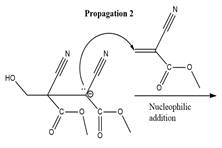
Explanation of Solution
The carbanion formed in initiation step reacts with another equivalent of
in the first nucleophilic addition step. The propagation step repeats the nucleophilic addition reaction.
The given explanation is obtained by applying the concept polymerization mechanism.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
The chemical reaction in which the monomer molecules reacts together to form polymer chains or three dimentional networks is termed as polymerization. This are classified by different syatem avaible for the different types if polymerization.
The polymerizations can be initiated by anions or cations, resulting in anionic polymerization or cationic polymerization, respectively. The polymerization involves, 1) initiation, 2) propagation, and 3) termination.
Initiation is the first step of the polymerization process. An active center is created during initiation, from which a polymer chain is generated. Not all monomers are susceptible to all types of initiators.
In propogation a reactive intermediate is repetitively redeveloped throughout the sequence of a chemical chain reaction. Then it is terminated by adding mono functional groups that having equal of different types of monomer.
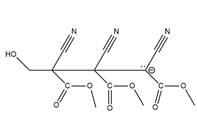
Answer to Problem 26.42P
The structure of
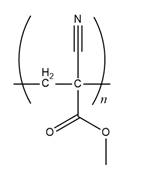
Explanation of Solution
The propagation step repeats the nucleophilic addition reaction to produce
The given explanation is obtained by applying the concept polymerization mechanism.
(d)
Interpretation:
Why is
Concept introduction:
The chemical reaction in which the monomer molecules reacts together to form polymer chains or three dimentional networks is termed as polymerization. This are classified by different syatem avaible for the different types if polymerization.
The polymerizations can be initiated by anions or cations, resulting in anionic polymerization or cationic polymerization, respectively. The polymerization involves, 1) initiation, 2) propagation, and 3) termination.
Initiation is the first step of the polymerization process. An active center is created during initiation, from which a polymer chain is generated. Not all monomers are susceptible to all types of initiators.
In propogation a reactive intermediate is repetitively redeveloped throughout the sequence of a chemical chain reaction. Then it is terminated by adding mono functional groups that having equal of different types of monomer.
Answer to Problem 26.42P
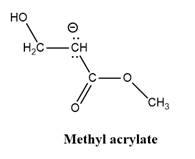
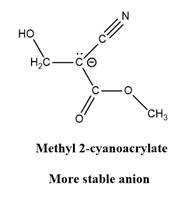
Explanation of Solution
The given explanation is obtained by applying the concept polymerization mechanism, resonance and inductive effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
Why or why not methyl 2-cyanoacrylate would be a good candidate for cationic polymerization is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
The chemical reaction in which the monomer molecules reacts together to form polymer chains or three dimentional networks is termed as polymerization. This are classified by different syatem avaible for the different types if polymerization.
The polymerizations can be initiated by anions or cations, resulting in anionic polymerization or cationic polymerization, respectively. The polymerization involves, 1) initiation, 2) propagation, and 3) termination.
Initiation is the first step of the polymerization process. An active center is created during initiation, from which a polymer chain is generated. Not all monomers are susceptible to all types of initiators.
In propogation a reactive intermediate is repetitively redeveloped throughout the sequence of a chemical chain reaction. Then it is terminated by adding mono functional groups that having equal of different types of monomer.
Answer to Problem 26.42P
Explanation of Solution
The given explanation is obtained by applying the concept polymerization mechanism.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- Benzoic acid is used to determine the heat capacity of bomb calorimeters because it can be obtained in pure form and its energy of combustion is known very accurately (−26.43 kJ/g). Determine the heat capacity of a calorimeter that had a temperature increase of 9.199°C when 3.500 g of benzoic acid was used.arrow_forwardGiven the standard enthalpies of formation for the following substances, determine the reaction enthalpy for the following reaction. 2N2H4(g) + 2NO2(g) → 3N2(g) + 4H2O(g) AHrxn ? kJ Substance AH in kJ/mol N2H4(g) +95.4 NO2(g) +33.1 H2O(g) -241.8arrow_forwardIf 7.3 kJ of energy are required to change the temperature of water from 5.0 to 70.0, what was the volume of water? (cs = 4.184 J/(g ⋅ ), d = 1.00 g/mL)arrow_forward
- BALANCE CHEMICAL REACTIONarrow_forwardPredict the product(s) of the following reactions. If no reaction, write "NR". a) Cl₂ FeCl3 e) HNO3 H2SO4 b) NO2 CI. HNO3 f) Br Br2 OH H2SO4 HO3S. FeBr3 c) Cl2 g) FeCl3 F d) O₂N Br2 FeBr3 O₂N OH HNO3 CH3 H2SO4arrow_forwardulating the pH salt solution Calculate the pH at 25 °C of a 0.75M solution of anilinium chloride (C6H5NH3C1). Note that aniline (C6H5NH2) is a weak base with a pK of 4.87. Round your answer to 1 decimal place. pH = ☐ ☑ ⑤ ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
- I apologize, but the app is not allowing me to post the other 4 pictures of the thermodynamics chart. But I believe the values are universal. Please help!arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a salt solution Calculate the pH at 25 °C of a 0.29M solution of potassium butanoate (KC3H,CO2). Note that butanoic acid (HC3H,CO2) is a weak acid with a pKa of 4.82. Round your answer to 1 decimal place. pH = -0 Х olo 18 Ararrow_forward: At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 1.58 × 10-12 N2(g) + O2(g) = 2 NO(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 38. L reaction vessel is filled with 0.93 mol of N2 and 0.93 mol of O2. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? There will be very little N2 and O2. There will be very little NO. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 NO(g) N2(9)+02(9) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3 N2(9)+302(g) 6 NO(g) Neither of the above is true. K = ☐ K = ☐ ☐ X10 Х D ? 000 18 Ar Barrow_forward
- when performing the reaction that involves 2 equivalents of 3-(diethylamino)-phenol and Phthalic anhydride with sulfuric acid and water react to form rhodamine b where the Phthalic anhydride cleaves in acid and how does Excessive Washing (w/ Base) & Subsequent Resonance Structure get affectedarrow_forward3. The strongest acid of the following compounds is ___.A. p-nitrophenol; B. m-nitrophenol; C. o-chlorophenol;D. p-methoxyphenol; E. o-methylphenol Please explain your steps and thought process. Thank you!arrow_forwardUsing the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 1.3 × 10 4: Cl2(g) + CHCl3(g) HCl(g) + CC₁(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 16. L reaction vessel is filled with 1.6 mol of HCI and 1.6 mol of CCl4. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? There will be very little Cl2 and CHCl3. ☐ x10 There will be very little HCI and CCl4. Neither of the above is true. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. HCl(g)+CC14(g) 12 Cl2(9)+CHCl3(9) K = 0 ☐ What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 Cl₂(9)+2CHCl3(9) 2 HCl(9)+2CC₁₁(9) K = ✓ 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





