
Concept explainers
Two point charges, q1 = −2.0 μC and q2 = 2.0 μC, are placed on the x axis at x = 1.0 m and x = −1.0 m, respectively (Fig. P26.24).
- a. What are the electric potentials at the points P (0, 1.0 m) and R (2.0 m, 0)?
- b. Find the work done in moving a 1.0-μC charge from P to R along a straight line joining the two points.
- c. Is there any path along which the work done in moving the charge from P to R is less than the value from part (b)? Explain.
(a)
The electric potential at
Answer to Problem 24PQ
The electric potential at
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for electric potential due to two charges.
Write the expression for distance between two points.
Conclusion:
Consider the figure 1 below.
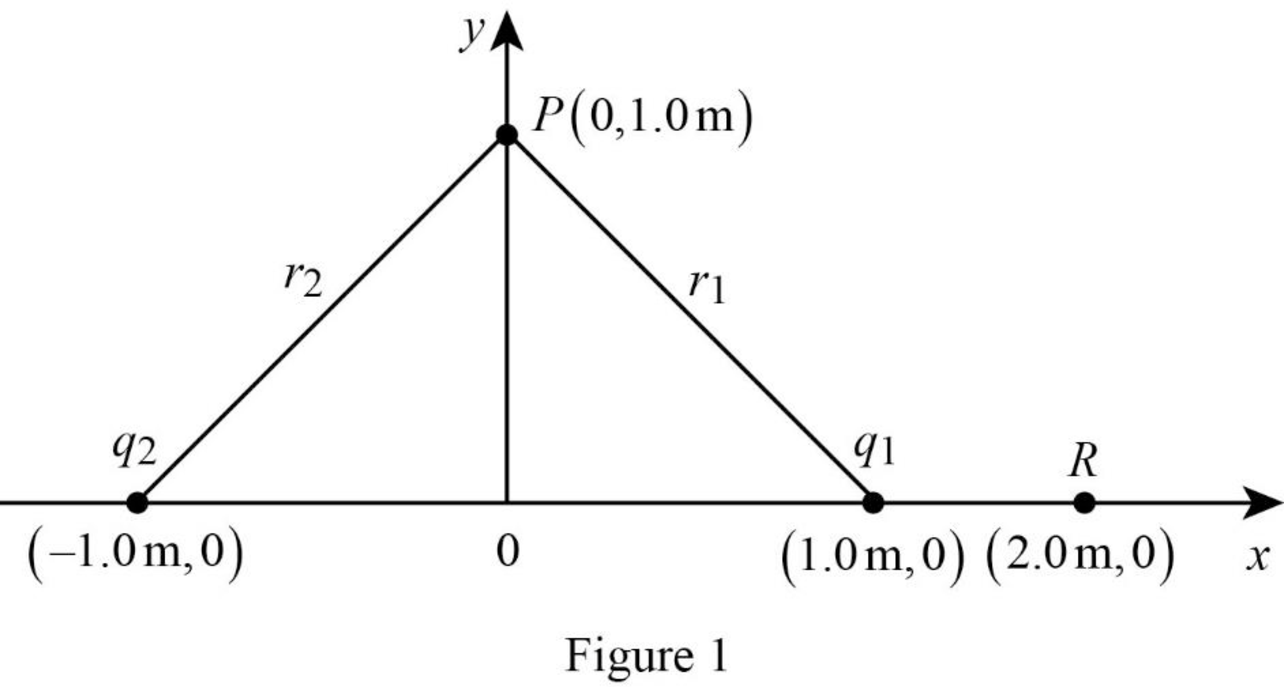
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Consider figure 2 given below.
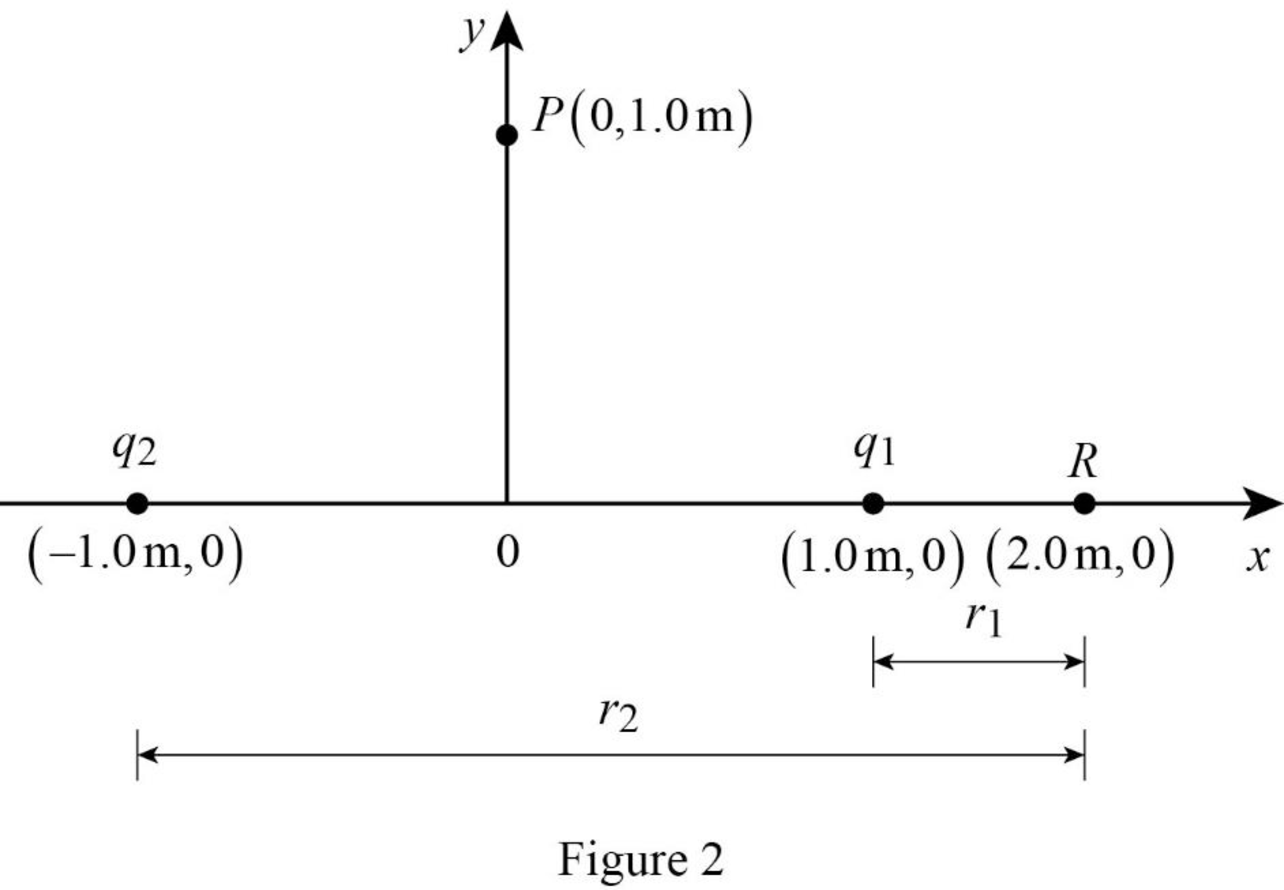
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Therefore, the electric potential at
(b)
The work done in moving a
Answer to Problem 24PQ
The work done in moving a
Explanation of Solution
The work done will be equal to change in potential energy between two points.
Write the expression for change in electric potential energy.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the work done in moving a
(c)
The path along which the work done is less than the value obtained in part (b).
Answer to Problem 24PQ
No, there is no other path through which the charge can move so that the work done is less than the value obtained part (b).
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for work done in terms of change in potential energy.
The work done is depends on charge and the change in potential, and does not depends on the path followed by the particle.
Hence, there is no other path in which work done is less than
Conclusion:
Therefore, the work done is not depends on the path followed by the particle, and only depends on the change in potential. There is no other path with work done less than
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forward3arrow_forward13. After a gust of wind, an orb weaver spider with a mass of 35 g, hanging on a strand of web of length L = .420 m, undergoes simple harmonic motion (SHO) with an amplitude A and period T. If the spider climbs 12.0 cm up the web without perturbing the oscillation otherwise, what is the period of oscillation, in Hz to three significant figures?arrow_forward
- 15. An object of mass m = 8.10 kg is attached to an ideal spring and allowed to hang in the earth's gravitational field. The spring stretches 23.10 cm before it reaches its equilibrium position. The mass then undergoes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10.5 cm. Calculate the velocity of the mass in m/s at a time t= 1.00s to three significant figures.arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. Thank you!!arrow_forward18arrow_forward
- 1. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .14 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forward16arrow_forward11. A small charged plastic ball is vertically above another charged small ball in a frictionless test tube as shown in the figure. The balls are in equilibrium at a distance d= 2.0 cm apart. If the charge on one ball is tripled, find the new equilibrium distance between the balls in cm and report it to the proper number of significant figures.arrow_forward
- 12. The electric field at a point 1.3 cm from a small object points toward the object with a strength of 180,000 N/C. Find the object's charge q, in nC to the proper number of significant figures. k = 1/4πε0 = 8.99 × 10^9 N ∙ m^2/C^2arrow_forward14. When the potential difference between the plates of an ideal air-filled parallel plate capacitor is 35 V, the electric field between the plates has a strength of 670 V/m. If the plate area is 4.0 × 10^-2 m^2, what is the capacitance of this capacitor in pF? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10^-12 C^2/N ∙ m^2)arrow_forward10. A small styrofoam ball of mass 0.500 g is placed in an electric field of 1140 N/C pointing downward. What excess charge must be placed on the ball for it to remain suspended in the field? Report your answer in micro-Coulombs to three significant figures.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





