
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The product formed on thermal electrocyclic ring opening of the given compounds is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: Electrocyclic reactions involve ring opening or ring closure in a conjugated polyene. According to Woodward-Hoffmann rules, the polyene containing even number of bonds in thermal conditions undergoes reaction in conrotatory fashion and polyene containing odd number of bonds undergo reaction in disrotatory fashion.
Answer to Problem 25P
The product formed on thermal electrocyclic ring opening of the compound A is,
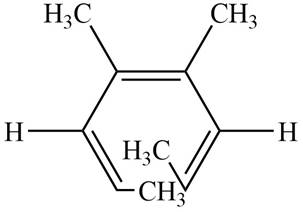
Figure 1
The product formed on thermal electrocyclic ring opening of the compound B is,
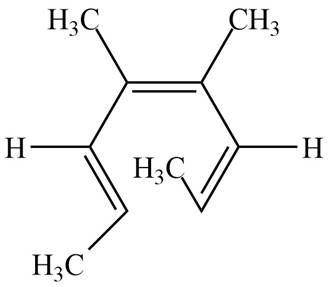
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The given compound A is,
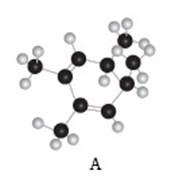
Figure 3
Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure is,
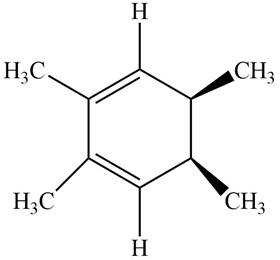
Figure 4
The given compound undergoes thermal electrocyclic ring opening to form product with three pi bonds. According to Woodward-Hoffmann rules, the ring opening takes place in disrotatory fashion. The atomic orbitals of the carbon atoms whose sigma bond is broken rotates in opposite direction. The corresponding
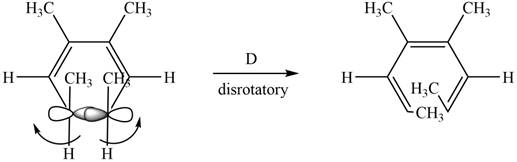
Figure 5
The given compound B is,
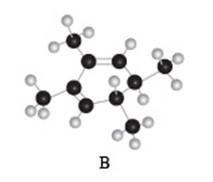
Figure 6
Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure is,
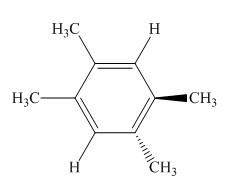
Figure 7
The given compound undergoes thermal electrocyclic ring opening to form product with three pi bonds. According to Woodward-Hoffmann rules, the ring opening takes place in disrotatory fashion. The atomic orbitals of the carbon atoms whose sigma bond is broken rotates in opposite direction. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
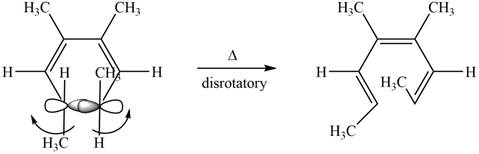
Figure 8
The products formed on thermal electrocyclic ring opening of the compound A and compound B is are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed on photochemical electrocyclic ring opening of the given compounds.
Concept introduction: Electrocyclic reactions involve ring opening or ring closure in a conjugated polyene. According to Woodward-Hoffmann rules, the polyene containing even number of bonds in photochemical conditions undergoes reaction in disrotatory fashion and polyene containing odd number of bonds undergo reaction in conrotatory fashion.
Answer to Problem 25P
The product formed on photochemical electrocyclic ring opening of the compound A is,
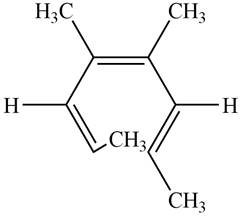
Figure 9
The product formed on photochemical electrocyclic ring opening of the compound B is,
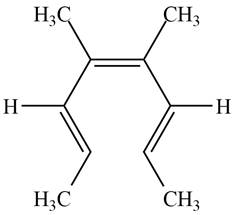
Figure 10
Explanation of Solution
The given compound A is,
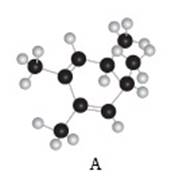
Figure 3
Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure is,
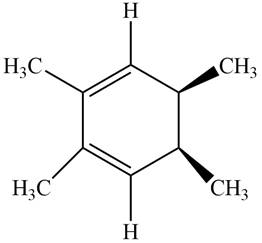
Figure 4
The given compound undergoes thermal electrocyclic ring opening to form product with three pi bonds. According to Woodward-Hoffmann rules, the ring opening takes place in disrotatory fashion. The atomic orbitals of the carbon atoms whose sigma bond is broken rotates in opposite direction. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
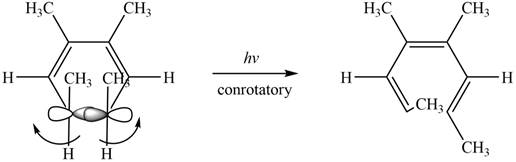
Figure 11
The given compound B is,
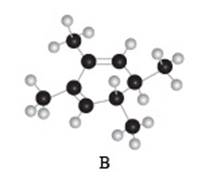
Figure 6
Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure is,

Figure 7
The given compound undergoes thermal electrocyclic ring opening to form product with three pi bonds. According to Woodward-Hoffmann rules, the ring opening takes place in disrotatory fashion. The atomic orbitals of the carbon atoms whose sigma bond is broken rotates in opposite direction. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
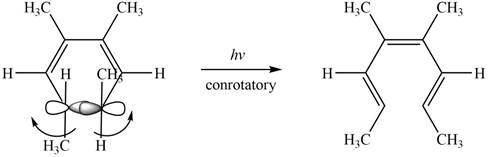
Figure 12
The products formed on photochemical electrocyclic ring opening of the compound A and compound B is are shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Identify the unknown compound from its IR and proton NMR spectra. C4H6O: 'H NMR: 82.43 (1H, t, J = 2 Hz); 8 3.41 (3H, s); 8 4.10 (2H, d, J = 2 Hz) IR: 2125, 3300 cm¹ The C4H6O compound liberates a gas when treated with C2H5 MgBr. Draw the unknown compound. Select Draw с H Templates Morearrow_forwardPlease help with number 6 I got a negative number could that be right?arrow_forward1,4-Dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene can undergo 1,2- or 1,4-addition with hydrogen halides. (a) 1,2-Addition i. Draw the carbocation intermediate(s) formed during the 1,2-addition of hydrobromic acid to 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. ii. What is the major 1,2-addition product formed during the reaction in (i)? (b) 1,4-Addition i. Draw the carbocation intermediate(s) formed during the 1,4-addition of hydrobromic acid to 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. ii. What is the major 1,4-addition product formed from the reaction in (i)? (c) What is the kinetic product from the reaction of one mole of hydrobromic acid with 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene? Explain your reasoning. (d) What is the thermodynamic product from the reaction of one mole of hydrobro-mic acid with 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene? Explain your reasoning. (e) What major product will result when 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of hydrobromic acid at - 78 deg * C ? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Give the product of the bimolecular elimination from each of the isomeric halogenated compounds. Reaction A Reaction B. КОВ CH₂ HotBu +B+ ко HOIBU +Br+ Templates More QQQ Select Cv Templates More Cras QQQ One of these compounds undergoes elimination 50x faster than the other. Which one and why? Reaction A because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups and to each other Reaction A because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups gauche to each other. ◇ Reaction B because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups gach to each other. Reaction B because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups anti to each other.arrow_forwardFive isomeric alkenes. A through each undergo catalytic hydrogenation to give 2-methylpentane The IR spectra of these five alkenes have the key absorptions (in cm Compound Compound A –912. (§), 994 (5), 1643 (%), 3077 (1) Compound B 833 (3), 1667 (W), 3050 (weak shoulder on C-Habsorption) Compound C Compound D) –714 (5), 1665 (w), 3010 (m) 885 (3), 1650 (m), 3086 (m) 967 (5), no aharption 1600 to 1700, 3040 (m) Compound K Match each compound to the data presented. Compound A Compound B Compound C Compound D Compoundarrow_forward7. The three sets of replicate results below were accumulated for the analysis of the same sample. Pool these data to obtain the most efficient estimate of the mean analyte content and the standard deviation. Lead content/ppm: Set 1 Set 2 Set 3 1. 9.76 9.87 9.85 2. 9.42 9.64 9.91 3. 9.53 9.71 9.42 9.81 9.49arrow_forward
- Draw the Zaitsev product famed when 2,3-dimethylpentan-3-of undergoes an El dehydration. CH₂ E1 OH H₁PO₁ Select Draw Templates More QQQ +H₂Oarrow_forwardComplete the clean-pushing mechanism for the given ether synthesia from propanol in concentrated sulfurica140°C by adding any mining aloms, bands, charges, nonbonding electron pairs, and curved arrows. Draw hydrogen bonded to cayan, when applicable. ore 11,0 HPC Step 1: Draw curved arrows Step 2: Complete the intend carved Q2Q 56 QQQ Step 3: Complete the intermediate and add curved Step 4: Modify the structures to draw the QQQ QQQarrow_forward6. In an experiment the following replicate set of volume measurements (cm3) was recorded: (25.35, 25.80, 25.28, 25.50, 25.45, 25.43) A. Calculate the mean of the raw data. B. Using the rejection quotient (Q-test) reject any questionable results. C. Recalculate the mean and compare it with the value obtained in 2(a).arrow_forward
- A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T G OH де OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardMacmillan Leaming Draw the major organic product of the reaction. 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H+ - G Select Draw Templates More H о QQarrow_forwardDraw the condensed structure of 3-hydroxy-2-butanone. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





