
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a. 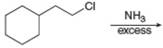 f.
f. 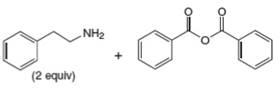
b. 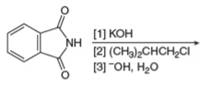 g.
g. 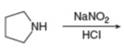
c. 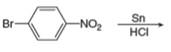 h.
h. 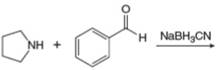
d.  i.
i. 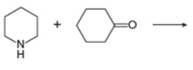
e. 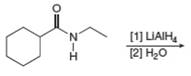 j.
j. 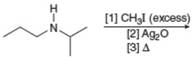
(a)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The reaction between amine and alkyl halide is direct nucleophilic substitution reaction. The amino group acts as nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon in alkyl halide followed by deprotonation to form amine or ammonium salt.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
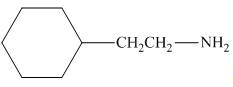
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between (
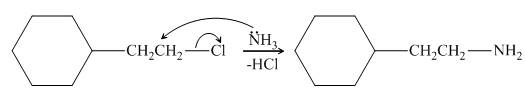
Figure 2
In the given reaction, the ammonia acts as nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom bonded to chlorine atom to produce the
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Gabriel synthesis is a method of preparation of primary amines. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The phthalimide in presence of base forms the resonance stabilized anion which acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of alkyl halides.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
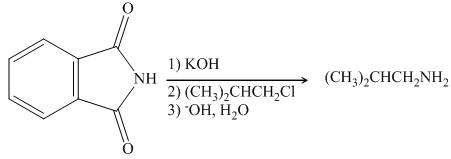
Figure 3
In presence of base, phthalimide forms the resonance stabilized anion which acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of
The organic product formed in the given reaction is
(c)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The synthesis of amine can be carried out by reduction of nitro compounds, nitriles and amides. Nitro compounds can be reduced to amines using catalytic hydrogenation or iron/palladium/tin metal in presence of acid. Nitriles and amides are reduced to amines using lithium aluminium hydride.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
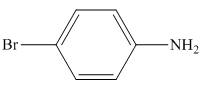
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of tin metal with acid,
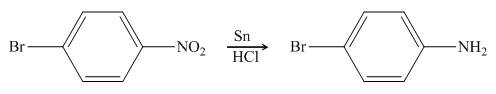
Figure 5
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The synthesis of amine can be carried out by reduction of nitro compounds, nitriles and amides. Nitro compounds can be reduced to amines using catalytic hydrogenation or iron/palladium/tin metal in presence of acid. Nitriles and amides are reduced to amines using lithium aluminium hydride.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
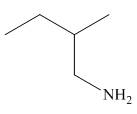
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of lithium aluminium hydride,
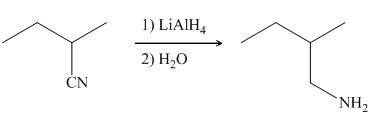
Figure 7
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(e)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The synthesis of amine can be carried out by reduction of nitro compounds, nitriles and amides. Nitro compounds can be reduced to amines using catalytic hydrogenation or iron/palladium/tin metal in presence of acid. Nitriles and amides are reduced to amines using lithium aluminium hydride.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
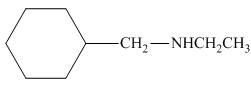
Figure 8
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of lithium aluminium hydride,
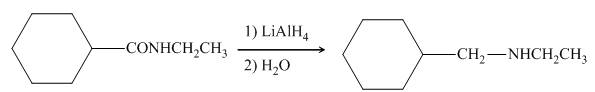
Figure 9
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 8.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Amines reacts with acid chlorides or anhydrides to form amides. The amino group acts as nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of acid chlorides or anhydrides resulting in formation of amides and loss of chlorides or carboxylate ion.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
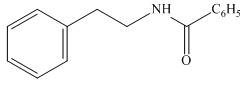
Figure 10
Explanation of Solution
The given amine,
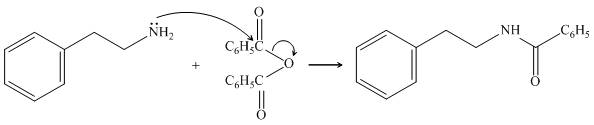
Figure 11
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 10.
(g)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid reacts to form nitrous acid. Nitrous acid in presence of acid forms nitrosonium ion which reacts with primary amines to produce diazonium salt and with secondary amines produce
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
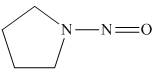
Figure 12
Explanation of Solution
Pyrrolidine reacts with nitrous acid to form
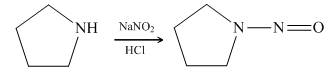
Figure 13
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 12.
(h)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The conversion of aldehydes and ketones into amines is known as reductive amination. The first step is the formation of imines using aldehydes or ketones and amines. The second step involves the reduction of imine to form amine. The best reagent for this reaction is sodiumcyanoborohydride.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
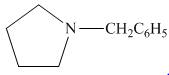
Figure 14
Explanation of Solution
Pyrrolidine reacts with benzaldehyde to form imine. The imine undergoes reduction to form
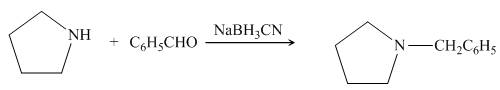
Figure 15
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 14.
(i)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Aldehyde or ketone on reaction with primary amine forms imine. Imine is also known as Schiff base. The nucleophilic attack of primary amine on carbonyl carbon results in the formation of intermediate carbinolamine. This intermediate loses water to form an imine.
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
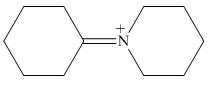
Figure 16
Explanation of Solution
Piperidine reacts with cyclohexanone to form imine. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
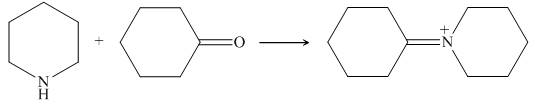
Figure 17
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 16.
(j)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The conversion of amines into alkenes can be achieved by Hoffmann elimination reaction. Amines have poor leaving groups. They react with excess of alkyl halides to form ammonium salts. These ammonium salts undergo
Answer to Problem 25.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
![]()
Figure 18
Explanation of Solution
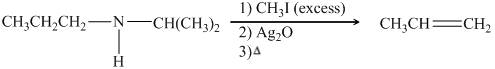
Figure 19
The organic product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 18.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward70 Suppose the molecule below is in acidic aqueous solution. Is keto-enol tautomerization possible? • If a keto-enol tautomerization is possible, draw the mechanism for it. Be sure any extra reagents you add to the left-hand sid available in this solution. • If a keto-enol tautomerization is not possible, check the box under the drawing area. : ☐ Add/Remove step Click and drag to st drawing a structure Check Save For Late. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe problem will not be graded for correctness, but you have to get a reasonable answer something that is either correct or very closer to the correct answer. The instructor professor wants us to do something that shows the answer but everything does not have to be correct. Ideally, yes, it has to be correct. Give it your best shot.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


