
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The sequence of steps for the given reaction involving the adenylation of aspartic acid, is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
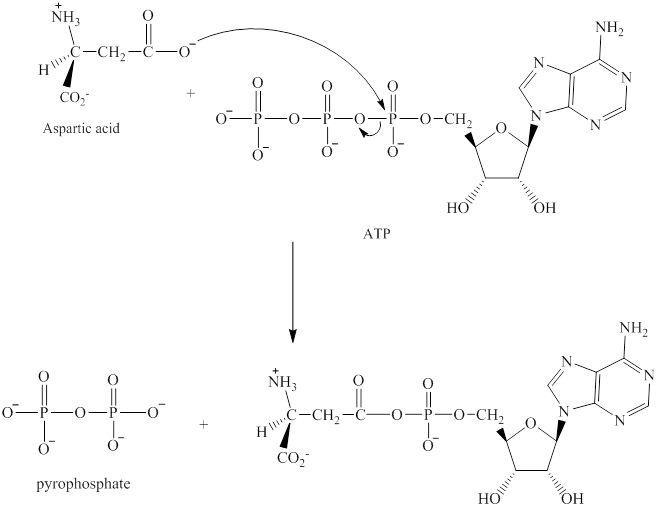
The adenylation of aspartic acid takes place in three steps. In the first step, aspartic acid reacts with ATP. The pyrophosphate is the leaving group in this
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
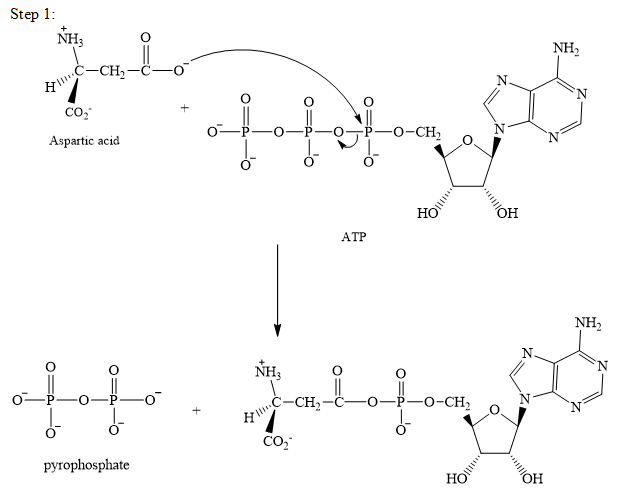
Step 2:
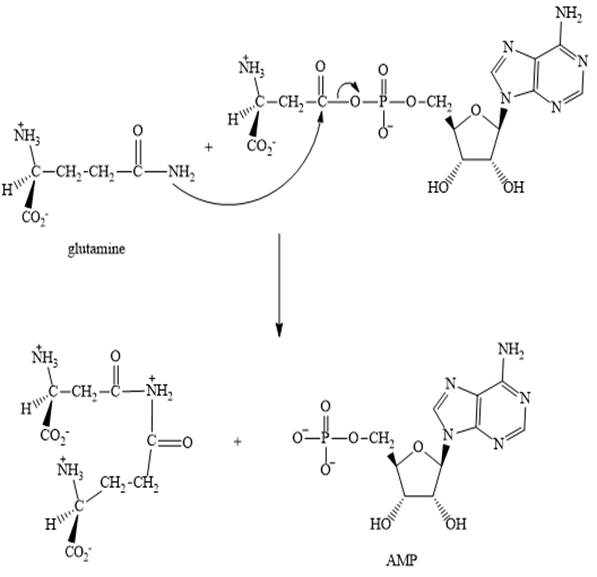
Step 3:
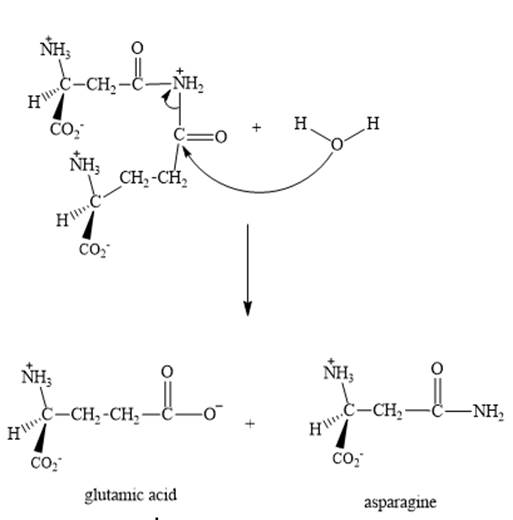
Explanation of Solution
The adenylation of aspartic acid takes place in three steps.
Step 1: In the first step, aspartic acid reacts with ATP. The pyrophosphate is the leaving group in this
Step 2: In the second step, glutamine displaces AMP by a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
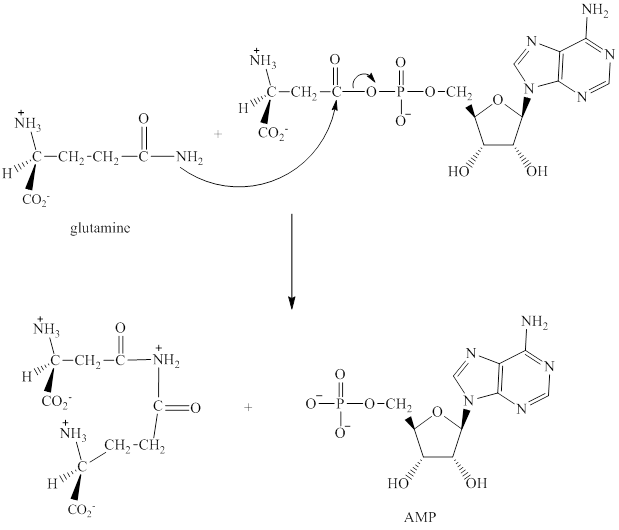
Step 3: The intermediate produced in the step 2 undergoes hydrolysis to the form of glutamic acid and asparagine.
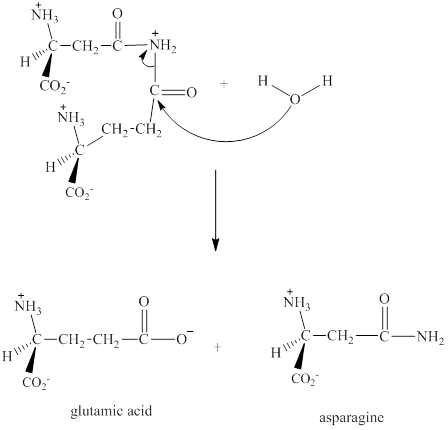
The sequence of steps for the given reaction involving the adenylation of aspartic acid is as shown above.
(b)
Interpretation:
The utilization of ATP in the equilibrium between glutamine and asparagine, is to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
ATP hydrolysis reactions are highly favorable. The reaction is used to help less favorable reactions which occur in high yield. In the adenylation of aspartic acid, the AMP group is a better leaving group than the hydroxyl group.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
ATP is highly energetically favorable and produces AMP, which is a better leaving group than
Explanation of Solution
To make the less favorable reactions occur in high yield, the high energetic favorability of ATP is utilized. AMP is a better leaving group than
ATP is highly energetically favorable and produces AMP, which is a better leaving group than
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
The free energy change of two or more reactions can be used to determine the free energy change of a third reaction. The reactions are treated just like algebraic equations.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
Explanation of Solution
_____________________________________________________________________
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The meaning of ATP hydrolysis in biosynthesis of asparagine is to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
ATP hydrolysis is a high energy reaction. It drives other reactions coupled to it, to completion.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
If ATP is removed from the process, then the reaction is unfavorable. ATP drives the reaction to completion.
Explanation of Solution
If ATP is removed from the process, then the reaction is unfavorable. ATP does not actually undergo hydrolysis, but when coupled to the adenylation of aspartic acid, it becomes favorable and drives the reactions towards completion.
If ATP is removed from the process, then the reaction is unfavorable. ATP drives the reaction to completion.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction that ensures the completion of asparagine biosynthesis, is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Pyrophosphatase catalyzes the irreversible conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate. This reaction ensures the completion of asparagine biosynthesis.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
The other reaction which drives asparagine synthesis towards completion is the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The other reaction which drives asparagine synthesis towards completion is the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate, which is irreversible. Pyrophosphate is generated as a by-product during the adenylation of aspartic acid.
The other reaction which drives asparagine synthesis towards completion is the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate, which is irreversible.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Predict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forwardWhat is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forward
- How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forward
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





