
(a)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
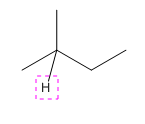
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
In the above compound there are three types of C atom; methyl, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to respective carbons are also methyl H, secondary H and tertiary H atoms.
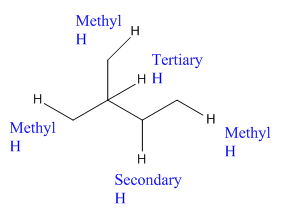
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
(b)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
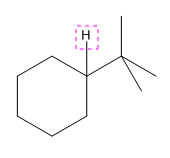
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
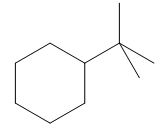
In the above compound there are three types of C atom; methyl, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to respective carbons are also methyl H, secondary H and tertiary H atoms.
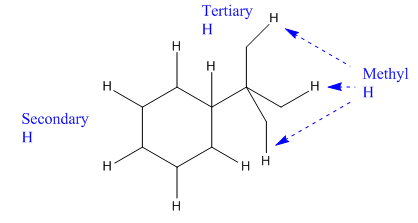
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
(c)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
Explanation of Solution
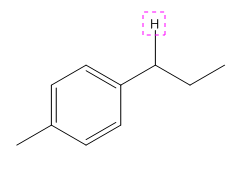
The given compound is:
In the above compound there are four types of C atom; methyl, secondary, secondary benzylic and
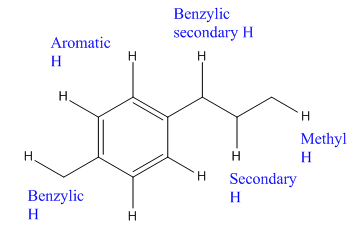
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Here, the another benzylic radical could form by abstracting a H atom from the benzylic
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
(d)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
Explanation of Solution
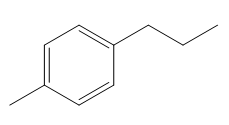
The given compound is:
In the above compound there are three types of C atom; methyl, allylic, and aromatic carbon atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to respective carbons are also methyl H, allylic, and aromatic H atoms.
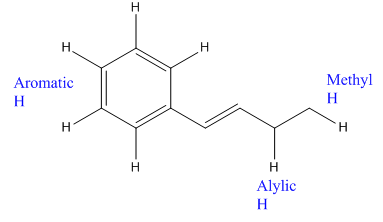
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- 5) Confidence interval. Berglund and Wichardt investigated the quantitative determination of Cr in high-alloy steels using a potentiometric titration of Cr(VI). Before the titration, samples of the steel were dissolved in acid and the chromium oxidized to Cr(VI) using peroxydisulfate. Shown here are the results (as %w/w Cr) for the analysis of a reference steel. 16.968, 16.922, 16.840, 16.883, 16.887, 16.977, 16.857, 16.728 Calculate the mean, the standard deviation, and the 95% confidence interval about the mean. What does this confidence interval mean?arrow_forwardIn the Nitrous Acid Test for Amines, what is the observable result for primary amines? Group of answer choices nitrogen gas bubbles form a soluble nitrite salt yellow oily layer of nitrosoaminearrow_forward3. a. Use the MS to propose at least two possible molecular formulas. For an unknown compound: 101. 27.0 29.0 41.0 50.0 52.0 55.0 57.0 100 57.5 58.0 58.5 62.0 63.0 64.0 65.0 74.0 40 75.0 76.0 20 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 m/z 99.5 68564810898409581251883040 115.0 116.0 77404799 17417M 117.0 12.9 118.0 33.5 119.0 36 133 0 1.2 157.0 2.1 159.0 16 169.0 219 170.0 17 171.0 21.6 172.0 17 181.0 1.3 183.0 197.0 100.0 198.0 200. 784 Relative Intensity 2 2 8 ō (ppm) 6 2arrow_forward
- Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra (IR and C-NMR)arrow_forward1. For an unknown compound with a molecular formula of C8H100: a. What is the DU? (show your work) b. Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra. 8 6 2 ō (ppm) 4 2 0 200 150 100 50 ō (ppm) LOD D 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI -11arrow_forward16. The proton NMR spectral information shown in this problem is for a compound with formula CioH,N. Expansions are shown for the region from 8.7 to 7.0 ppm. The normal carbon-13 spec- tral results, including DEPT-135 and DEPT-90 results, are tabulated: 7 J Normal Carbon DEPT-135 DEPT-90 19 ppm Positive No peak 122 Positive Positive cus и 124 Positive Positive 126 Positive Positive 128 No peak No peak 4° 129 Positive Positive 130 Positive Positive (144 No peak No peak 148 No peak No peak 150 Positive Positive してしarrow_forward
- 3. Propose a synthesis for the following transformation. Do not draw an arrow-pushing mechanism below, but make sure to draw the product of each proposed step (3 points). + En CN CNarrow_forwardShow work..don't give Ai generated solution...arrow_forwardLabel the spectrum with spectroscopyarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





