
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of a saturated fat is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Saturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is saturated. They consist of a single bond between them. These fats are solid at room temperature.
(a)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of a saturated fat is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
Saturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is saturated. They consist of a single bond between them. These fats are solid at room temperature.
An example of a saturated fat is tristearin. It is a triglyceride with chemical formula
The structure of tristearin is shown below.
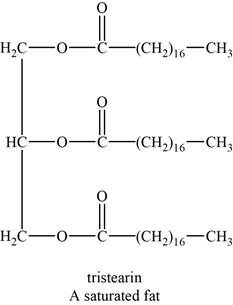
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of polyunsaturated oil is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Polyunsaturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is unsaturated. They consist of a double bond between them. These fats are liquid at room temperature.
(b)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of a polyunsaturated fat is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
Polyunsaturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is unsaturated. They consist of a double bond between them. These fats are liquid at room temperature.
An example of a polyunsaturated fat is triolein. It is a triglyceride with chemical formula
The structure of triolein is shown below.
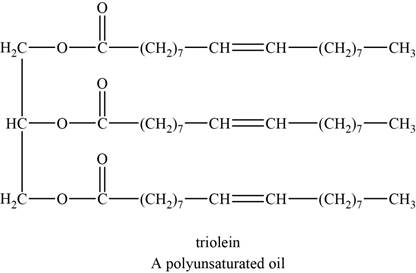
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of wax is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Waxes occur widely in nature and are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain alcohols.
(c)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of a polyunsaturated fat is shown in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
Waxes occur widely in nature and are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain alcohols.
An example of wax can be spermaceti. It helps animals to regulate the buoyancy for deep diving.
The structure of spermaceti is shown below.
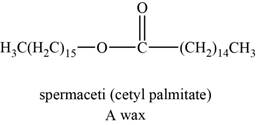
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of soap is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of fatty acids with sodium hydroxide leads to the formation of sodium salt of fatty acid and soap is the sodium salt of a fatty acid. The carboxylate group is negatively charged and is hydrophilic in nature, whereas long hydrocarbon is hydrophobic and lipophilic in nature.
(d)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of soap is shown in Figure 4.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of fatty acids with sodium hydroxide leads to the formation of sodium salt of fatty acid and soap is the sodium salt of a fatty acid. The carboxylate group is negatively charged and is hydrophilic in nature, whereas long hydrocarbon is hydrophobic and lipophilic in nature.
An example of soap is sodium stearate. The structure of sodium stearate is shown below.
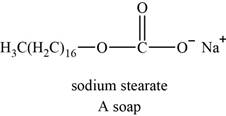
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of detergent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Synthetic detergents are the sodium salts of sulfonic acids.
(e)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of detergent is shown in Figure 5.
Explanation of Solution
Synthetic detergents are the sodium salts of sulfonic acids. Carboxylic acid is less acidic than sulfonic acids; therefore salts of sulfonic acids do not protonate in acidic wash water. The salts of sulfonic acid are soluble in water and can be used in hard water without formation of scum.
An example of detergent is alkylbenzenesulfonate. The structure of alkylbenzenesulfonate is shown below.
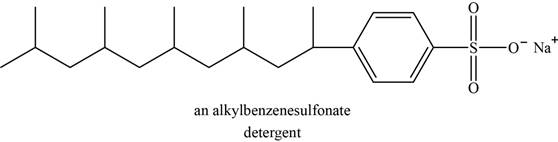
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of phospholipids is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lipids that contain groups derived from phosphoric acid are phospholipids. The common phospholipids are phosphogylcerides. Generally it contains phosphoric acid in place of one fatty acids of a triglyceride.
(f)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of soap is shown in Figure 6.
Explanation of Solution
Lipids that contain groups derived from phosphoric acid are phospholipids. The common phospholipids are phosphogylcerides. Generally it contains phosphoric acid in place of one fatty acids of a triglyceride.
An example of phospholipids can be phosphatidic acids. The structure of phosphatidic acids is shown below.
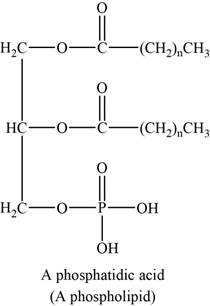
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of prostaglandins is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Prostaglandins are the powerful biochemical regulators than steroids. These are the fatty derivatives and are isolated from the secretions of the prostate gland. They have an important role in regulating blood pressure, blood clotting.
They have cyclopentane ring with two long side chains that are trans to each other. And one side chain end with a carboxylic acid.
(g)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of prostaglandin is shown in Figure 7.
Explanation of Solution
Prostaglandins are the powerful biochemical regulators than steroids. These are the fatty derivatives and are isolated from the secretions of the prostate gland. They have an important role in regulating blood pressure, blood clotting.
They have cyclopentane ring with two long side chains that are trans to each other. And one side chain ends with a carboxylic acid.
The structure of prostaglandin is shown below.
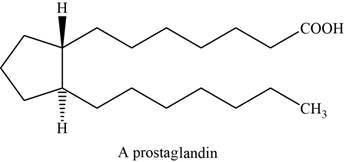
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of steroid is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Steroids are the polycyclic molecules found in all plants and animals. They do not undergo hydrolysis; therefore they are classified as simple lipids. Their structure is based on the tetracyclic andostane ring.
(h)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of steroid is shown in Figure 8.
Explanation of Solution
Steroids are the polycyclic molecules found in all plants and animals. They do not undergo hydrolysis; therefore they are classified as simple lipids. Their structure is based on the tetracyclic andostane ring.
An example of steroid is androsterone. The structure of androsterone is shown below.
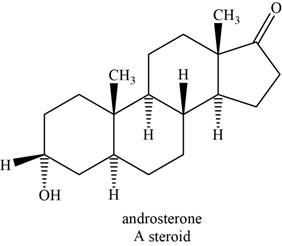
Figure 8
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of sesquiterpene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An isoprene unit is bunched of five-carbon atoms. In terpenes, the isoprene units are connected to each other in head to tail fashion. The head part of an isoprene unit is branched, whereas the tail part of an isoprene unit is unbranched.
(i)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of sesquiterpene is shown in Figure 9.
Explanation of Solution
An isoprene unit is bunched of five-carbon atoms. In terpenes, the isoprene units are connected to each other in head to tail fashion. The head part of an isoprene unit is branched, whereas the tail part of an isoprene unit is unbranched.
An example of sesquiterpene is
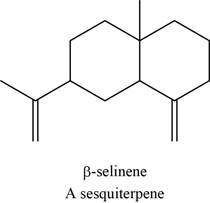
Figure 9
There are three isoprene units in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Plus Masteringchemistry With Pearson Etext, Global Edition
- 151.2 254.8 85.9 199.6 241.4 87.6 242.5 186.4 155.8 257.1 242.9 253.3 256.0 216.6 108.7 239.0 149.7 236.4 152.1 222.7 148.7 278.2 268.7 234.4 262.7 283.2 143.6 QUESTION: Using this group of data on salt reduced tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardResults Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unloc xb Success Confirmation of Q x O Google Pas alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCavJ17dZtpxbFD0Qggd1J O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Gabr 3/5 he pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 101. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to nd your answer. pressure (atm) 24- 12 solid liquid gas 200 400 temperature (K) 600 ote: your answer must be within 0.15 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm Thanation Check © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center I Q Search L³ ملةarrow_forward301.7 348.9 193.7 308.6 339.5 160.6 337.7 464.7 223.5 370.5 326.6 327.5 336.1 317.9 203.8 329.8 221.9 331.7 211.7 309.6 223.4 353.7 334.6 305.6 340.0 304.3 244.7 QUESTION: Using this group of data on regular tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forward
- Search Results Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unlo x b Success Confirmation of Q aleks.com/alekscgi/x/sl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTIOHz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCav States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 0. 32- 16 solid liquid gas 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Дос Xarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions: Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. 1. NaOEt, EtOH H&C OCH CH3 2 H30 H3C CH2 OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. OEtarrow_forwardUse the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 32 16 solid liquid gas 0 0 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Шос ☑ كarrow_forward
- Starting from bromoethane, how could you prepare the following compounds: a. Ethanol. b. Acetaldehyde f. Acetone. e. 2-Propanol i. Acetoacetic ester. d. 2-Bromoacetic acid. c. Acetic acid g. Acetamide. j. Ethylmalonate k. Gama ketoacid. h. Ethyl magnesium bromide.arrow_forward- The pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 60. °C is raised. At what pressure will the sample melt? Use the phase diagram of X below to find your answer. pressure (atm) 02 0.4 solid Hliquid gas 0 0 200 400 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 0.025 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. ☐ atmarrow_forward15. What is the order of decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic acyl substitution for the carboxylic acid derivatives? (most reactive first) 0 O H3C COC CH3 H₂C C N(CH3)2 H3C C OCH3 A. a. I, 11, 111, b. I, III, IV, II C. II, IV, III, I ° (CH3)2CH C OCH3 IV d. II, I, III, IV B. R COCR 0 0 0 13= RC NH2 RC OR RC CI === IV a. I, III, II, IV b. II, III, I, IV C. III, II, I, IV d. IV, I, III, IIarrow_forward
- Draw the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Tallose with bromine water.arrow_forwardChoose the best reagent(s) for carrying out the following conversions from the list below. Place the letter corresponding to the best choice in the blank to the left of the conversion. a. KMnO4, H3O+ b. Tollens' Reagent [oxidizing reagent] C. NaBH4, ethanol d. 1. BH3 2. H3O+ e. 1. CH3MgBr, ether 2. H3O+ f. CrO3, H2SO4, H₂O g. 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ h. 1. NaCN 2. H2SO4, H2, heat i. O3, then Zn and HOAC j. CH₂I A. B. C. CH CH=CHCH2COOH Br CEN CH COOH + HOOCCH COOH COOH 010 CH3arrow_forwardDraw the structures for each of the intermediates in the boxes provided for the synthesis below. OCH3 Fe HO HNO (CHOO pynding H₂504 LHNO2 NACH-I Fa H₂O HCL HNO 180arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning  General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





