
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Thegiven molecular models are to be converted into a condensed structural formula, a Kekule structure, and a skeletal (line) structure.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular model of a chemical compound represents the three-dimensional position of the atoms along with the bonds between them. The atoms are represented by spheres, connected by rods, which represent the bonds.
Wedges represent the bonds toward the viewer, dashes represent the bonds away from the viewer, and solid lines represent the bonds in the plane of the image.
The structural formula of a chemical compound consists of the graphic representation of the molecular structure and the arrangement of atoms.
In an organic molecule, the structure representation of atoms takes place by single or double bonds without lone pairs; it is called theKekule structure.
In an organic molecule, bonds are not represented by single lines or branched chains; it is called the condensed structural formula.
In an organic molecule, when the structure consists of straight lines that represent
Answer to Problem 24QP
Solution: The structures of the compounds are represented below.
(a)
Condensed:
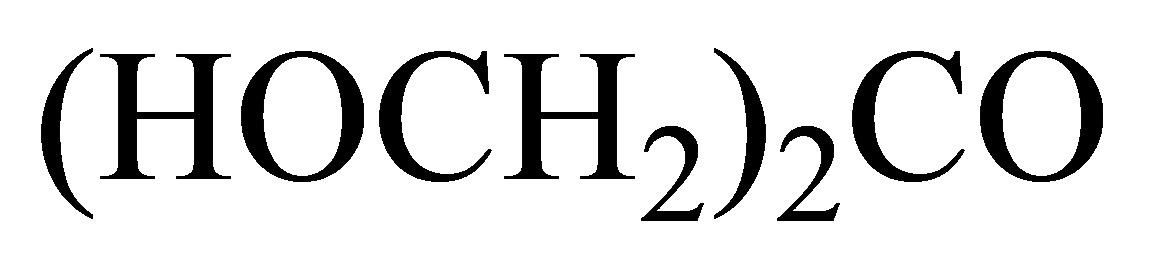
Kekule:

Skeletal (line):

(b)
Condensed:
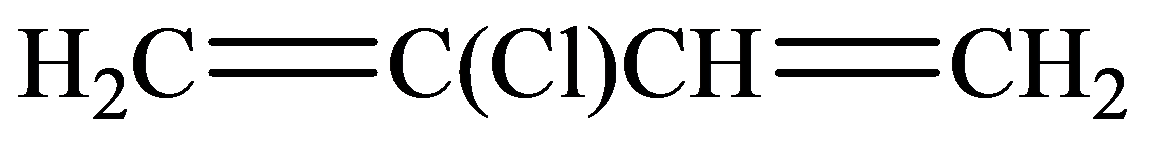
Kekule:
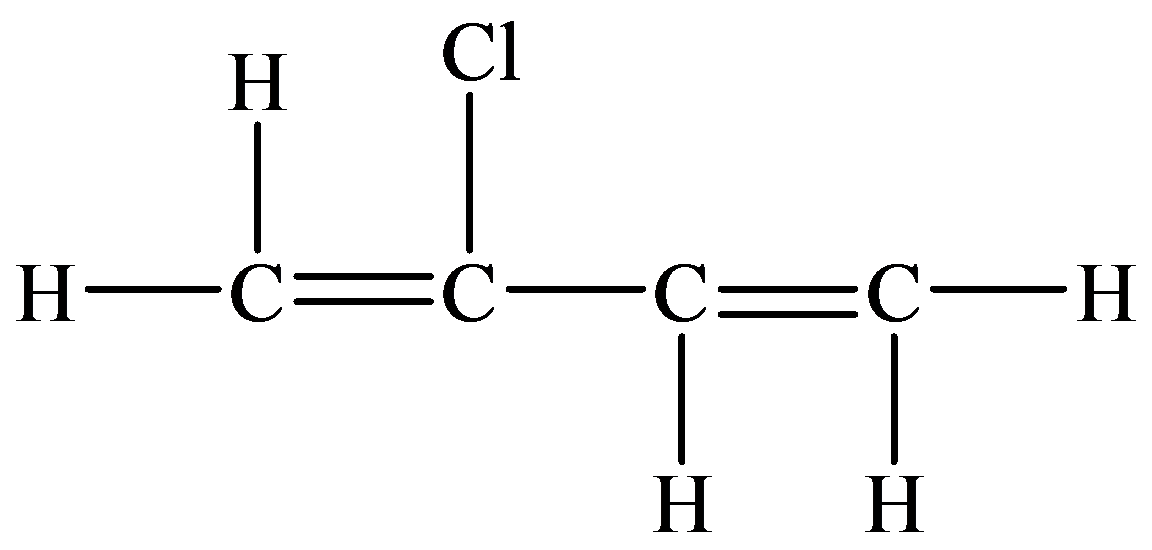
Skeletal (line)
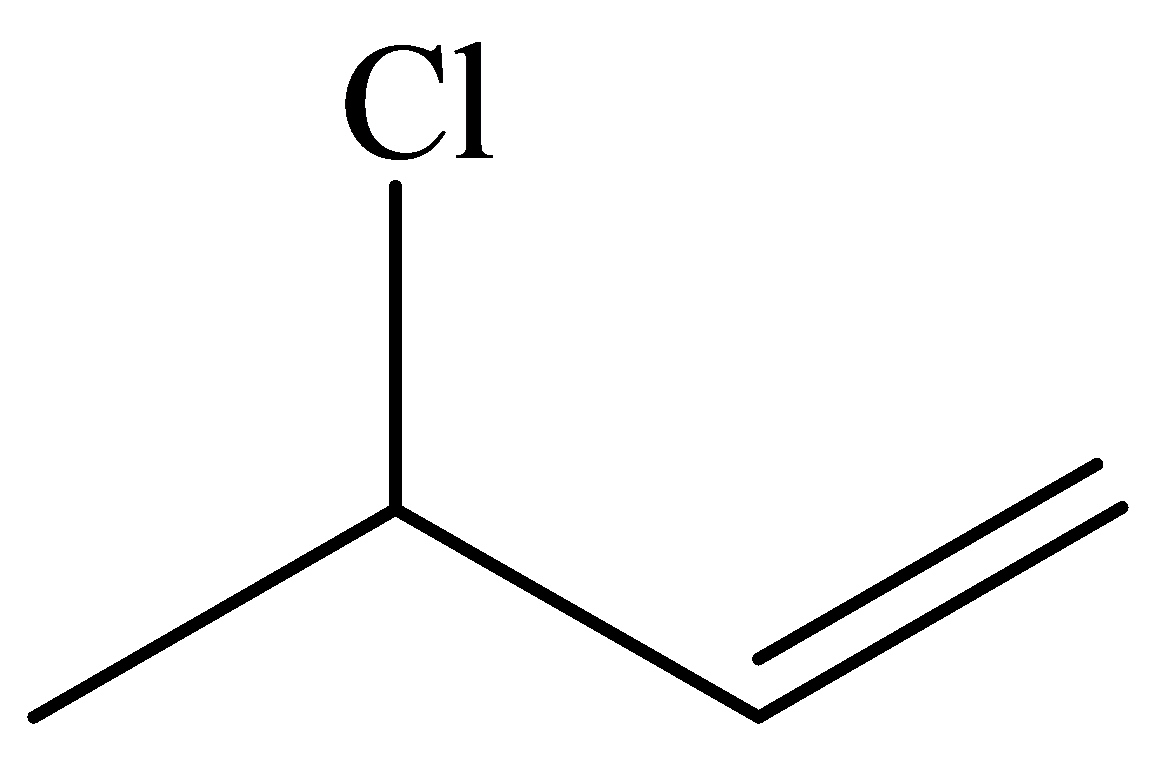
(c)
Condensed
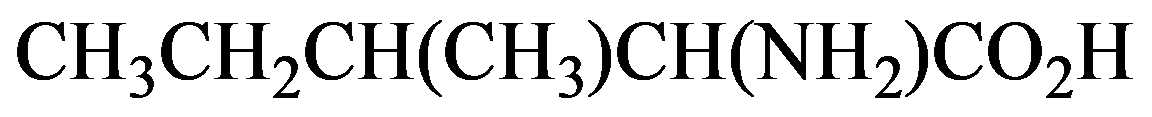
Kekule
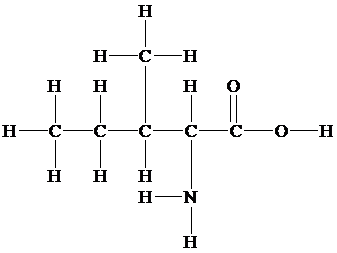
Skeletal (line):
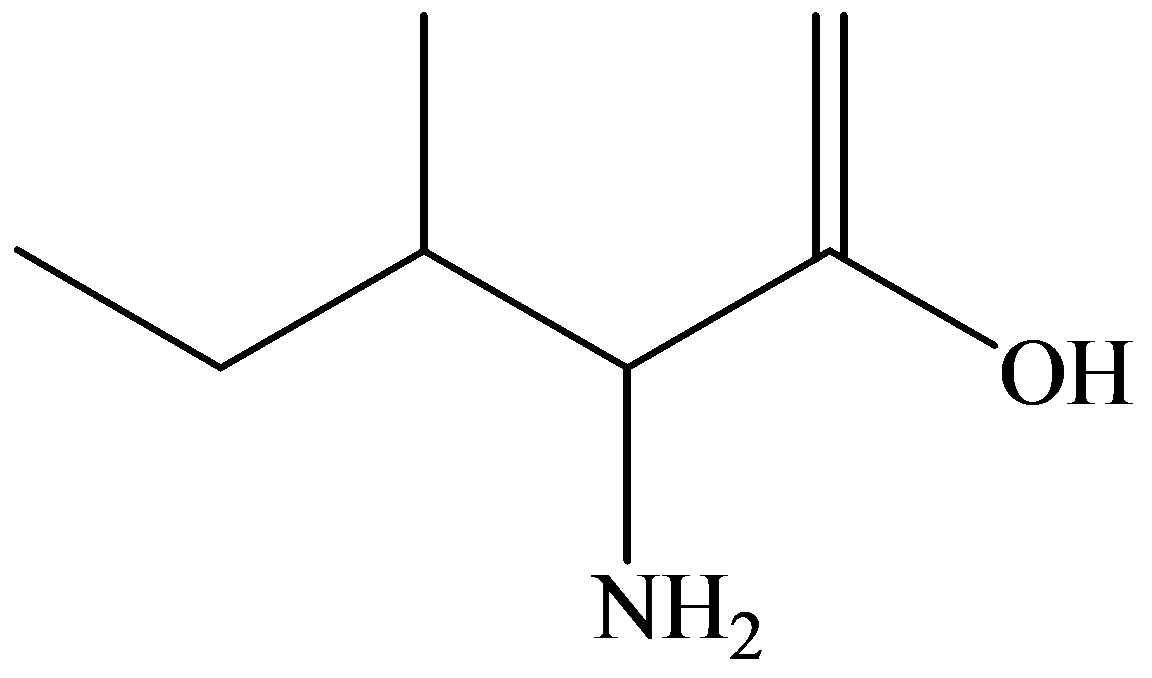
Explanation of Solution
a)
In the condensed structural formula, the compound consists of two
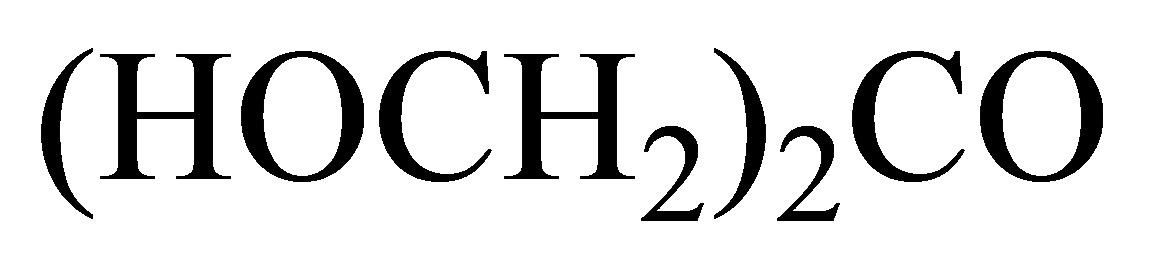
In thestructure given below, there are three carbon atoms, in which two carbon atoms are linked to the

The skeletal structure consists of a line representation of the bond between atoms. In this structure, carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown except heteroatoms. Two oxygen atoms are linked by a single line and one oxygen atom is linked by double lines. A single line representsa single bond and double lines represent double bonds.

b)
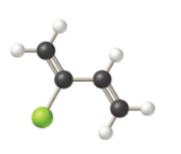
The condensed structural formula consists of two functional groups that are
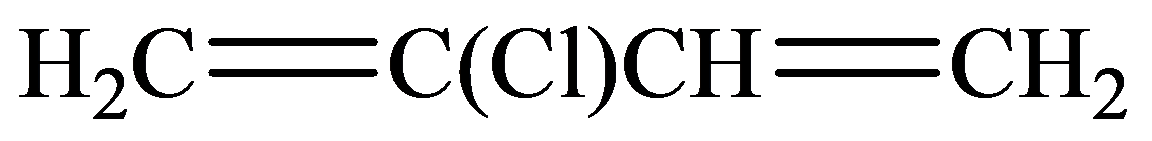 .
.
In the structure given below, there are four carbon atoms in the compounds that are linked by alternate single and double bonds, in which one carbon atom is linked to the
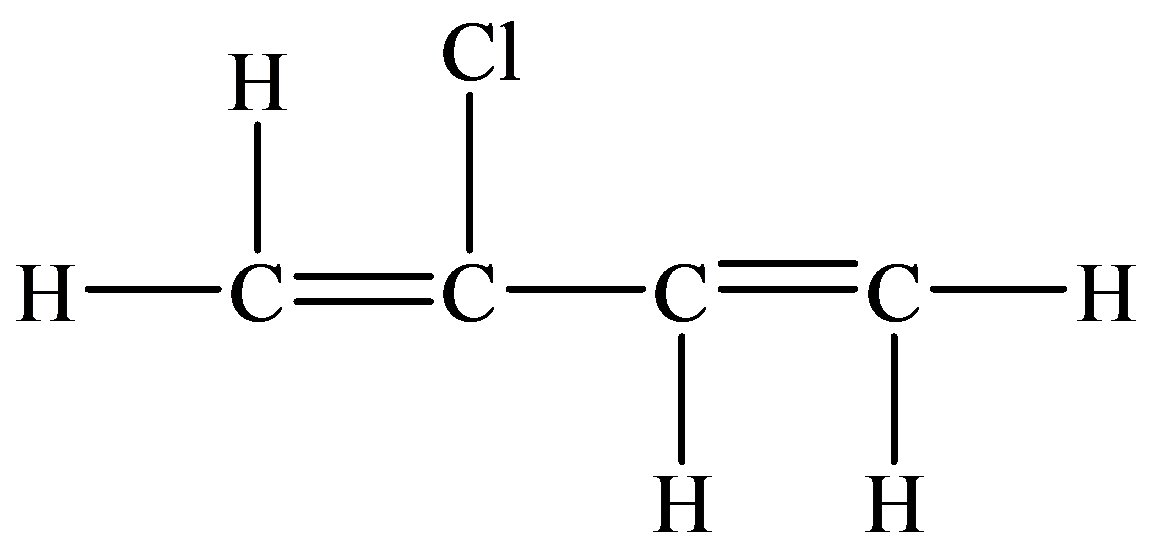
The skeletal structure consists of the line representation of the bond between atoms. In this structure, carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown except heteroatoms. A single line represents single bonds and double lines represent double bonds. The
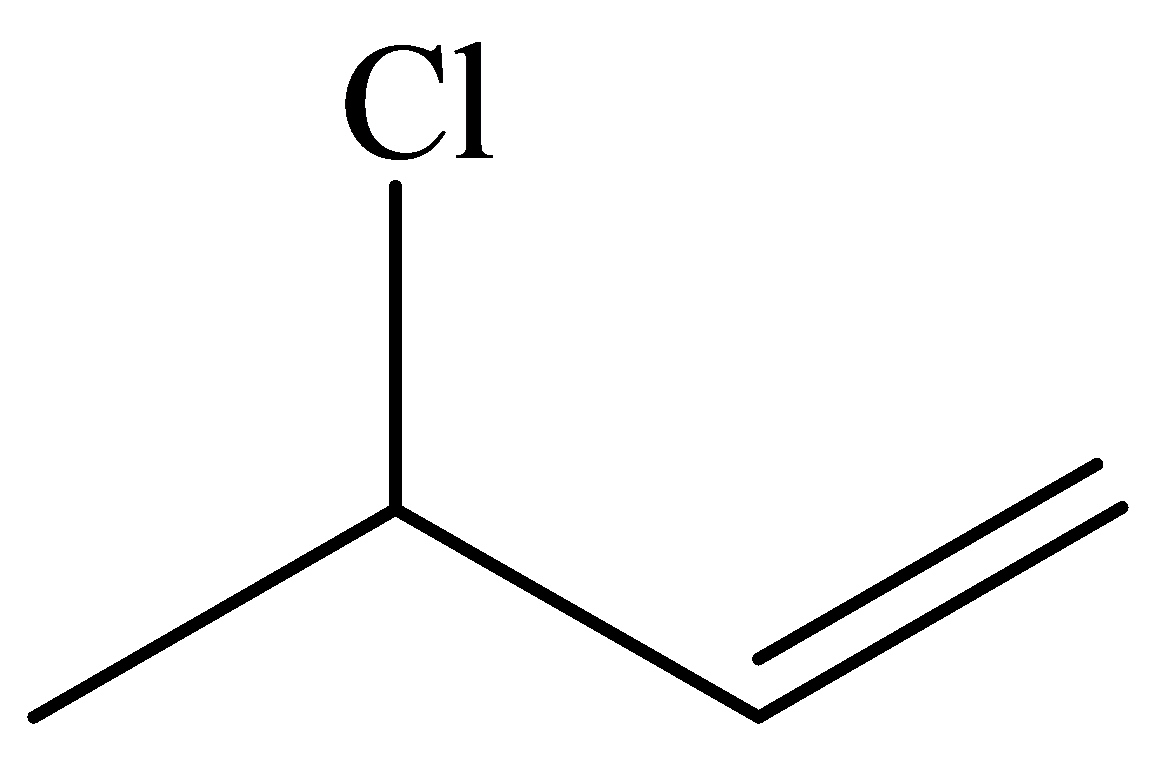
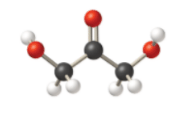
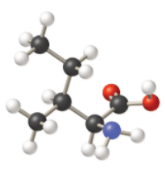
Given information: The molecular model of the compound is represented below:
c)
In thecompound given below, there are two
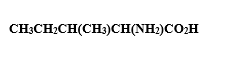
In the structure given below, there are sixcarbon atoms including the
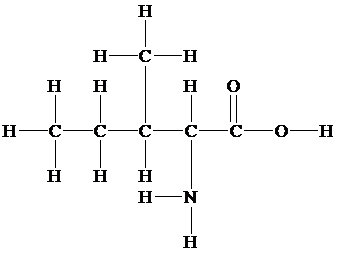
The skeletal structure contains the line representation to show the bond between atoms. In this structure, carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown except heteroatoms. Oxygen atoms are linked to the carbon atom with single and double lines, and the
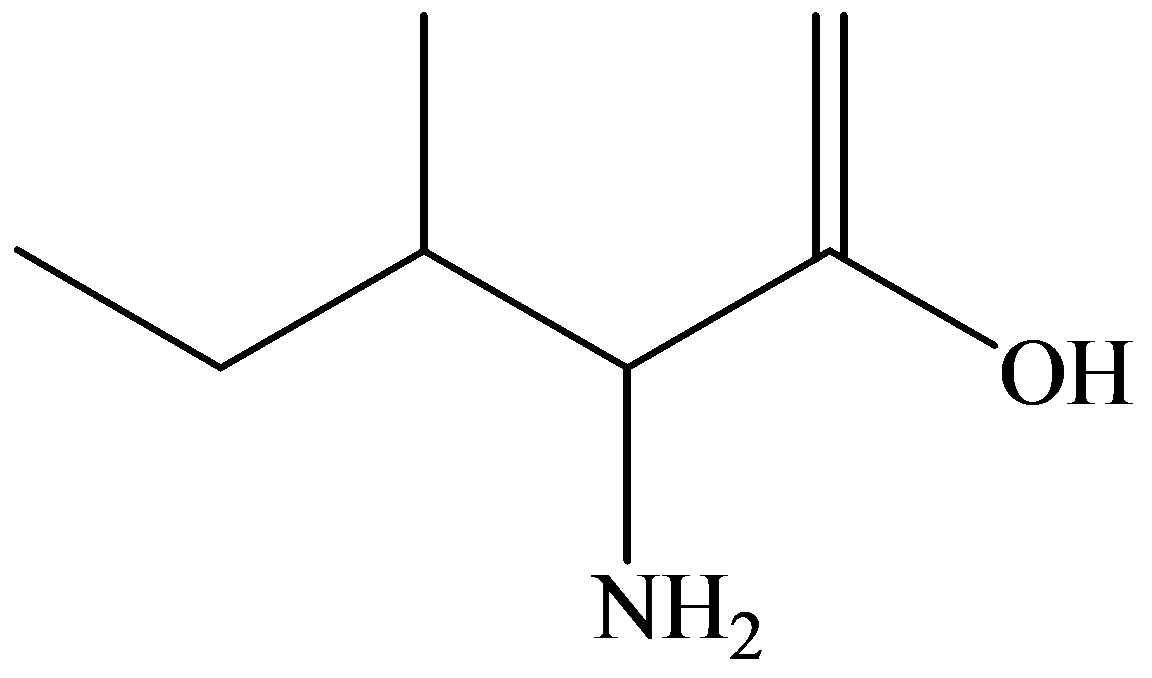
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Chemistry
- Determine whether each of the following molecules is a hemiacetal, acetal, or neither and select the appropriate box in the table. CH3O OH OH OH hemiacetal acetal neither hemiacetal acetal neither Xarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? N N དལ་ད་་ + R • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㄖˋarrow_forwardDraw the condensed structure of 4-hydroxy-3-methylbutanal. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward
- Using the bond energy values, calculate the energy that must be supplied or is released upon the polymerization of 755 monomers. If energy must be supplied, provide a positive number; if energy is released, provide a negative number. Hint: Avogadro’s number is 6.02 × 1023.arrow_forward-AG|F=2E|V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: Acidic solution -0.93 +0.38 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 H3PO3 H3PO2 → P→ PH3 -0.28 -0.50 → -0.50 Basic solution 3-1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO →→H2PO2 P PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P2O6 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH, 0.0 -0.5- 2 3 9 3 -1.5 -2.0 Pa H,PO H,PO H,PO -3 -1 0 2 4 Oxidation state, N 2 b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) c) Elemental phosphorus tends to disproportionate under basic conditions. Use data in…arrow_forwardThese two reactions appear to start with the same starting materials but result in different products. How do the chemicals know which product to form? Are both products formed, or is there some information missing that will direct them a particular way?arrow_forward
- What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Priva ×arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: Explanation Check IN NaBH3CN H+ ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. D 5 C +arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: H3O+ + ? • Draw all the reasonable products in the drawing area below. If there are no products, because no reaction will occur, check the box under the drawing area. • Include both major and minor products, if some of the products will be more common than others. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if you need to distinguish between enantiomers. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. dmarrow_forward
- Iarrow_forwardDraw the anti-Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for esc esc ☐ Explanation Check F1 1 2 F2 # 3 F3 + $ 14 × 1. BH THE BH3 2. H O NaOH '2 2' Click and drag to start drawing a structure. F4 Q W E R A S D % 905 LL F5 F6 F7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility < & 6 7 27 8 T Y U G H I F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 9 0 J K L P + // command option Z X C V B N M H H rol option commandarrow_forwardAG/F-2° V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: -0.93 +0.38 -0.50 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 →H3PO3 →→H3PO₂ → P → PH3 Acidic solution Basic solution -0.28 -0.50 3--1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO H₂PO₂ →P → PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P206 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH P 0.0 -0.5 -1.0- -1.5- -2.0 H.PO, -2.3+ -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 2 H,PO, b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) H,PO 4 S Oxidation stale, Narrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





