
Interpretation:
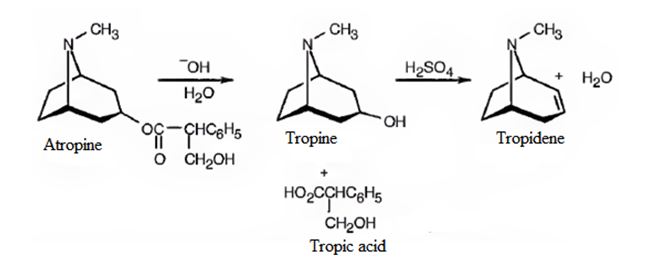
A structure for atropine (C17H23NO3) is to be proposed from the following observations: i) On basic hydrolysis atropine yields tropic acid C6H5CH(CH2OH)COOH and tropine (C8H15NO). ii) Tropine is an optically inactive alcohol that yields tropidene on dehydration with H2SO4.
Concept introduction:
Esters when hydrolyzed with bases yield alcohols and
To predict:
A structure for atropine (C17H23NO3) from the following observations: i) On basic hydrolysis atropine yields tropic acid C6H5CH(CH2OH)COOH and tropine (C8H15NO). ii) Tropine is an optically inactive alcohol that yields tropidene on dehydration with H2SO4.
Answer:
Structure of atropine is
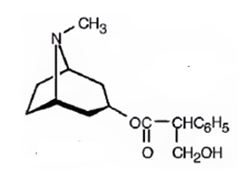
Explanation:
Atropine gives tropic acid and an alcohol, tropine when hydrolyzed in the presence of bases. Hence it must be an ester. Tropine upon dehydration gives tropidene. Hence structure of tropine (optically inactive) can be obtained by adding water to the structure of tropidene.
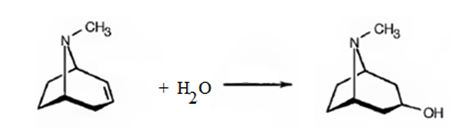
The formation of the ester linkage between the OH of atropine and COOH of tropic acid gives atropine. The reactions can be represented as below.
Conclusion:
Structure of atropine is

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 24 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDetermine whether the following reaction is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction: Br OH HO 2 -- Molecule A Molecule B + Br 义 ollo 18 Is this a nucleophilic substitution reaction? If this is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, answer the remaining questions in this table. Which of the reactants is referred to as the nucleophile in this reaction? Which of the reactants is referred to as the organic substrate in this reaction? Use a ŏ + symbol to label the electrophilic carbon that is attacked during the substitution. Highlight the leaving group on the appropriate reactant. ◇ Yes O No O Molecule A Molecule B Molecule A Molecule B टेarrow_forward
- Show work..don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work..don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardPheromone G of the maize stalk borer, chilo partelus, can be synthesized based on the partial scheme shown below. Complete the scheme by identifying the structures of the intermediate compounds A, B, C, D, E, F and pheromone G. Indicate stereochemistry where relevantarrow_forward
- Q8: Draw the resonance structures for the following molecule. Show the curved arrows (how you derive each resonance structure). Circle the major resonance contributor. одarrow_forwardQ9: Explain why compound I is protonated on O while compound II is protonated on N. NH2 DD I II NH2arrow_forwardComplete the following reaction by identifying the principle organic product of the reactionarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning



