
Concept explainers
The graph of the magnitude of electric field due to the given configuration versus
Answer to Problem 55AP
The graph of the magnitude of electric field due to the given configuration versus
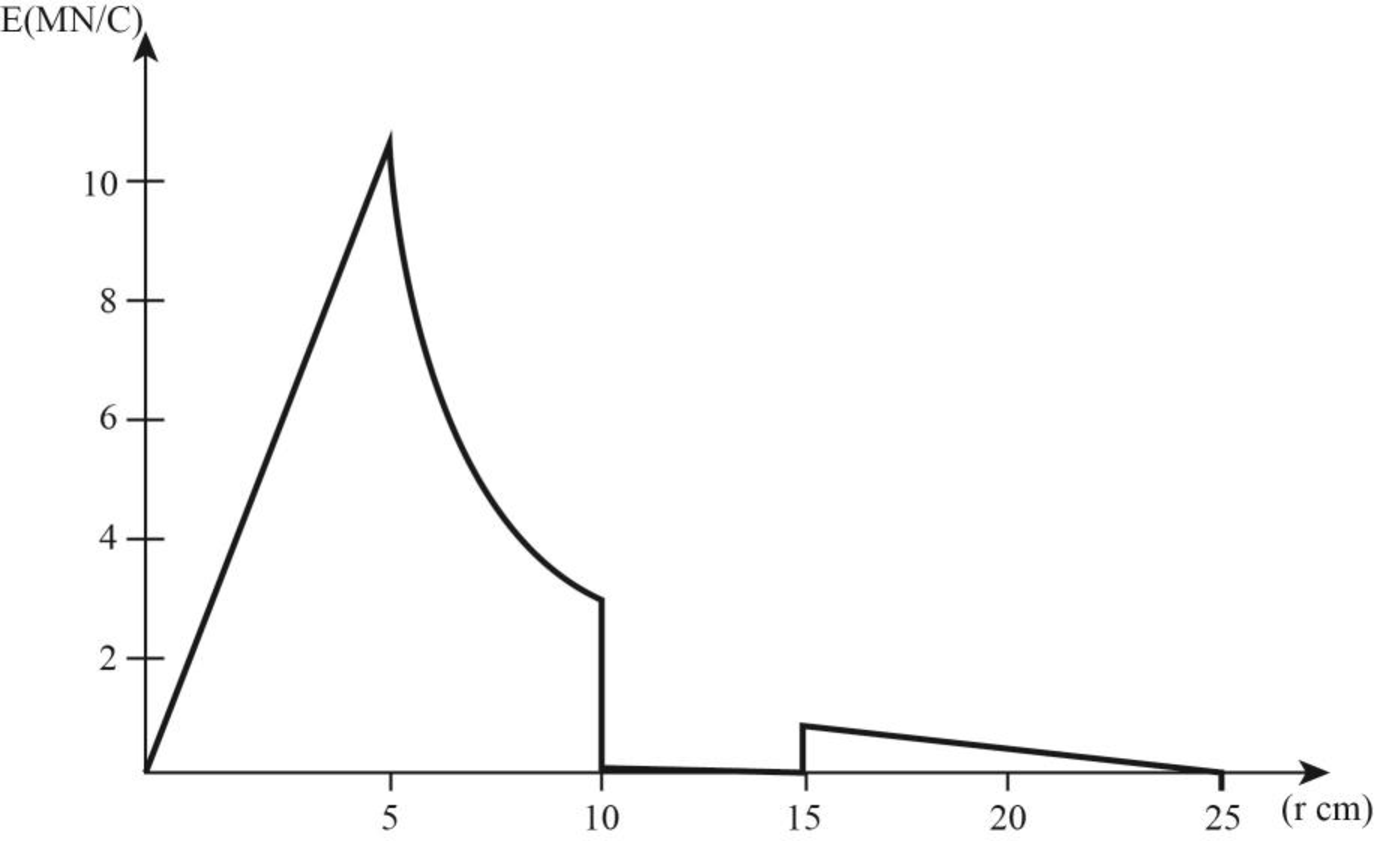
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the electric field on uniformly charged sphere for
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the electric field on uniformly charged sphere for
The electric field inside a conductor is
So, for the region
Write the expression to calculate the net charge outside the sphere.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the electric field outside the uniformly charged sphere.
Conclusion:
For
Assume
Substitute
Calculate the electric field at
Substitute
For region
At
Substitute
At
Substitute
For region
Substitute
At
The graph of the magnitude of electric field due to the given configuration versus
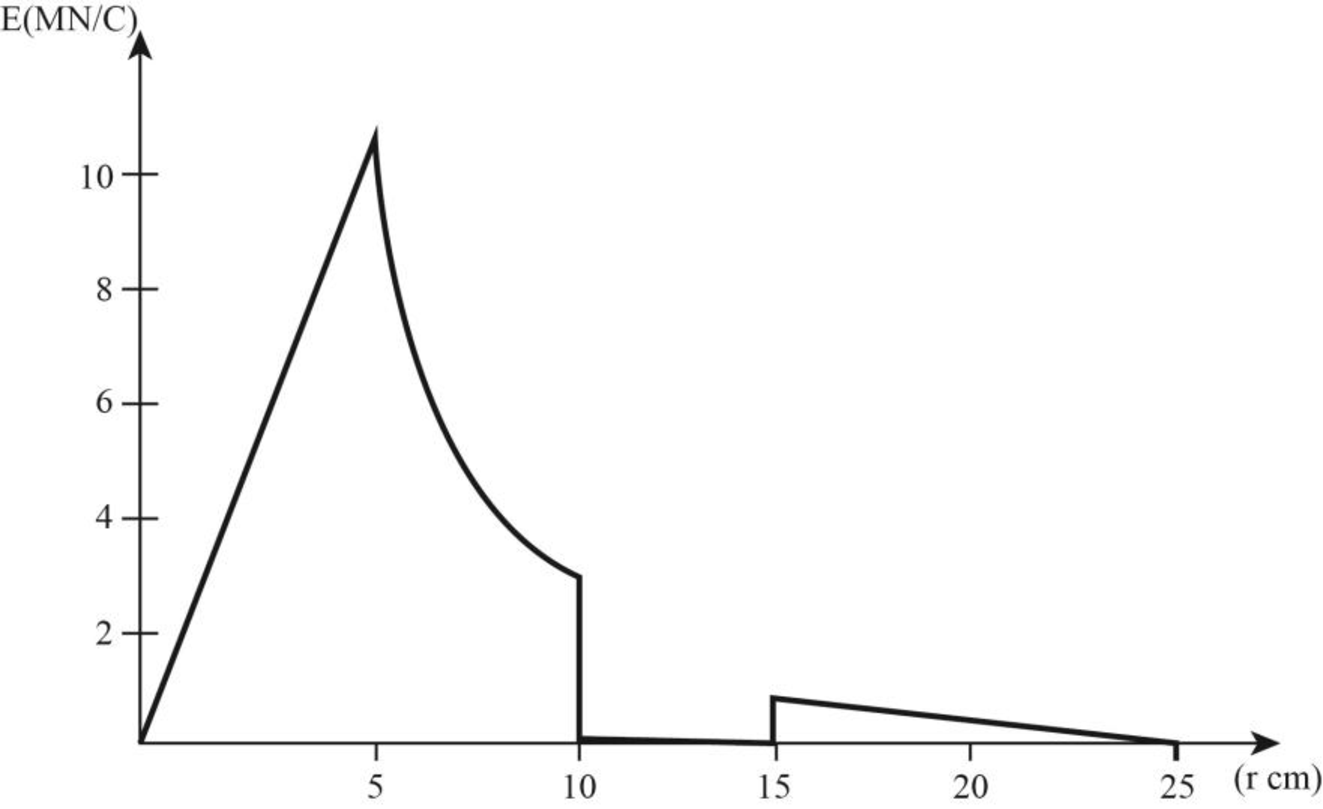
Figure (1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
- The rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forwardGive a more general expression for the magnitude of the torque τ. Rewrite the answer found in Part A in terms of the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment of the current loop m. Define the angle between the vector perpendicular to the plane of the coil and the magnetic field to be ϕ, noting that this angle is the complement of angle θ in Part A. Give your answer in terms of the magnetic moment mm, magnetic field B, and ϕ.arrow_forwardCalculate the electric and magnetic energy densities at thesurface of a 3-mm diameter copper wire carrying a 15-A current. The resistivity ofcopper is 1.68×10-8 Ω.m.Prob. 18, page 806, Ans: uE= 5.6 10-15 J/m3 uB= 1.6 J/m3arrow_forward
- A 15.8-mW laser puts out a narrow beam 2.0 mm in diameter.Suppose that the beam is in free space. What is the rms value of E in the beam? What isthe rms value of B in the beam?Prob. 28, page 834. Ans: Erms= 1380 V/m, Brms =4.59×10-6 Tarrow_forwardA 4.5 cm tall object is placed 26 cm in front of a sphericalmirror. It is desired to produce a virtual image that is upright and 3.5 cm tall.(a) What type of mirror should be used, convex, or concave?(b) Where is the image located?(c) What is the focal length of the mirror?(d) What is the radius of curvature of the mirror?Prob. 25, page 861. Ans: (a) convex, (b) di= -20.2 cm, i.e. 20.2 cm behind the mirror,(c) f= -90.55 cm, (d) r= -181.1 cm.arrow_forwardA series RCL circuit contains an inductor with inductance L=3.32 mH, and a generator whose rms voltage is 11.2 V. At a resonant frequencyof 1.25 kHz the average power delivered to the circuit is 26.9 W.(a) Find the value of the capacitance.(b) Find the value of the resistance.(c) What is the power factor of this circuit?Ans: C=4.89 μF, R=4.66 Ω, 1.arrow_forward
- A group of particles is traveling in a magnetic field of unknown magnitude and direction. You observe that a proton moving at 1.70 km/s in the +x-direction experiences a force of 2.06×10−16 N in the +y-direction, and an electron moving at 4.40 km/s in the −z-direction experiences a force of 8.10×10−16 N in the +y-direction. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on an electron moving in the −y-direction at 3.70 km/s ? What is the direction of this the magnetic force? (in the xz-plane)arrow_forwardA particle with a charge of −5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of B =−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be F=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the x component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardIs it possible for average velocity to be negative?a. Yes, in cases when the net displacement is negative.b. Yes, if the body keeps changing its direction during motion.c. No, average velocity describes only magnitude and not the direction of motion.d. No, average velocity describes only the magnitude in the positive direction of motion.arrow_forward
- Tutorial Exercise An air-filled spherical capacitor is constructed with an inner-shell radius of 6.95 cm and an outer-shell radius of 14.5 cm. (a) Calculate the capacitance of the device. (b) What potential difference between the spheres results in a 4.00-μC charge on the capacitor? Part 1 of 4 - Conceptualize Since the separation between the inner and outer shells is much larger than a typical electronic capacitor with separation on the order of 0.1 mm and capacitance in the microfarad range, we expect the capacitance of this spherical configuration to be on the order of picofarads. The potential difference should be sufficiently low to avoid sparking through the air that separates the shells. Part 2 of 4 - Categorize We will calculate the capacitance from the equation for a spherical shell capacitor. We will then calculate the voltage found from Q = CAV.arrow_forwardI need help figuring out how to do part 2 with the information given in part 1 and putting it in to the simulation. ( trying to match the velocity graph from the paper onto the simulation to find the applied force graph) Using this simulation https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/cheerpj/forces-1d/latest/forces-1d.html?simulation=forces-1d.arrow_forwardI need help running the simulation to get the result needed.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





