
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The role of coenzymes NAD+ and NADH in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 32P
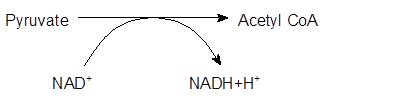
Explanation of Solution
The
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
The pyruvate from glycolysis synthesizes acetyl CoA by the loss of one C atom in the form of CO2 gas in the presence of CoenzymeA. This breakdown of pyruvate molecule occurs by transfer of electrons to NAD+ to form NADH. Further, NADH will be used by the cell to produce ATP.
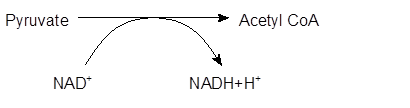
(b)
Interpretation:
The role of coenzymes NAD+ and NADH in the conversion of pyruvate to lactate should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 32P
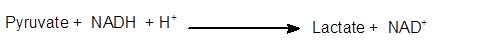
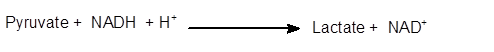
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions that involve the glucose molecules into pyruvate with the production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
The conversion of pyruvate to lactate is an enzymatical process. It is a hydrogenation reaction in which NADH changes to NAD+whereas the reversible process is catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenases.
(c)
Interpretation:
The role of coenzymes NAD+ and NADH in the conversion of pyruvate to ethanol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 32P
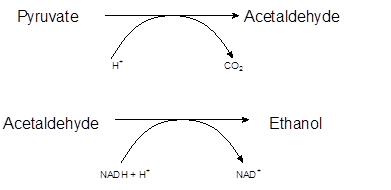
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions which involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
In the anaerobic conditions and presence of yeast, pyruvate converts to carbon dioxide and ethanol. Enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase catalyzes this reaction and removes a carbon dioxide molecule from the pyruvate to yield acetaldehyde which further changes to ethanol in the presence of NADH.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- Assign these COSY Spectrumarrow_forwardAssign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward
- 个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forward
- DE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic products of the reaction below and draw them on right side of the arrow. If there will be no significant reaction, check the box below the drawing area instead. C Cl CH, OH There will be no significant reaction. + pyridine G Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





