
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis in which ATP are formed should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, ATP's are formed in step-7 and 10.
Explanation of Solution
The
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
Two steps; 7th and 10th step are involved in the production of ATP;
- Conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate occurs with the conversion of ADP to form ATP in the presence of Phosphoglycerate kinase that transfers a phosphate group.
- Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvic acid with the conversion of ATP in the presence enzyme pyruvate kinase
(b)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis which uses ATP molecules should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, ATP's are formed in step-1 and 3.
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions that involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with the production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
Two steps; 1st and 3rdstep use ATP molecules.
- The first step in glycolysis, glucose converts to glucose-6-phosphate in the presence of hexokinase. It uses energy in the form of ATP and converts it to ADP molecule.
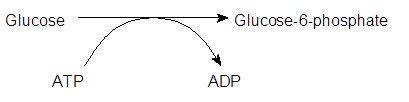
- Phosphofructokinase, with magnesium as a cofactor, changes fructose 6-phosphate into fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate.
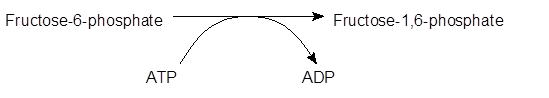
(c)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis which forms a reduce coenzyme should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, step-6 forms a reduced coenzyme NADH.
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions which involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with the production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
In the 6th step of glycolysis, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate converts to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. It is a dehydrogenation step that occurs in the presence of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and converts NAD+ to NADH and H+ ions.
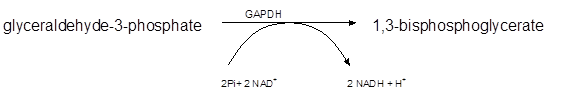
(c)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis which breaks a C-C bond should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
- Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, step-4breaks a C-C bond.
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions which involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
In the 4thstep of glycolysis, in the presence of enzyme Aldolase, fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate breaks into two sugar molecules. These sugar molecules are isomers of each other; dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP).
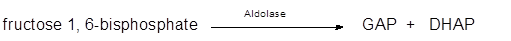
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- What is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward. M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forward
- Please use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forwardBriefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forward
- Answe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward3. A gas mixture contains 50 mol% H2 and 50 mol% He. 1.00-L samples of this gas mixture are mixed with variable volumes of O2 (at 0 °C and 1 atm). A spark is introduced to allow the mixture to undergo complete combustion. The final volume is measured at 0 °C and 1 atm. Which graph best depicts the final volume as a function of the volume of added O2? (A) 2.00 1.75 Final Volume, L 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 2.00 (B) 1.75 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50- 0.25 0.00 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 2 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2 2.00 2.00 (C) (D) 1.75 1.75 1.50 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2arrow_forward
- Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pai 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60. H2N-C(R)H-COOH and R is -CH2-CH(CH3)2 A. Draw the condensed structure for leucine, and label all chirality centers with an asterisk. B. How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there? C. Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S. D. What is the p/ of leucine? E. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at 10.00. F. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50. G. Leucine is described as an essential amino acid. What does this mean? H. Show the alkyl halide you would use to prepare leucine by the amidomalonate method. =arrow_forwarda) Write out 6 completely different reactions of acetophenone (reagent, product). b) Write out 3 preparations of 1-methylcyclohexanol, using a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain. c) Write out 3 preparations of 2-ethoxybenzoic acid, a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain.arrow_forward12. CH3 OH OH H&C CH3 H₂C N OH H₂C CH3 H&C CH3 H₂C' CH3 H.C CH3OH H.C CH2CH3OH CH3CEN Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR spectrum? IR Spectrum 3000 4000 3000 NMR Spectrum 2000 £500 RAVENUMBER 2000 1500 9 8 6 5 10 HP-00-290 ppm m 1000 500 1000 4 °arrow_forward
 Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





