
Sulfide ion (S2- ) is formed in wastewater by the action of an aerobic bacteria on organic matter. Sulfide can be readily protonated to form volatile, toxic H2S. In addition to the toxicity and noxious odor, sulfide and H2S cause corrosion problems because they can be easily converted to sulfuric acid when conditions change to aerobic. One common method to determine sulfide is by coulometric titration with generated silver ion.At the generator electrode, the reaction is Ag
(a) A digital chloridometer was used to determine the mass of sulfide in a wastewater sample. The chloridometer reads out directly in ng Cl-.In chloride determinations, the same generator reaction is used,but the titration reaction is Cl- + Ag+
(b) A particular wastewater standard gave a reading of 1689.6 ng Cl-. What total charge in coulombs was required to generate the Ag+ needed to precipitate the sulfide in this standard?
(c) The following results were obtained on 20.00-mL samples containing known amounts of sulfide.17
Each standard was analyzed in triplicate and the mass of chloride recorded. Convert each of the chloride results to mass S2- (ng).
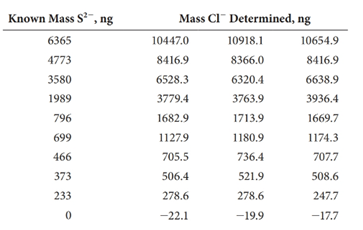
(d) Determine the average mass of S2- (ng), the standard deviation, and the %RSD) of each standard.
(e) Prepare a plot ofthe average mass of S2- determined (ng) versus the actual mass (ng). Determine theslope, the intercept, the standard error, and the R2 value. Comment on the fit of the data to a linear model.
(f) Determine the detection limit (ng) and in parts per million using a k factor of 2 (see Equation 1-12).
(g) An unknown wastewater sample gave an average reading of 893.2 ng Cl. What is the mass of sulfide (ng)? If 20.00 mL of the wastewater sample was introduced into the titration vessel, what is the concentration of S2- n parts per million?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- Rank the compounds below from lowest to highest melting point.arrow_forward18 Question (1 point) Draw the line structure form of the given partially condensed structure in the box provided. :ÖH HC HC H2 ΙΩ Н2 CH2 CH3 CH3 partially condensed formarrow_forwardsomeone else has already submitted the same question on here and it was the incorrect answer.arrow_forward
- The reaction: 2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) is an exothermic reaction, ΔH=-58.0 kJ/molrxn at 0°C the KP is 58.If the initial partial pressures of both NO2(g) and N2O4(g) are 2.00 atm:A) Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what is the value of Q? B) Which direction will the reaction go to reach equilibrium? C) Use an ICE table to find the equilibrium pressures.arrow_forwardThe dissociation of the weak acid, nitrous acid, HNO2, takes place according to the reaction: HNO2 (aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + NO2–(aq) K=7.2 X 10-4 When 1.00 mole of HNO2 is added to 1.00 L of water, the H+ concentration at equilibrium is 0.0265 M.A) Calculate the value of Q if 1.00 L of water is added? B) How will reaction shift if 1.00 L of water is added?arrow_forwardSuppose a certain copolymer elastomeric material “styrene-butadiene rubber”) contains styrene ("S") monomers –(C8H8)– and butadiene ("B") monomers –(C4H6)– and that their numerical ratio S:B = 1:8. What is the mass ratio mS:mB of the two monomers in the material? What is the molecular mass M of a macromolecule of this copolymer with degree of polymerization n = 60,000? Data: AC = 12.01 u, AH = 1.008 u.arrow_forward
- Lab Questions from Lab: Gravimetric Determination of Calcium as CaC2O4•H2O What is the purpose of the methyl red indicator? Why does a color change to yellow tell you that the reaction is complete? Why is the precipitate rinsed with ice-cold water in step 4? Why not room temperature or hot water? Why is it important that the funnels be placed in a desiccator before weighing (steps 1 and 5)?arrow_forwardWhat mass of ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, Mustbe added to 5.50 kg of water to antifreeze that would work for the car radiator to -10.0 degrees celcius? MM (g/mol): 62.07arrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of a 0.393 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 g/molarrow_forward
- The rate constant for the decay of a radioactive element is 2.28 × 10⁻³ day⁻¹. What is the half-life of this element in days?arrow_forwardHandwritten pleasearrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





