
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether B vitamin thiamin is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(a)
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
None of the given processes includes B vitamin thiamin as a cofactor. B vitamin thiamin is needed as a cofactor in the conversion of pyruvate to
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin thiamin is encountered in the form of thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP) in the carbohydrate metabolism. TPP in not involved in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lactate fermentation, and glycogenolysis. Hence, none of the given processes includes vitamin thiamin as a cofactor.
Pyruvate is converted to
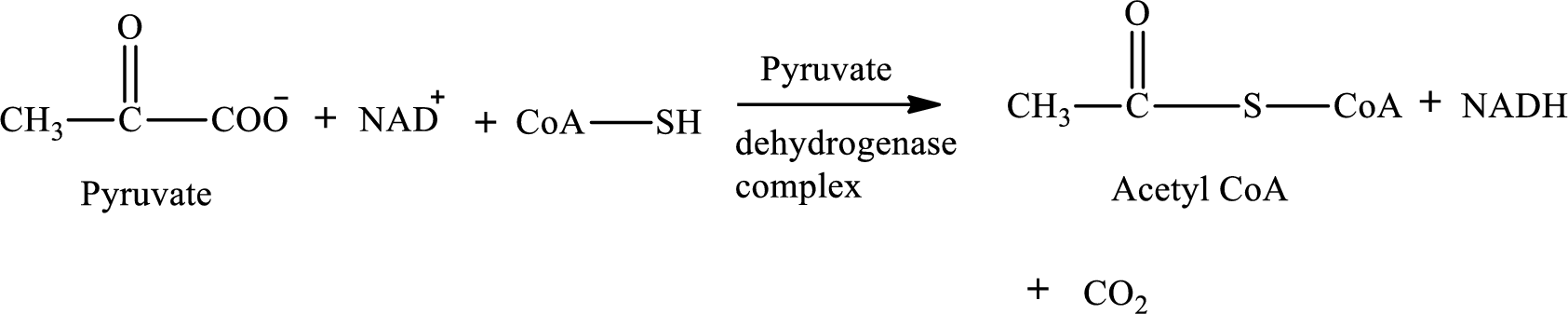
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains three different enzymes. Each enzyme contains numerous subunits. The overall reaction requires FAD,
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate B vitamin riboflavin is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(b)
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
None of the given processes includes vitamin riboflavin as a cofactor. B vitamin riboflavin is needed as a cofactor in the citric acid cycle.
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin riboflavin is encountered in the form of FAD(Flavin adenine dinucleotide) in the carbohydrate metabolism. FAD in not involved in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lactate fermentation, and glycogenolysis. Hence, none of the given processes includes B vitamin riboflavin as a cofactor.
The citric acid cycle is the third stage of the biochemical energy production process. The cycle includes the reactions in which the acetyl part of acetyl CoA is oxidized and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether B vitamin pantothenic acid is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(c)
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
None of the given processes includes B vitamin pantothenic acid as a cofactor. B vitamin pantothenic acid is needed as a cofactor in the conversion of pyruvate to
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin pantothenic acid is encountered in the form of
Pyruvate is converted to
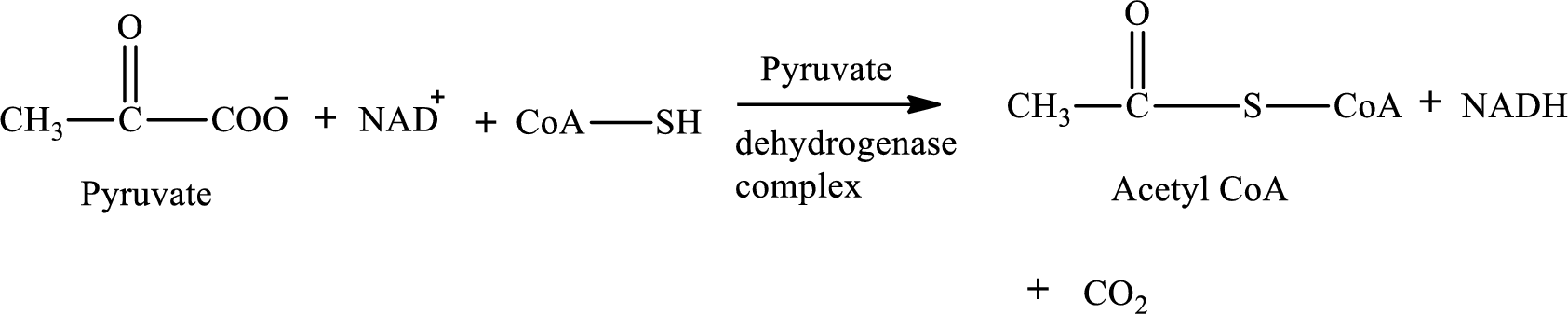
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains three different enzymes. Each enzyme contains numerous subunits. The overall reaction requires FAD,
(d)
Interpretation: To indicate
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
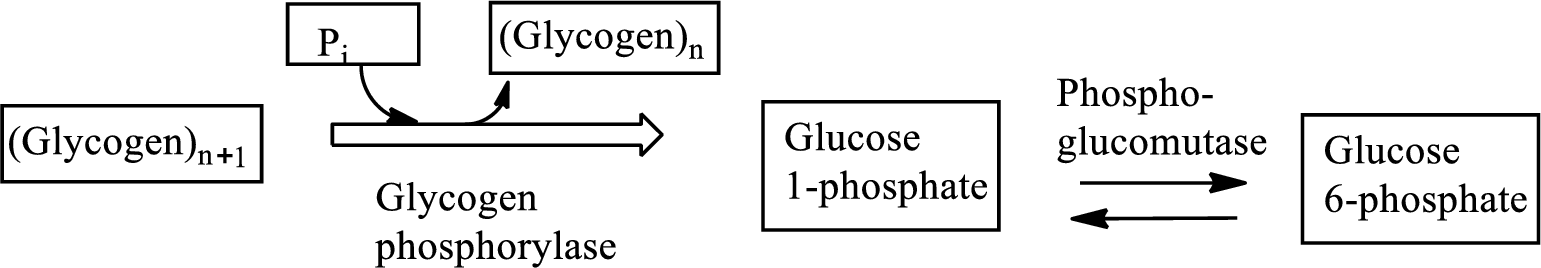
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
Answer to Problem 24.117EP
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





