
Concept explainers
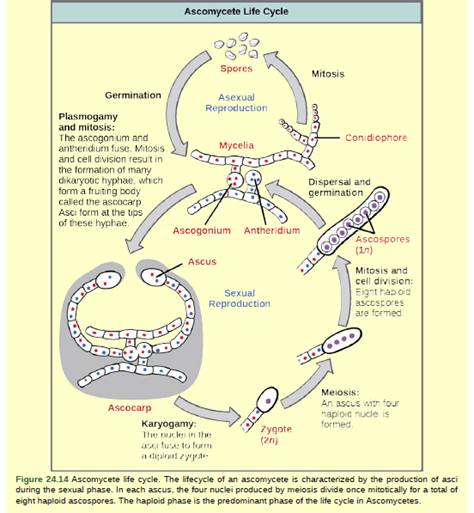
Figure 24.14 Which of the following statements is true?
- A dikaryotic ascus that forms in the ascocarp undergoes karyogamy, meiosis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores.
Introduction:
Among fungi, Asus is found as the sac-like structure, which contains the haploid structures known as ascospores. These filamentous ascomycetes from the hyphae, which are divided by the septa. These hyphae allow streaming of cytoplasmic matrix from one cell to another.
Answer to Problem 1VCQ
Correct answer:
The correct answer is an option (a).
Explanation of Solution
Explanation for the correct answer:
Option (a)- Dikaryotic hyphae are produced, in which two haploid nuclei. These dikaryotichyphae can be homo or heterokaryotic. In each cell, two haploid nuclei fuse in the process of karyogamy and result in the diploid nucleus, then undergo meiosis and led to the ascospore formation. After the formation, the ascospores germinate and form hyphae.
Explanation for incorrect answer:
Option (b)- A diploid ascus does not undergo karyogamy, meiosis,and mitosis to form the eight ascospores because only dikaryotic undergo karyogamy. Hence, this option is incorrect.
Option (c)- In the same way, a haploid zygote does not undergo the karyogamy, meiosis,andmitosis. Hence, this option is incorrect.
Option (d)- A dikaryotic ascus only formed by the process of karyogamy not by the plasmogamy meiosis and mitosis to form eight ascospores. Hence, this option is incorrect.
Dikaryotic hyphae are produced in which two haploid nuclei with the help of karyogamy, not by the plasmogamy. Hence, the correct answer is option (a).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Biology 2e
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Can you fill out those termsarrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forwardAn 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forward
- The patient needs a solution of 2.5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s solution to run at 75 ml/hr for at least the next 12hours. LRS comes in fluid bags of 500 ml, 1 Liter, 3 Liters and 5 Liters. How can a 2.5% solution be made by adding50% dextrose to the LRS?arrow_forward“Gretchen” was a 68-pound canine who came to the VMTH as small animal surgery patient. She receivedacepromazine, 0.2 mg/kg from a 10 mg/ml solution and oxymorphone, 0.08 mg/kg from a 1 mg/ml solution before surgery.What are the mechanisms of action of acepromazine and oxymorphone? Why would they be given together?How many mg provide each dose and how many ml of each of these solutions were given?arrow_forwardAfter surgery, “Gretchen” was put on carprofen, 1 mg/pound bid (twice a day). The tablets come in 25, 75 and 100 mgsizes. Which size tablet would be appropriate?What is the mechanism of action of carprofen?An outpatient prescription was written for her so she would have enough for 10 days. How many tablets did she need?What information needs to be on her out-patient prescription?arrow_forward
- Joden Koepp olor in chickens is due to incomplete dominance. BB = Black chicken, WW = White BLOOD TYPES Arhite chicken is In humans, Rh positive blood is dominant (R) over Rh negative blood (r). A man with type 0, Rh positive blood (whose mother had Rh negative blood), marries a woman with type AB, Rh negative blood. Several children were born. is? R R Genotypes Phenotypes RRR RR Rr Rr 4/16 RR R RR RK Rr Rr 4/16 rr 3/4 Rh posi 1/4 Rh negu 1/2 Rr rr rr rrrr 88 888 75 e genotype of the man? the genotype of the woman? The mother of the man had type AB blood.arrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forward
- Please indentify the unknown organismarrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forward5G JA ATTC 3 3 CTIA A1G5 5 GAAT I I3 3 CTIA AA5 Fig. 5-3: The Eco restriction site (left) would be cleaved at the locations indicated by the arrows. However, a SNP in the position shown in gray (right) would prevent cleavage at this site by EcoRI One of the SNPs in B. rapa is found within the Park14 locus and can be detected by RFLP analysis. The CT polymorphism is found in the intron of the Bra013780 gene found on Chromosome 1. The Park14 allele with the "C" in the SNP has two EcoRI sites and thus is cleaved twice by EcoRI If there is a "T" in that SNP, one of the EcoRI sites is altered, so the Park14 allele with the T in the SNP has only one EcoRI site (Fig. 5-3). Park14 allele with SNP(C) Park14 allele with SNPT) 839 EcoRI 1101 EcoRI 839 EcoRI Fig. 5.4: Schematic restriction maps of the two different Park14 alleles (1316 bp long) of B. rapa. Where on these maps is the CT SNP located? 90 The primers used to amplify the DNA at the Park14 locus (see Fig. 5 and Table 3 of Slankster et…arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





