
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.3, Problem 3aT
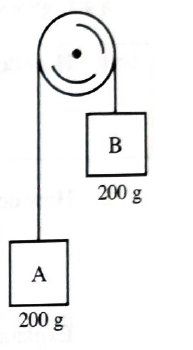
Predict the subsequent motions of objects A and B after they are released.
Explain the basis for your description. Do not use algebra.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule00:53
Students have asked these similar questions
The cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field?
V/m
Consider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...?
a. Both rods have less mass
b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass
c. both rods have more mass
d. the masses of both rods are unchanged
e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe mass
8) 9)
Chapter 2 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 2.1 - Draw a large dot on your large sheet of paper to...Ch. 2.1 - Describe the remaining forces you have indicated...Ch. 2.1 - All forces arise from interactions between...Ch. 2.1 - There are many different types of forces,...Ch. 2.1 - Consider the following discussion between two...Ch. 2.1 - Label each of the forces on your free-body diagram...Ch. 2.1 - Sketch a free-body diagram for a book at rest on a...Ch. 2.1 - A second book of greater mass is placed on top of...Ch. 2.1 - Compare the free-body diagram for the lower book...Ch. 2.1 - Which, if any, Newton’s third law force pairs are...
Ch. 2.1 - A magnet is supported by another magnet as shown...Ch. 2.1 - An iron rod is held up by a magnet as shown. The...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the net force (magnitude and direction) on...Ch. 2.2 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for system A and...Ch. 2.2 - Is the magnitude of the force exerted on system A...Ch. 2.2 - D. Identify all the Newton's third law...Ch. 2.2 - Rank the magnitudes of the horizontal forces that...Ch. 2.2 - Suppose the mass of each brick is 2.5 kg, the...Ch. 2.2 - Describe the motions of systems A and B. How does...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the net force (magnitude and direction) on...Ch. 2.2 - Draw and label separate free-body diagrams for...Ch. 2.2 - Consider the following discussion between two...Ch. 2.2 - Rank the magnitudes of all the horizontal forces...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the magnitude of the netforce on system C...Ch. 2.2 - Draw and label a free-body diagram for system C....Ch. 2.2 - At right is a free-body diagram for a cart. All...Ch. 2.3 - Describe the motions of block A, block B, and the...Ch. 2.3 - On a large sheet of paper, draw a separate...Ch. 2.3 - Identify all the Newton's third law...Ch. 2.3 - Rank, from largest to smallest, the magnitudes of...Ch. 2.3 - Consider the horizontal components of the forces...Ch. 2.3 - If the motion of the blocks is the same as in...Ch. 2.3 - Suppose the mass of the string that connects...Ch. 2.3 - A string exerts a force on each of the two objects...Ch. 2.3 - If you know that the net force on a massless...Ch. 2.3 - Predict the subsequent motions of objects A and B...Ch. 2.3 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for objects A and...Ch. 2.3 - Predict: • what will happen to object C when it is...Ch. 2.3 - Draw and label separate free-body diagrams for...Ch. 2.3 - The weight of a 200 g mass has magnitude...Ch. 2.3 - Consider the following statement about the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Why is petroleum jelly used in the hanging-drop procedure?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Define and discuss these terms: (a) synapsis, (b) bivalents, (c) chiasmata, (d) crossing over, (e) chromomeres,...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
The glycine cleavage system is a group of four enzymes that together catalyze the following reaction: glycine+T...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY