
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.3, Problem 2aT
If the motion of the blocks is the same as in section I, how does the net force on the string compare to the net force on the rope?
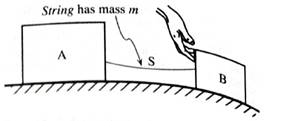
1. Determine whether the net force on each of the objects is greater than, less than, or equal to the net force on the object in section I. Explain.
- block A
- block B
- the system composed of the blocks and the connecting rope or string
2. Compare the horizontal components of the following pairs of forces:
- the forces on the string by block A and the rope by block A. Explain.
- the forces on the string by block B and the rope by block B. Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2
3
Imagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 2.1 - Draw a large dot on your large sheet of paper to...Ch. 2.1 - Describe the remaining forces you have indicated...Ch. 2.1 - All forces arise from interactions between...Ch. 2.1 - There are many different types of forces,...Ch. 2.1 - Consider the following discussion between two...Ch. 2.1 - Label each of the forces on your free-body diagram...Ch. 2.1 - Sketch a free-body diagram for a book at rest on a...Ch. 2.1 - A second book of greater mass is placed on top of...Ch. 2.1 - Compare the free-body diagram for the lower book...Ch. 2.1 - Which, if any, Newton’s third law force pairs are...
Ch. 2.1 - A magnet is supported by another magnet as shown...Ch. 2.1 - An iron rod is held up by a magnet as shown. The...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the net force (magnitude and direction) on...Ch. 2.2 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for system A and...Ch. 2.2 - Is the magnitude of the force exerted on system A...Ch. 2.2 - D. Identify all the Newton's third law...Ch. 2.2 - Rank the magnitudes of the horizontal forces that...Ch. 2.2 - Suppose the mass of each brick is 2.5 kg, the...Ch. 2.2 - Describe the motions of systems A and B. How does...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the net force (magnitude and direction) on...Ch. 2.2 - Draw and label separate free-body diagrams for...Ch. 2.2 - Consider the following discussion between two...Ch. 2.2 - Rank the magnitudes of all the horizontal forces...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the magnitude of the netforce on system C...Ch. 2.2 - Draw and label a free-body diagram for system C....Ch. 2.2 - At right is a free-body diagram for a cart. All...Ch. 2.3 - Describe the motions of block A, block B, and the...Ch. 2.3 - On a large sheet of paper, draw a separate...Ch. 2.3 - Identify all the Newton's third law...Ch. 2.3 - Rank, from largest to smallest, the magnitudes of...Ch. 2.3 - Consider the horizontal components of the forces...Ch. 2.3 - If the motion of the blocks is the same as in...Ch. 2.3 - Suppose the mass of the string that connects...Ch. 2.3 - A string exerts a force on each of the two objects...Ch. 2.3 - If you know that the net force on a massless...Ch. 2.3 - Predict the subsequent motions of objects A and B...Ch. 2.3 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for objects A and...Ch. 2.3 - Predict: • what will happen to object C when it is...Ch. 2.3 - Draw and label separate free-body diagrams for...Ch. 2.3 - The weight of a 200 g mass has magnitude...Ch. 2.3 - Consider the following statement about the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Fill in the blanks: The nose is to the mouth. The ankle is to the knee. The ring finger is to the inde...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
12. FIGURE Q7.12 shows two masses at rest. The string is massless and the pullies are frictionless. The spring ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
explain the function of fermentation and the conditions under which it occurs?
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Flask A contains yeast cells in glucose-minimal salts broth incubated at 30C with aeration. Flask B contains ye...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY