
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.70P
The formation of the given product from
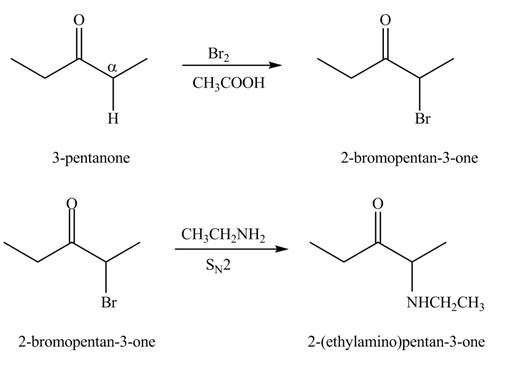
Explanation of Solution
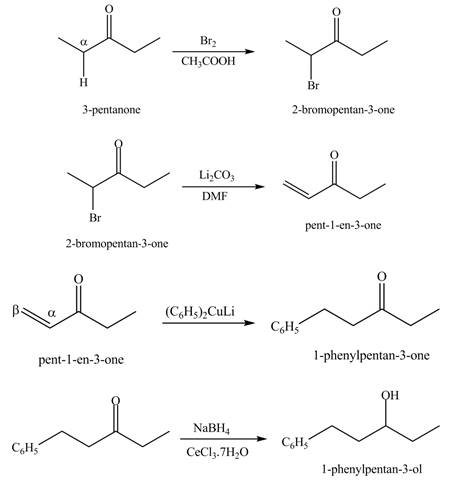
A chemical equation for the given synthesis is shown below.
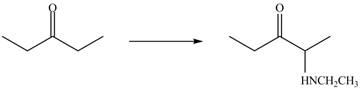
Figure 1
The formation of a given product by using
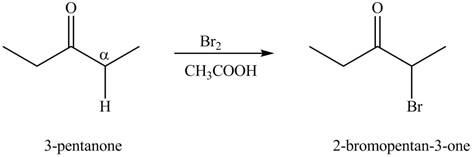
Figure 2
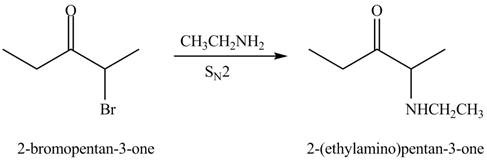
Figure 3
The first step of the reaction involves the bromination of
The formation of the given product from
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.70P
The synthesis of a given compound from
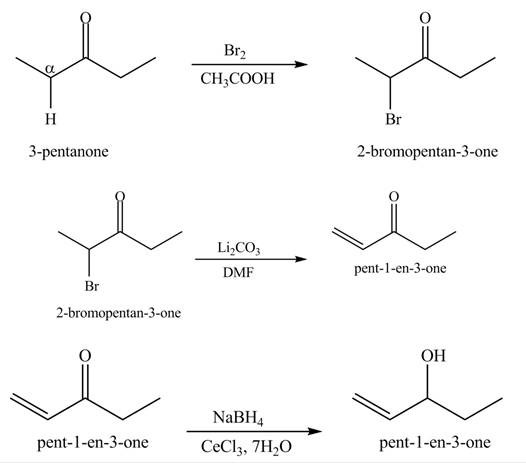
Explanation of Solution
A chemical equation for the given synthesis is shown below.

Figure 4
The formation of the given product by using
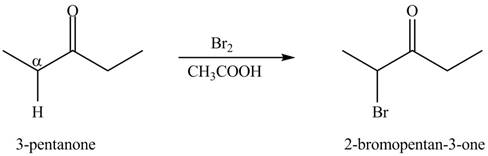
Figure 5
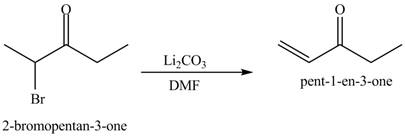
Figure 6
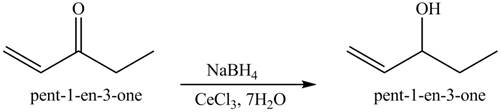
Figure 7
The first step of the reaction involves the bromination of
The synthesis of a given compound from
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.70P
The synthesis of a given compound from
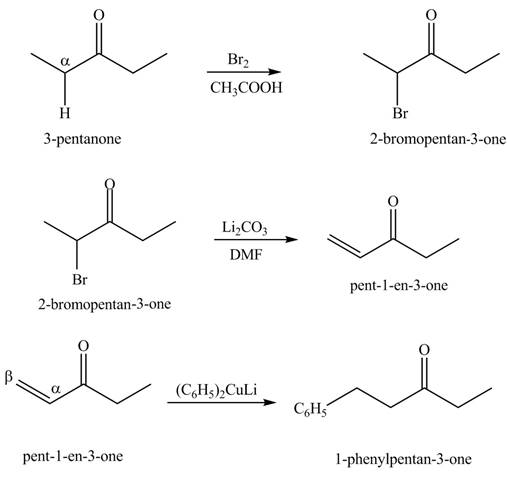
Explanation of Solution
A chemical equation for the given synthesis is shown below.
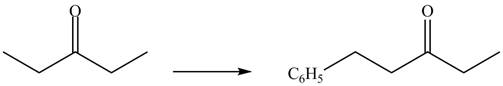
Figure 8
The formation of a given product by using
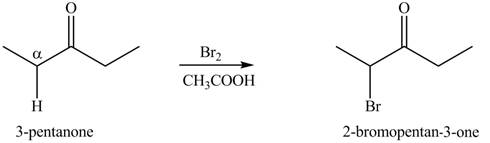
Figure 9
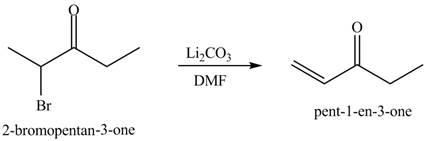
Figure 10
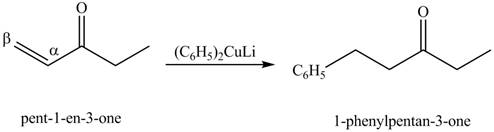
Figure 11
The first step of the reaction involves the bromination of
The synthesis of a given compound from
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.70P
The synthesis of a given compound from
Explanation of Solution
A chemical equation for the given synthesis is shown below.
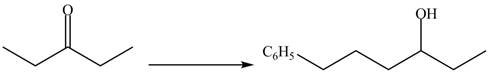
Figure 12
The formation of a given product by using
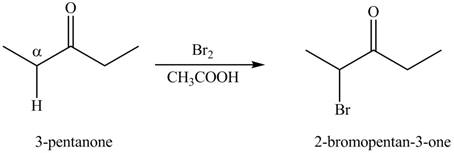
Figure 13
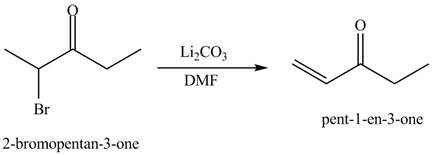
Figure 14
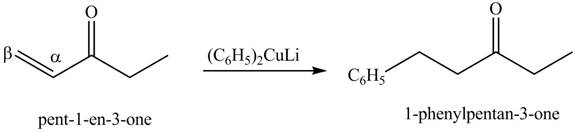
Figure 15
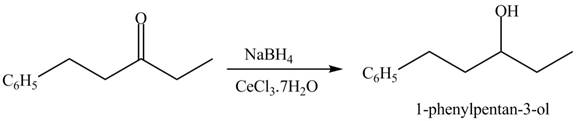
Figure 16
The first step of the reaction involves the bromination of
The synthesis of a given compound from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





