
HORNGRENS COST ACCOUNTING W/ACCESS
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323687604
Author: Datar
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 23.35P
Multinational firms, differing risk, comparison of profit,
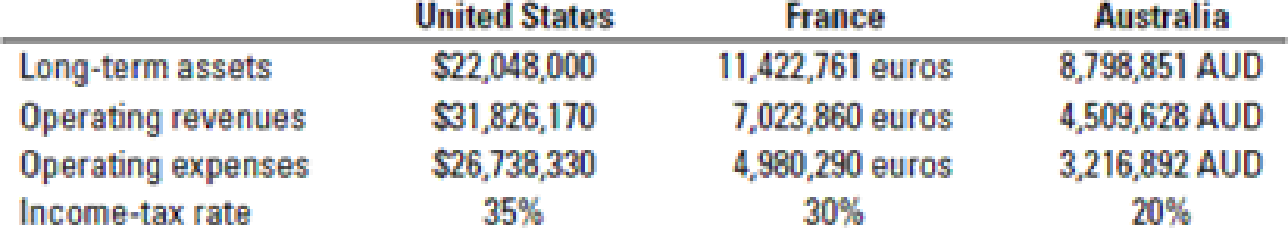
- 1. Translate the French and Australian information into dollars to make the divisions comparable. Find the after-tax operating income for each division and compare the profits.
Required
- 2. Calculate ROI using after-tax operating income. Compare among divisions.
- 3. Use after-tax operating income and the individual cost of capital of each division to calculate residual income and compare.
- 4. Redo requirement 2 using pretax operating income instead of net income. Why is there a big difference, and what does this mean for performance evaluation?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What is the company's price earnings ratio for this financial accounting question?
Current Attempt in Progress
* Your answer is incorrect.
On January 1, 2024, Ellison Co. issued eight-year bonds with a face value of $6000000 and a stated interest rate of 6%, payable
semiannually on June 30 and December 31. The bonds were sold to yield 8%. Table values are:
Present value of 1 for 8 periods at 6%
0.62741
Present value of 1 for 8 periods at 8%
0.54027
Present value of 1 for 16 periods at 3%
Present value of 1 for 16 periods at 4%
Present value of annuity for 8 periods at 6%
Present value of annuity for 8 periods at 8%
Present value of annuity for 16 periods at 3%
Present value of annuity for 16 periods at 4%
0.62317
0.53391
6.20979
5.74664
12.56110
11.65230
The present value of the principal is
$3764460.
$3739020.
$3203460.
$3241620.
Can you please solve this general account query??
Chapter 23 Solutions
HORNGRENS COST ACCOUNTING W/ACCESS
Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.1QCh. 23 - Prob. 23.2QCh. 23 - What factors affecting ROI does the DuPont method...Ch. 23 - RI is not identical to ROI, although both measures...Ch. 23 - Describe EVA.Ch. 23 - Give three definitions of investment used in...Ch. 23 - Distinguish between measuring assets based on...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.8QCh. 23 - Why is it important to distinguish between the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.10Q
Ch. 23 - Managers should be rewarded only on the basis of...Ch. 23 - Explain the role of benchmarking in evaluating...Ch. 23 - Explain the incentive problems that can arise when...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.14QCh. 23 - Prob. 23.15QCh. 23 - During the current year, a strategic business unit...Ch. 23 - Assuming an increase in price levels over time,...Ch. 23 - If ROI Is used to evaluate a managers performance...Ch. 23 - The Long Haul Trucking Company is developing...Ch. 23 - ABC Inc. desires to maintain a capital structure...Ch. 23 - ROI, comparisons of three companies. (CMA,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.22ECh. 23 - ROI and RI. (D. Kleespie, adapted) The Sports...Ch. 23 - ROI and RI with manufacturing costs. Excellent...Ch. 23 - ROI, RI, EVA. Hamilton Corp. is a reinsurance and...Ch. 23 - Goal incongruence and ROI. Comfy Corporation...Ch. 23 - ROI, RI, EVA. Performance Auto Company operates a...Ch. 23 - Capital budgeting, RI. Ryan Alcoa, a new associate...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.29ECh. 23 - ROI, RI, EVA, and performance evaluation. Cora...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.31ECh. 23 - Prob. 23.32ECh. 23 - ROI performance measures based on historical cost...Ch. 23 - ROI, measurement alternatives for performance...Ch. 23 - Multinational firms, differing risk, comparison of...Ch. 23 - ROI, Rl, DuPont method, investment decisions,...Ch. 23 - Division managers compensation, levers of control...Ch. 23 - Executive compensation, balanced scorecard. Acme...Ch. 23 - Financial and nonfinancial performance measures,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.40PCh. 23 - Prob. 23.41PCh. 23 - RI, EVA, measurement alternatives, goal...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hy expert give me solutionarrow_forwardShipCo. produces storage crates that require 1.2 meters of material at $0.85 per meter and 0.1 direct labor hours at $15.00 per hour. Overhead is assigned at the rate of $9 per direct labor hour. What is the total standard cost for one unit of product that would appear on a standard cost card? a. $25.02. b. $11.52. c. $2.40. d. $2.52. e. $3.42.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2020, Nexus Technologies purchased a machine for $15,000. The machine was estimated to have a 10-year useful life and a residual value of $800. Straight-line depreciation is used. On January 1, 2022, the machine was exchanged for office equipment with a fair value of $12,500. Assuming that the exchange had commercial substance, how much would be recorded as a gain on disposal of the machine on January 1, 2022? I want helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:9781337514835
Author:MOYER
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Risks - Part 1; Author: KnowledgEquity - Support for CPA;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mFjSYlBS-VE;License: Standard youtube license