
Concept explainers
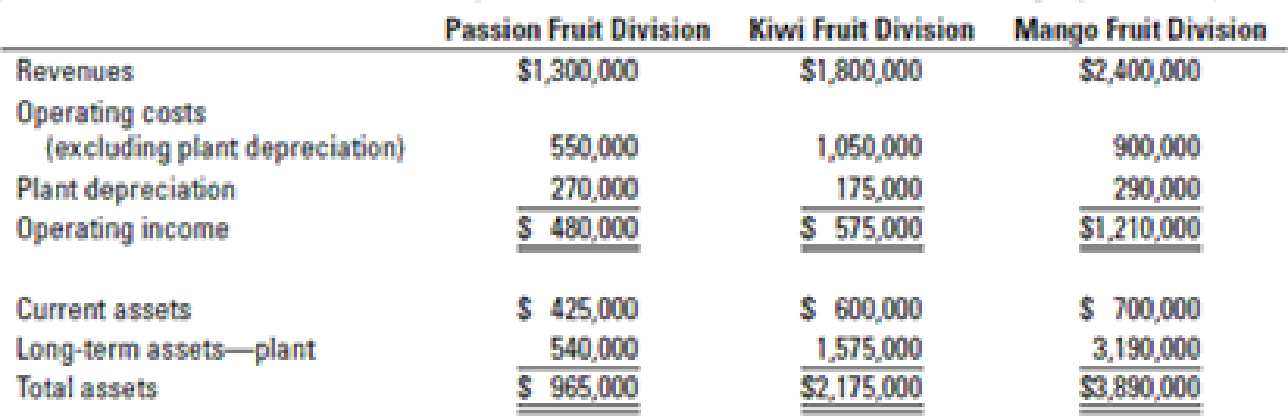
Nature’s Juice estimates the useful life of each plant to be 12 years, with no terminal disposal value. The
| 2007 | 2014 | 2016 | 2017 |
| 100 | 120 | 185 | 200 |
Given the high turnover of current assets, management believes that the historical-cost and current-cost measures of current assets are approximately the same.
- 1. Compute the ROI ratio (operating income to total assets) of each division using historical-cost measures. Comment on the results.
Required
- 2. Use the approach in Figure 23-2 (page 902) to compute the ROI of each division, incorporating current-cost estimates as of 2017 for depreciation expense and long-term assets. Comment on the results.
- 3. What advantages might arise from using current-cost asset measures as compared with historical-cost measures for evaluating the performance of the managers of the three divisions?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
HORNGRENS COST ACCOUNTING W/ACCESS
- Bayside Manufacturing's budgeted variable overheads for a period amounted to $30,000. During this period, the company spent $29,400 on variable overheads. The company's level of production was expected to require 15,000 labor hours, but the actual amount of labor hours used was only 13,500 hours. What was the variable overhead expenditure variance for the period?solve thisarrow_forwardWhat is the contribution margin per unit on these general accounting question?arrow_forwardBayside Manufacturing's budgeted variable overheads for a period amounted to $30,000. During this period, the company spent $29,400 on variable overheads. The company's level of production was expected to require 15,000 labor hours, but the actual amount of labor hours used was only 13,500 hours. What was the variable overhead expenditure variance for the period?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

