
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Combustion reaction is the one in which, the substance is burnt in presence of oxygen. If any hydrocarbon is burnt in presence of oxygen, the products obtained are carbon dioxide and water only.
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction in the problem statement is an combustion reaction and hence, the product obtained will be carbon dioxide and water only. Hence, the raw equation can be written as,
As the total number of atoms present in both reactants and products must be equal, balancing has to be done. To balance the carbon atom in both sides, the product side has to be multiplied by 4 for carbon dioxide and 5 for water. This leads, balancing of both carbon and hydrogen atoms on both sides.
Oxygen count was thirteen in product side. But in the reactant side it is two. Hence, multiplying by 13/2 on reactant side balances the oxygen atom also on both sides. Therefore, the balanced chemical equation for the given reaction can be given as,
To remove the fraction multiply all the compounds by 2. This gives the balanced equation as,
The given incomplete combustion reaction is completed and the balanced chemical equation also written.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation is loss of electron by a species. This also can be said as addition of oxygen. Reduction is a process in which electrons are gained by a species.
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
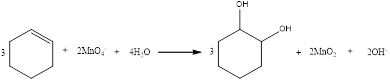
Explanation of Solution
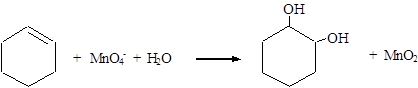
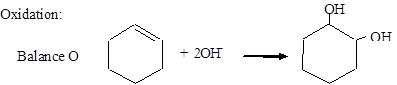
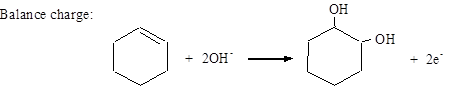
Reduction: MnO4− → MnO2
Balance O: MnO4− + 2H2O → MnO2 + 4OH−
Balance charge: MnO4− + 2H2O + 3e− → MnO2 + 4OH−
Add half-reactions:
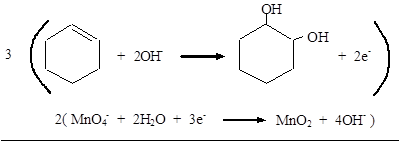
Therefore, the complete equation for the given reaction can be given as,

The balanced equation for the given reaction was written.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Bromination of
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
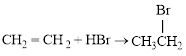
Explanation of Solution
Bromination across the double bond.
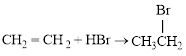
The given bromination reaction was completed and the product was written with balanced equation.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Nitration of
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
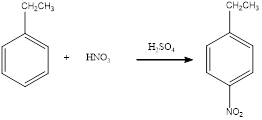
Explanation of Solution
Nitration of ethylbenzene takes place in presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. As ethyl is a para directing group, the nitro group is substituted in the para position. By considering this, the complete reaction can be given as,
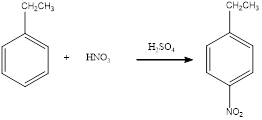
The given nitration reaction product was drawn and the equation was completed.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Chlorination of aromatic compound happens in presence of catalyst. Usually this does not occur in absence of catalyst. The position of chlorination in the aromatic ring depends upon the group already substituted in the ring.
(e)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
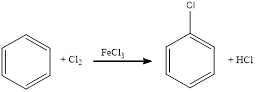
Explanation of Solution
Chlorination of benzene takes place in presence of catalyst with chlorine. By considering this, the complete reaction can be given as,
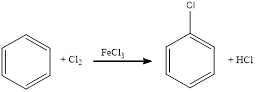
The given chlorination reaction was completed and the product was written with balanced equation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: General Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- 10. Stereochemistry. Assign R/S stereochemistry for the chiral center indicated on the following compound. In order to recieve full credit, you MUST SHOW YOUR WORK! H₂N CI OH CI カー 11. () Stereochemistry. Draw all possible stereoisomers of the following compound. Assign R/S configurations for all stereoisomers and indicate the relationship between each as enantiomer, diastereomer, or meso. NH2 H HNH, -18arrow_forwardb) 8. Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur Please explain your rational using 10 words or less not likely to occur • The double bond is still in the Same position + Likely to oc occur WHY? -3 H3C Brave Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less. CI 2 -cobs ?? MUST INDICATE H -2 -2 Br EQ Cl OR AT Br H& most stable WHY? - 4arrow_forwardCH 12 Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided. NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below -4 NOT HOH OH 3 Conformer A: Br OH A Samo Br H 04 Br H H3 CH₂ H anti stagere Br CH clipsed H Brott H IV H MISSING 2 -2 B C D E F X 6 Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY: 13. (1 structure LOWEST ENERGY: Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry when applicable. a) ८८ 2 "Br {t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa Parent name (noname) 4 Bromo Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane # -2 -2arrow_forward
- in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





