
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134382593
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.3, Problem 16P
Force F acts on the frame such that its component acting along member AB is 650 lb, directed from B towards A. Determine the required angle ϕ (0° ≤ ϕ ≤ 45°) and the component acting along member BC. Set F = 850 lb and θ = 30°.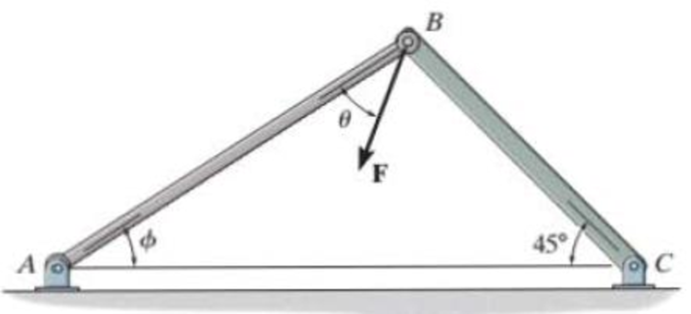
Probs. 2–15/16
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3-55 A multifluid container is connected to a U-tube,
as shown in Fig. P3–55. For the given specific gravities
and fluid column heights, determine the gage pressure at
A. Also determine the height of a mercury column that
would create the same pressure at A. Answers: 0.415 kPa,
0.311 cm
I need help answering parts a and b
Required information
Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is contained in a piston-cylinder device fitted with stops. The water is allowed to cool
at constant pressure until it exists as a saturated vapor and the piston rests on the stops. Then the water continues to cool
until the pressure is 100 kPa.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Water
200 kPa
300°C
On the T-V diagram, sketch, with respect to the saturation lines, the process curves passing through the initial, intermediate, and final states of the water. Label the
T, P, and V values for end states on the process curves.
Please upload your response/solution by using the controls provided below.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Ch. 2.3 - In each case, construct the parallelogram law to...Ch. 2.3 - In each case, show how to resolve the force F into...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force....Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 6FPCh. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the two components of...Ch. 2.3 - Solve Prob. 24 with F = 350 lb. 24. Determine the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F1 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F2 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force acting on the support is to...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60, determine the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the angle for connecting member A to...Ch. 2.3 - The force acting on the gear tooth is F = 20 lb....Ch. 2.3 - The component of force F acting along line aa is...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - If F1 = 30 lb and F2 = 40 lb, determine the angles...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of FA so...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 20PCh. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is 3...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force into its x and y components....Ch. 2.4 - F28. Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 2.4 - Prob. 10FPCh. 2.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 25PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 26PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 28PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 30PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 31PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 35PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.6 - Sketch the following forces on the x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - In each case, establish F as a Cartesian vector,...Ch. 2.6 - Show how to resolve each force into its x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 14FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 15FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 16FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 17FPCh. 2.6 - Determine the resultant force acting on the hook....Ch. 2.6 - The force F has a magnitude of 80 lb. Determine...Ch. 2.6 - The bolt is subjected to the force F, which has...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 41PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 42PCh. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form and...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 44PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 47PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 50PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 51PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 53PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 54PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, establish a position vector from...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, express F as a Cartesian vector. (a)...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 19FPCh. 2.8 - Determine the length of the rod and the position...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 21FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 23FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 24FPCh. 2.8 - Determine the length of the connecting rod AB by...Ch. 2.8 - Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then...Ch. 2.8 - Express each force as a Cartesian vector, and then...Ch. 2.8 - If F = {350i 250j 450k} N and cable AB is 9 m...Ch. 2.8 - The 8-m-long cable is anchored to the ground at A....Ch. 2.8 - The 8-m-long cable is anchored to the ground at A....Ch. 2.8 - Express each of the forces in Cartesian vector...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - The plate is suspended using the three cables...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 66PCh. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 68PCh. 2.8 - The load at A creates a force of 60 lb in wire AB....Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.9 - In each case, set up the dot product to find the...Ch. 2.9 - In each case, set up the dot product to find the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projected component of the force...Ch. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the components of the force acting...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 31FPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 71PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between BA and BC. Probs. 273Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 75PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the pole and the wire...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 80PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables. Prob....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projected component of the force...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angles and between the flag pole...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 85PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the pipe segments BA...Ch. 2.9 - If the force F = 100 N lies in the plane DBEC,...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Two cables exert forces on the pipe. Determine the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two forces. Prob....Ch. 2 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2 - Resolve the force into components along the u and...Ch. 2 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2 - The cable exerts a force of 250 lb on the crane...Ch. 2 - The cable attached to the tractor at B exerts a...Ch. 2 - Express F1 and F2 as Cartesian vectors. Prob. R26Ch. 2 - Determine the angle between the edges of the...Ch. 2 - Determine the projection of the force F along the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the final pressure of the refrigerant-134a. The final pressure is kPa.arrow_forwardThe hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward
- ! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forwardThe primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License