
a)
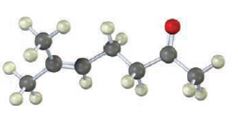
Interpretation:
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model, using either malonic ester synthesis or an acetoacetic ester synthesis, are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
Answer to Problem 17VC
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using acetoacetic ester synthesis are given below.
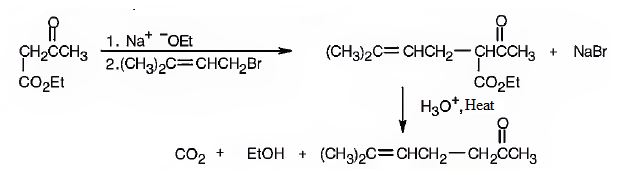
Explanation of Solution
The compound represented by the model is 6-methylhept-5-ene-2-one. It is a methyl ketone and hence it can be prepared using acetoacetic ester synthesis. The ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of the ester to form the enolate ion. The enolate ion then attacks 1-bromo-3-methy-2-butene and displaces the bromine as bromide ion. The product obtained upon hydrolysis with dilute acids and decarboxylation by heating yields the product.
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using acetoacetic ester synthesis are given below.

b)
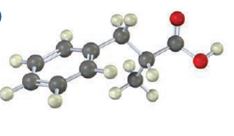
Interpretation:
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using either malonic ester synthesis or an acetoacetic ester synthesis are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
Answer to Problem 17VC
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using malonic ester synthesis are given below.
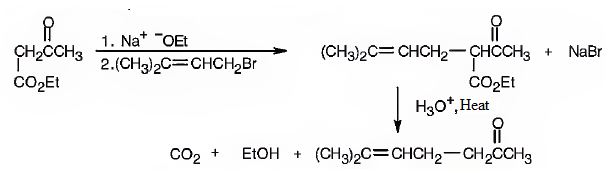
Explanation of Solution
The compound represented by the model is 2-methyl-3-phenylpropanoic acid and hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group to form the enolate ion. The enolate ion then attacks benzyl bromide and displaces the bromine as bromide ion. The abstraction of another acidic hydrogen in the product by the base and the nucleophilic displacement of bromine from methyl bromide by enolate ion introduces a methyl group at α- position of the diester. The alkylated diester obtained upon hydrolysis with aqueous acids and decarboxylation by heating yields the product.
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using malonic ester synthesis are given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/OWL
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

