
a)
Interpretation:
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model, using either malonic ester synthesis or an acetoacetic ester synthesis, are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
Answer to Problem 17VC
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using acetoacetic ester synthesis are given below.
Explanation of Solution
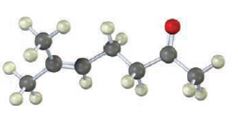
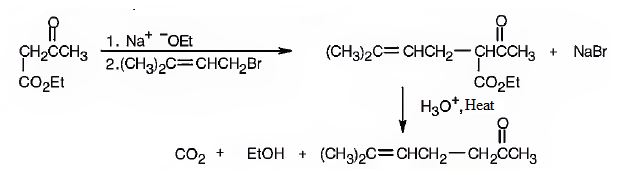
The compound represented by the model is 6-methylhept-5-ene-2-one. It is a methyl ketone and hence it can be prepared using acetoacetic ester synthesis. The ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of the ester to form the enolate ion. The enolate ion then attacks 1-bromo-3-methy-2-butene and displaces the bromine as bromide ion. The product obtained upon hydrolysis with dilute acids and decarboxylation by heating yields the product.
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using acetoacetic ester synthesis are given below.

b)
Interpretation:
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using either malonic ester synthesis or an acetoacetic ester synthesis are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
Answer to Problem 17VC
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using malonic ester synthesis are given below.
Explanation of Solution
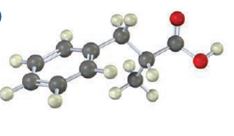
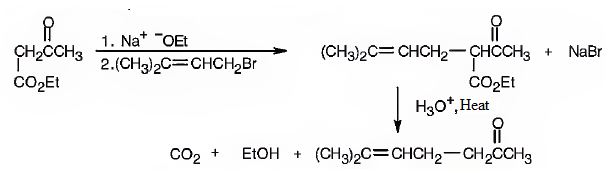
The compound represented by the model is 2-methyl-3-phenylpropanoic acid and hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group to form the enolate ion. The enolate ion then attacks benzyl bromide and displaces the bromine as bromide ion. The abstraction of another acidic hydrogen in the product by the base and the nucleophilic displacement of bromine from methyl bromide by enolate ion introduces a methyl group at α- position of the diester. The alkylated diester obtained upon hydrolysis with aqueous acids and decarboxylation by heating yields the product.
The steps involved in preparing the compound represented by the model using malonic ester synthesis are given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-EBOOK>I<
- Consider this step in a radical reaction: Y What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ionization propagation initialization passivation none of the abovearrow_forward22.16 The following groups are ortho-para directors. (a) -C=CH₂ H (d) -Br (b) -NH2 (c) -OCHS Draw a contributing structure for the resonance-stabilized cation formed during elec- trophilic aromatic substitution that shows the role of each group in stabilizing the intermediate by further delocalizing its positive charge. 22.17 Predict the major product or products from treatment of each compound with Cl₁/FeCl₂- OH (b) NO2 CHO 22.18 How do you account for the fact that phenyl acetate is less reactive toward electro- philic aromatic substitution than anisole? Phenyl acetate Anisole CH (d)arrow_forwardShow how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.7 Predict the monoalkylated products of the following reactions with benzene. (a) AlCl3 Ya (b) AlCl3 (c) H3PO4 (d) 22.8 Think-Pair-Share AICI3 The reaction below is a common electrophilic aromatic substitution. SO3 H₂SO4 SO₂H (a) Draw the reaction mechanism for this reaction using HSO,+ as the electrophile. (b) Sketch the reaction coordinate diagram, where the product is lower in energy than the starting reactant. (c) Which step in the reaction mechanism is highest in energy? Explain. (d) Which of the following reaction conditions could be used in an electrophilic aro- matic substitution with benzene to provide substituted phenyl derivatives? (i) AICI3 HNO3 H₂SO4 K2Cr2O7 (iii) H₂SO4 (iv) H₂PO₁arrow_forwardIs an acid-base reaction the only type of reaction that would cause leavening products to rise?arrow_forward
- Help me understand this! Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.22 For each compound, indicate which group on the ring is more strongly activating and then draw a structural formula of the major product formed by nitration of the compound. Br CHO (a) CH3 (b) (c) CHO CH3 SO₂H (d) ☑ OCHS NO₂ (e) (f) CO₂H NHCOCH3 NHCOCH, (h) CHS 22.23 The following molecules each contain two aromatic rings. (b) 000-100- H3C (a) (c) Which ring in each undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily? Draw the major product formed on nitration.arrow_forwardV Consider this step in a radical reaction: Br: ? What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ⚫ionization termination initialization neutralization none of the abc Explanation Check 80 Ο F3 F1 F2 2 F4 01 % do5 $ 94 #3 X 5 C MacBook Air 25 F5 F6 66 ©2025 ˇ F7 29 & 7 8arrow_forward
- Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardno aiarrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

