
(a)
Interpretation: The more basic
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (a)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized
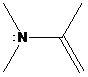
(b)
Interpretation: The more basic amine compound has to be found for the given pairs of compounds
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in aromatic stabilization. As a result, a number of resonance structures are drawn for the delocalization of electrons in the structures. So, the compound has less basic character. If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is localized, that compound doesn’t involve in resonance stabilization. So, that compound has more basic character.
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (b)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized
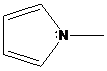
(c)
Interpretation: The more basic amine compound has to be found for the given pairs of compounds
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in aromatic stabilization. As a result, a number of resonance structures are drawn for the delocalization of electrons in the structures. So, the compound has less basic character. If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is localized, that compound doesn’t involve in resonance stabilization. So, that compound has more basic character.
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (c)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized

(d)
Interpretation: The more basic amine compound has to be found for the given pairs of compounds
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in aromatic stabilization. As a result, a number of resonance structures are drawn for the delocalization of electrons in the structures. So, the compound has less basic character. If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is localized, that compound doesn’t involve in resonance stabilization. So, that compound has more basic character.
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (d)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized
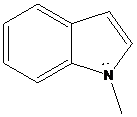
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM PRINT STUDY GDE & SSM
- All of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forward
- Name the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward1b. Br LOHarrow_forwardI would like my graphs checked please. Do they look right? Do I have iodine and persulfate on the right axis ?arrow_forward
- Reaction Fill-ins Part 2! Predict the product(s) OR starting material of the following reactions. Remember, Hydride shifts are possible if/when a more stable carbocation can exist (depending on reaction mechanism)! Put your answers in the indicated boxes d. d. ง HCIarrow_forwardA cylinder contains 12 L of water vapour at 150˚C and 5 atm. The temperature of the water vapour is raised to 175˚C, and the volume of the cylinder is reduced to 8.5 L. What is the final pressure of the gas in atmospheres? assume that the gas is idealarrow_forwardOn the next page is an LC separation of the parabens found in baby wash. Parabens are suspected in a link to breast cancer therefore an accurate way to quantitate them is desired. a. In the chromatogram, estimate k' for ethyl paraben. Clearly indicate what values you used for all the terms in your calculation. b. Is this a "good" value for a capacity factor? Explain. c. What is the resolution between n-Propyl paraben and n-Butyl paraben? Again, indicate clearly what values you used in your calculation. MAU | Methyl paraben 40 20 0 -2 Ethyl paraben n-Propyl paraben n-Butyl paraben App ID 22925 6 8 minarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





