
MCAT-Style Passage Problems
Lightbulb Failure
You’ve probably observed that the most common time for an incandescent lightbulb to fail is the moment when it is turned on. Let’s look at the properties of the bulb’s filament to see why this happens.
The current in the tungsten filament of a lightbulb heats the filament until it glows. The filament is so hot that some of the atoms on its surface fly off and end up sticking on a cooler part of the bulb. Thus the filament gets progressively thinner as the bulb ages. There will certainly be one spot on the filament that is a bit thinner than elsewhere. This thin segment will have a higher resistance than the surrounding filament. More power will be dissipated at this spot, so it won’t only be a thin spot, it also will be a hot spot.
Now, let’s look at the resistance of the filament. The graph in Figure P22.70 shows data for the current in a lightbulb as a function of the potential difference across it. The graph is not linear, so the filament is not an ohmic material with a constant resistance. However, we can define the resistance at any particular potential difference ∆V to be R = ∆V/I. This ratio, and hence the resistance, increases with ∆V and thus with temperature.
Figure P22. 70
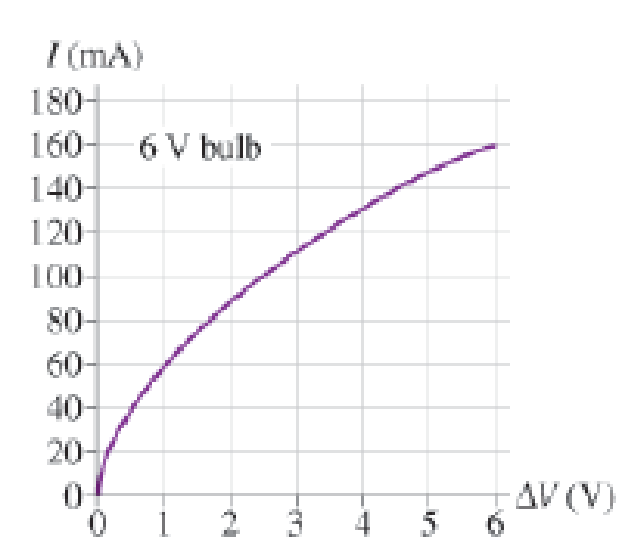
When the bulb is turned on, the filament is cold and its resistance is much lower than during normal, high-temperature operation. The low resistance causes a surge of higher-than-normal current lasting a fraction of a second until the filament heats up. Because power dissipation is I2R, the power dissipated during this first fraction of a second is much larger than the bulb’s rated power. This current surge concentrates the power dissipation at the high-resistance thin spot, perhaps melting it and breaking the filament.
70. For the bulb in Figure P22.70, what is the approximate resistance of the bulb at a potential difference of 6.0 V?
A. 7.0 Ω
B. 17 Ω
C. 27 Ω
D. 37 Ω
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
MODIFIED MASTERING COLLEGE PHYSICS 18WK.
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- 220 volts is supplied across 1200 winding of the primary coil of the autotransformer.If 1650 windings are tapped, what voltage will be supplied to the primary coil of thehigh-voltage transformer?2. A kVp meter reads 86 kVp and the turns ratio of the high-voltage step-up transformeris 1200. What is the true voltage across the meter?3. The supply voltage from the autotransformer to the filament transformer is 60 volts. If theturns ratio of the filament transformer is 1/12, what is the filament voltage?4. If the current in the primary side of the filament transformer in question 3 were 0.5 A,what would be the filament current?5. The supply to a high-voltage step-up transformer with a turns ratio of 550 is 190 volts.What is the voltage across the x-ray tube?arrow_forward220 V is supplied to 800 primary turns of an autotransformer. What will the outputvoltage be across 200 secondary turns? 2. A filament transformer has a turns ratio of 1:20. What current must be supplied to theprimary windings if 5 A is required by the filament? 3. The filament transformer in the previous question is supplied with 150 V to theprimary side. What is the secondary voltage? 4. 440 V is supplied to 1000 primary turns of an autotransformer. If the desired outputvoltage is 100 V how many secondary turns must be tapped?arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer thw question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- One strain of bacteria was found to have a membrane potential of -120 mVmV at a pHpH of 7.5. A bacterium can be modeled as a 1.5-μmμm-diameter sphere. How many positive ions are needed on the exterior surface to establish this membrane potential? (There are an equal number of negative ions on the interior surface.) Assume that the membrane properties are the same as those of mammalian cells.arrow_forwardQ: Draw the fabrication layers of a transistor with metal and semiconductor MS junction (Schottkyj unction).arrow_forwardphysicsarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





