
Concept explainers
Devise efficient syntheses of each of the following compounds from the designated startingmaterials. You may also use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.

Interpretation:
Efficient syntheses are to be designed for each of the five compounds with designated starting materials and necessary organic or inorganic compounds.
Concept introduction:
Synthesis of amines can be done in a variety of ways, based on forming a bond between a carbon and a nitrogen.
Nucleophilic substitution reactions on alkyl halides or alcohols by a nitrogen containing reagent is one of the common methods.
Primary amines can be synthesized by nucleophilic substitution of an alkyl halide with cyanide. The resulting compound, called a nitrile, yields a primary amine on catalytic reduction with hydrogen.
Secondary and particularly tertiary amines can be formed by reaction between ammonia and an excess of alkyl halide.
Another method involves nucleophilic addition of simpler amines to an aldehyde or a ketone.
Carboxylic acid derivatives such as acid halides, anhydrides, and esters undergo nucleophilic substitution by ammonia or a variety of simpler amines to give amides. The amides on reduction gives amines.
Benzyl radical is stabilized by delocalization of the unpaired electron on to the benzene ring. This helps in selective radical substitution of hydrogens and halogens in benzylic position.
Answer to Problem 45P
Solution:
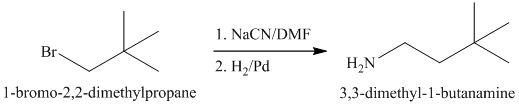
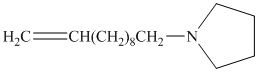 from
from
c)
 from
from 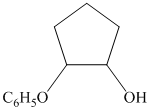 :
:
d)
e)
 from
from 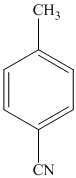 :
:
Explanation of Solution
a)
The substrate is a primary alkyl halide; therefore, substitution of the bromine requires a strong nucleophile such as cyanide ion via an
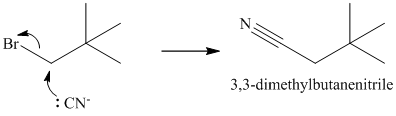
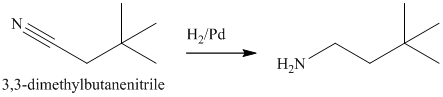
The nitrile yields the desired amine on catalytic reduction.
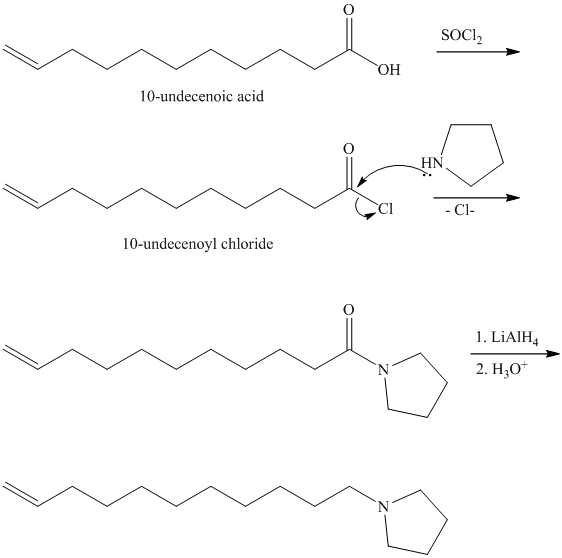
b)
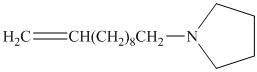 from
from
Carboxylic acids and amines can react to form amides by nucleophilic substitution of the hydroxyl group by the amine. However, carboxylic acids are poor electrophiles and are relatively unreactive. The first step is then to activate the acid by converting it to a stronger electrophile such as an acid chloride.
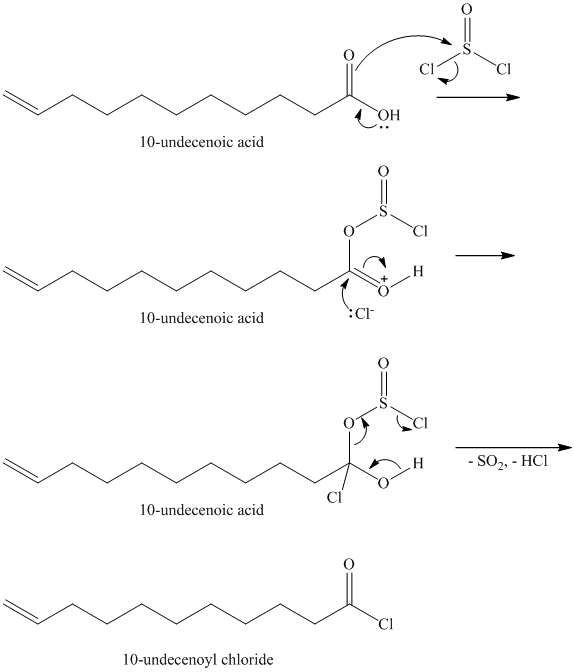
The chloride then undergoes substitution by
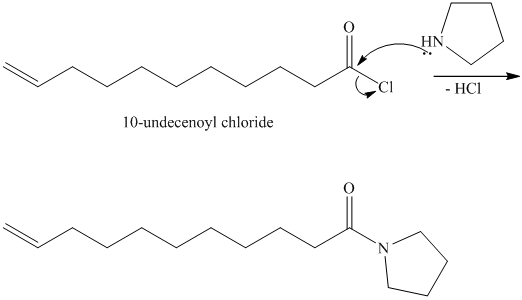
This contains both a carbonyl group that needs to be reduced to a methylene and a double bond. Catalytic reduction will result in reduction of the carbonyl group as well as an unwanted reduction of the double bond. Therefore, reduction of the carbonyl to methylene bridge is done with lithium aluminum hydride.
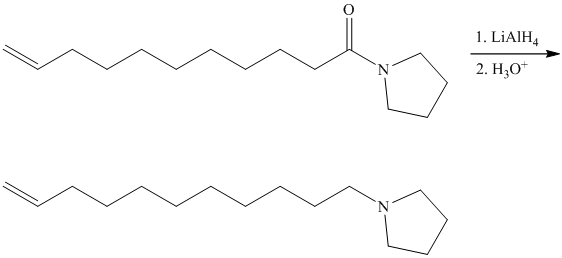
The hydride ion (
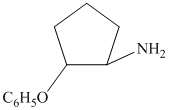
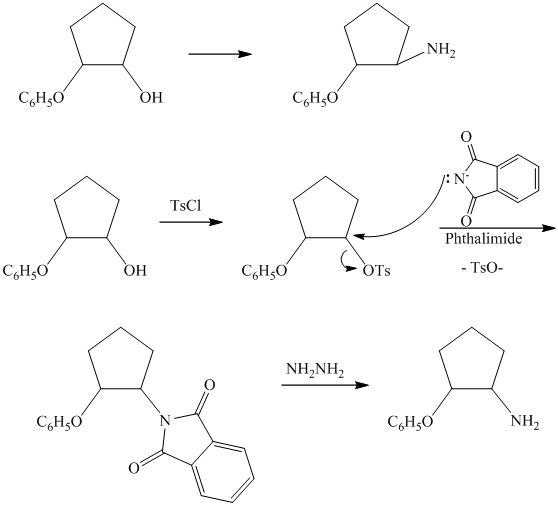
c)
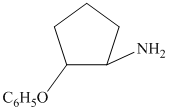 from
from 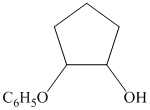 :
:
The synthesis requires substitution of the hydroxyl group of the substrate. Hydroxyl group is a poor leaving group as the hydroxide ion is a strong base. It first needs to be converted to a better leaving group. This is done by reaction with tosyl chloride, to give a tosylate.
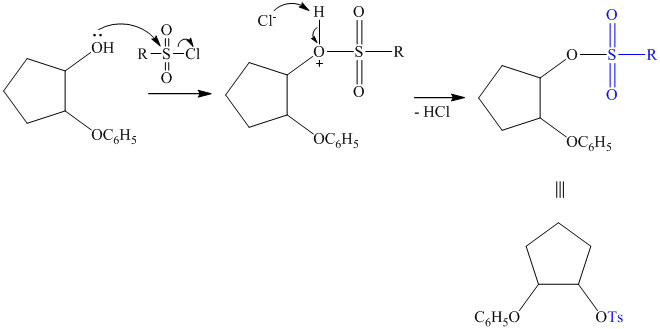
Tosylate ion is the conjugate base of a strong acid, so it can be easily replaced by a suitable nucleophile like phthalimide.
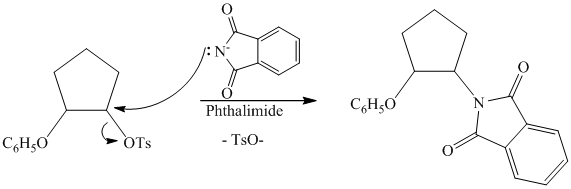
Reaction of the tosylate with phthalimide is an
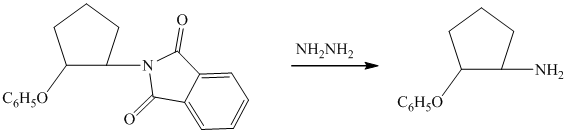
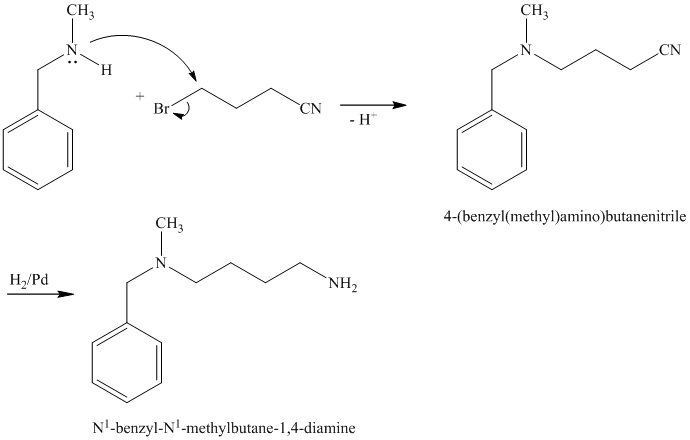
d)
The first of the designated starting compounds
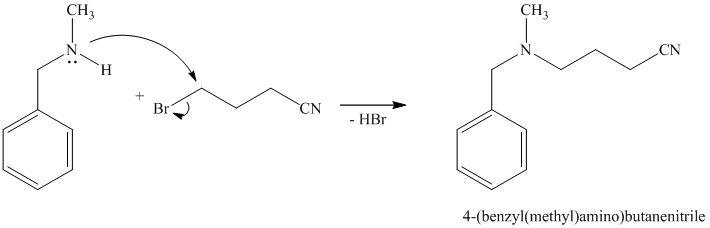
The nitrile (cyanide) function can then be reduced with hydrogen over palladium to yield the desired product.
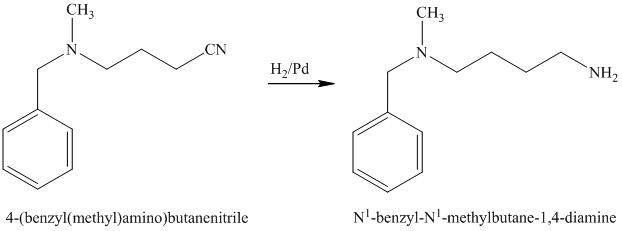
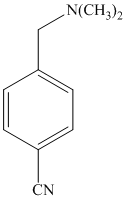
e)
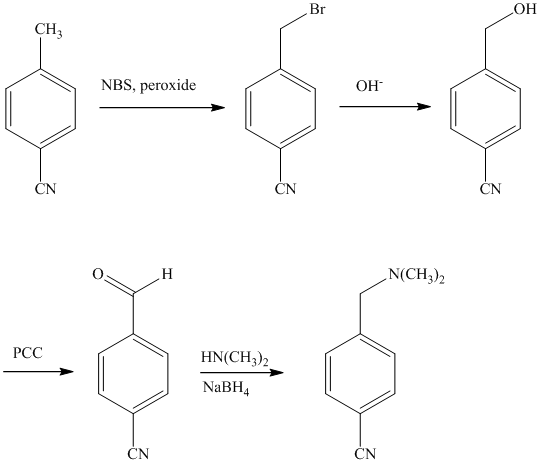
The methyl substituent on the benzene ring needs to be converted to an amine. This requires first converting it to an alkyl halide. This is a substitution of a hydrogen in a benzylic position. A convenient method is to treat it with
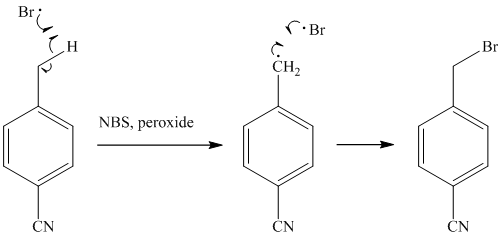
The resulting bromide can be reacted directly with dimethyl amine to yield the product. However, there is a possibility of formation of a quaternary ammonium compound. Therefore, the bromide is converted to a primary alcohol by reacting it with hydroxide.
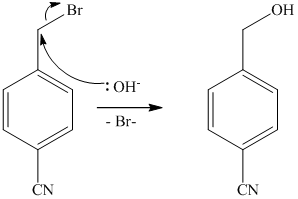
The alcohol is then oxidized to aldehyde using pyridiniumchlorochromate.
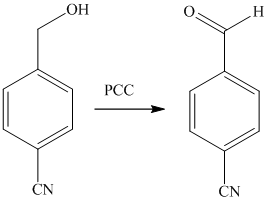
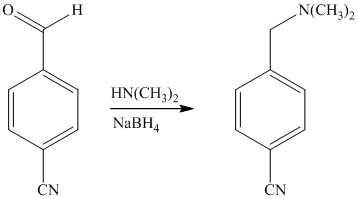
Reaction of the aldehyde can then be subjected to reductive amination, reaction with dimethyl amine in the presence of sodium borohydride, to yield the desired product. The reaction initially forms an imine, but that is directly reduced by sodium borohydrideinstead of isolating it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- H2SO4 (cat.), H₂O 100 °C NH₂arrow_forwardX Draw the major products of the elimination reaction below. If elimination would not occur at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ది www. Cl + OH Elimination will not occur at a significant rate. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- 1A H 2A Li Be Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. 8A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A He B C N O F Ne Na Mg 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 8B-1B 2B Al Si P 1B 2B Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe * Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Ac Rf Ha ****** Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr Analyze the following reaction by looking at the electron configurations given below each box. Put a number and a symbol in each box to show the number and kind of the corresponding atom or ion. Use the smallest integers possible. cation anion + + Shell 1: 2 Shell 2: 8 Shell 3: 1 Shell 1 : 2 Shell 2 : 6 Shell 1 : 2 Shell 2: 8 Shell 1: 2 Shell 2: 8arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardIV. Show the detailed synthesis strategy for the following compounds. a. CH3CH2CH2CH2Br CH3CH2CCH2CH2CH3arrow_forward
- Do the electrons on the OH participate in resonance with the ring through a p orbital? How many pi electrons are in the ring, 4 (from the two double bonds) or 6 (including the electrons on the O)?arrow_forwardPredict and draw the product of the following organic reaction:arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


