
Interpretation:
The principal product of each of the given reactions is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The nitro group can be reduced to primary amine by the catalytic hydrogenation or by the action of iron or tin in hydrochloric acid.
The amides are reduced to
The arenes undergo acylation when reacted with acyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride.
When primary amines react with an
The amide can be prepared by the nucleophilic substitution of acyl chloride by amine.
The secondary amine can be converted to tertiary amine when reacted with a primary
In an acidic condition, the amide gets hydrolyzed to corresponding
The aryl diazonium salt is a key intermediate in the synthesis of
Electron donating groups activate the arenes and give electrophilic substitution at ortho-para position.
The reaction of aryl diazonium salt with potassium iodide gives the iodobenzene derivatives.
The aryl cyanide is prepared by the reaction of an aryl diazonium salt with
Chlorobenzene or a bromobenzene can be synthesized from aryl diazonium salt by heating it with cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide in
The aryl amine diazonium salt on reaction with hypophosphorous acid or ethanol
The aromatic fluoride substitution occurs by heating aryl diazonium salt with
The diazonium salt, on hydrolysis, gets converted to phenol.
In the reaction of the phenol and a diazonium salt, the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with diazonium salt.
The
Answer to Problem 39P
Solution:
a)
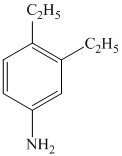
b)
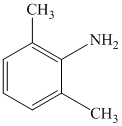
c)
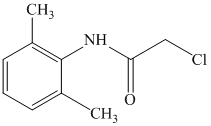
d)
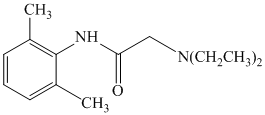
e)
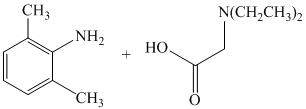
f)
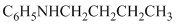
g)
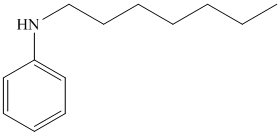
h)
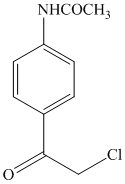
i)
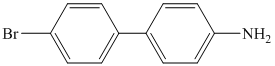
j)
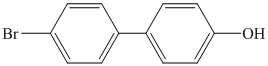
k)
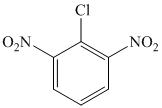
l)
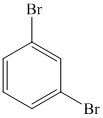
m)
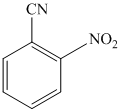
n)
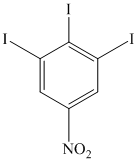
o)
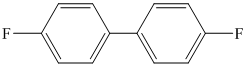
p)
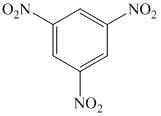
q)
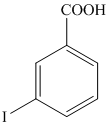
r)
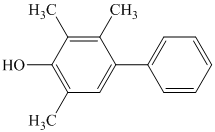
s)
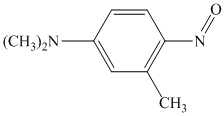
Explanation of Solution
a) The given reaction is shown below:
The given reactant has a nitro
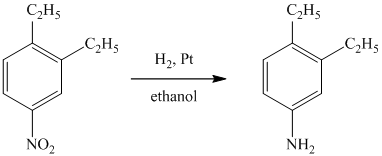
b) The given reaction is shown below:

The given reactant has a nitro functional group that gets reduced in the presence of tinchloride in hydrochloric acid followed by hydroxide and converted to amine functional group, as shown in following equation.
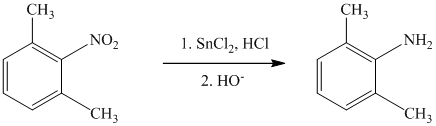
c) The given reaction is shown below:
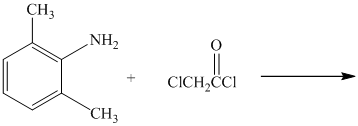
The primary amine, on reaction with acyl chloride, undergoes acylation and forms secondary amide by replacing the chlorine atom directly bonded to carbonyl carbon.
The complete reaction is shown below:
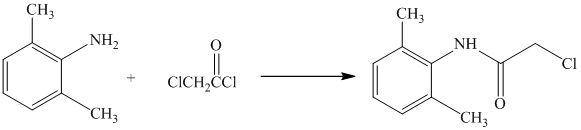
d) The given reaction is shown below:
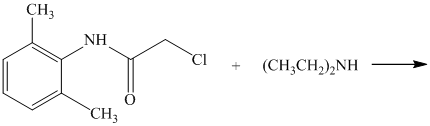
In the above reaction, the reactants are primary alkyl chloride and secondary amine. The nitrogen atom in a secondary amine acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon bonded to the chlorine atom. This nucleophilic substitution converts the secondary amine to a tertiary amine. The complete reaction is shown below:
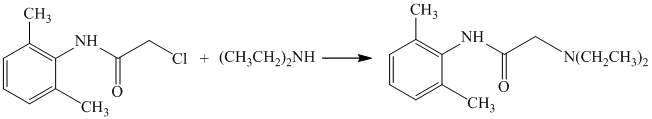
e) The given reaction is shown below:
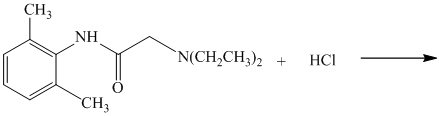
The given reactant has amide functional group in an acidic condition that gets hydrolyzed and produces derivatives of carboxylic acid and amine.
Their structures are shown in the following equation:
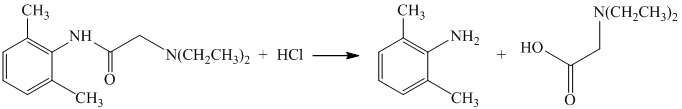
f) The given reaction is shown below:
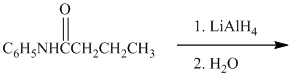
The reactant given in this reaction is a secondary amide, which is subjected to reduction by using the reagent lithium aluminum hydride and produces secondary amine, i.e.,
The complete reaction is shown below:
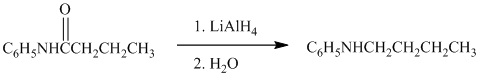
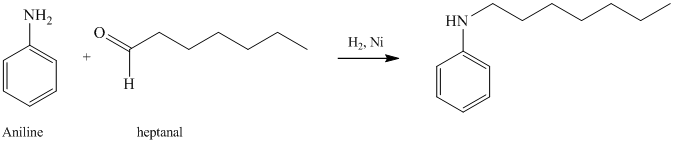
g) The given reaction is shown below:

The aniline, on reaction with heptanal, forms an imine which, on catalytic hydrogenation, forms
h) The given reaction is shown below:
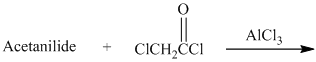
Acetanilide is an aromatic compound; the nitrogen atom bonded to benzene activates the ring and gives acylation at para position when reacted with acyl chloride in presence of aluminum chloride. The structure of the product formed is shown in following equation:
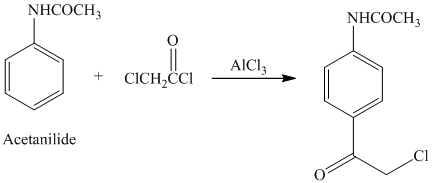
i) The given reaction is shown below:
The given reactant has a nitro functional group that gets reduced to iron in hydrochloric acid followed by hydroxide and converted to amine functional group, as shown in following equation.

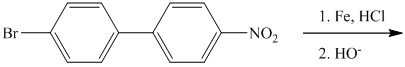
j) The given reaction is shown below:
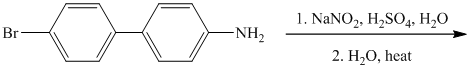
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt, on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. This diazonium salt, on hydrolysis, forms a phenol derivative.
The complete equation is shown below:
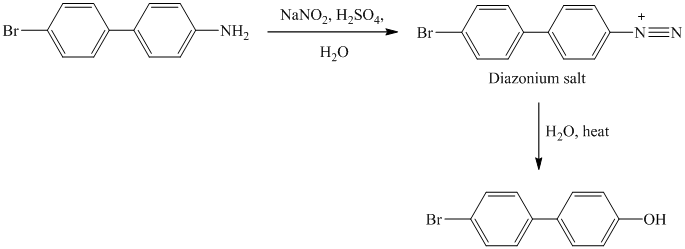
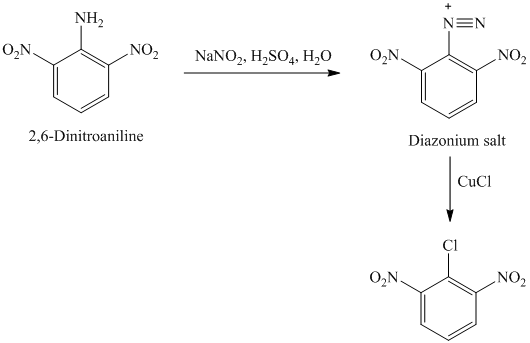
k) The given reaction is shown below:
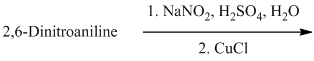
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The chloride substitution is done by treating this diazonium salt with cuprous chloride. The complete equation is shown below:
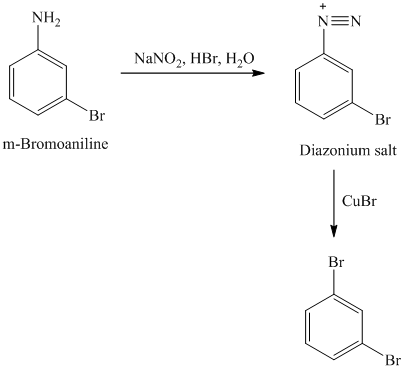
l) The given reaction is shown below:
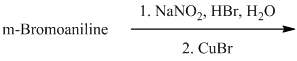
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The bromide substitution is done by treating this diazonium salt with cuprous bromide. The complete equation is shown below:
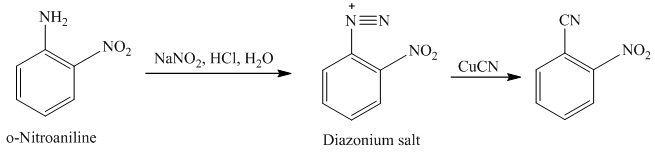
m) The given reaction is shown below:
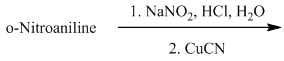
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. This diazonium salt, on reaction with
The complete equation is shown below:
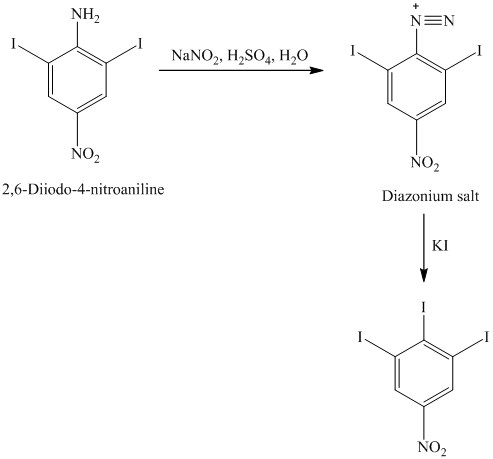
n) The given reaction is shown below:
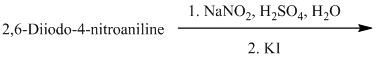
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. This aryl diazonium salt, on reaction with potassium iodide, introduces iodine to aryl by substitution reaction. The complete equation is shown below:
o) The given reaction is shown below:
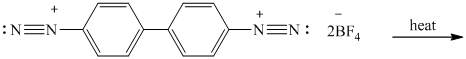
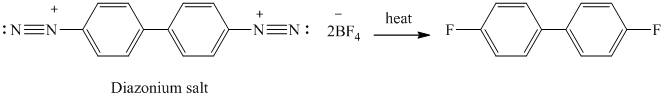
The given reactant has two diazonium saltsand on heating with two molar equivalent of
p) The given reaction is shown below:
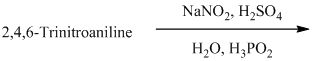
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The diazonium salt on treatment with hypophosphorous acid
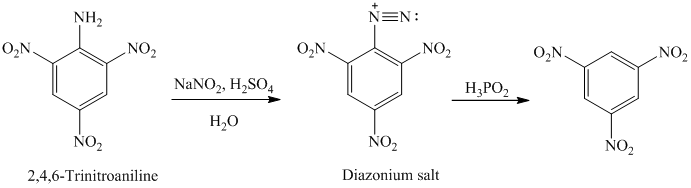
q) The given reaction is shown below:
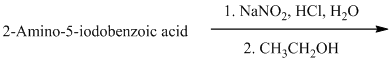
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The
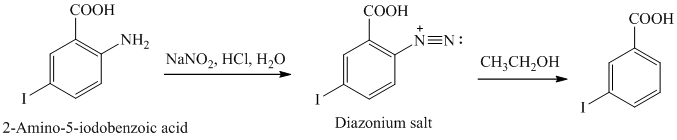
r) The given reaction is shown below:
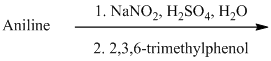
The aniline, when reacted with sodium nitrite in acidic condition, produces aryl diazonium salt and gets coupled at para position to the of hydroxide group of
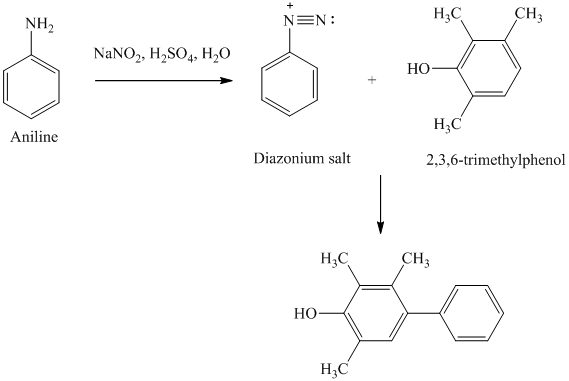
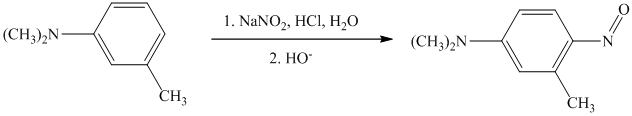
s) The given reaction is shown below:
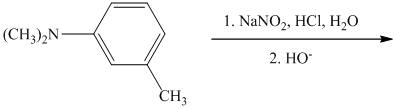
In the given aryl amine, the nitrogen is substituted with methyl groups; therefore, like primary aryl amines, the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- Interpreting NMR spectra is a skill that often requires some amount of practice, which, in turn, necessitates access to a collection of NMR spectra. Beyond Labz Organic Synthesis and Organic Qualitative Analysis have spectral libraries containing over 700 1H NMR spectra. In this assignment, you will take advantage of this by first predicting the NMR spectra for two closely related compounds and then checking your predictions by looking up the actual spectra in the spectra library. After completing this assignment, you may wish to select other compounds for additional practice. 1. Write the IUPAC names for the following two structures: Question 2 Question 3 2. Predict the NMR spectra for each of these two compounds by listing, in the NMR tables below, the chemical shift, the splitting, and the number of hydrogens associated with each predicted peak. Sort the peaks from largest chemical shift to lowest. **Not all slots must be filled**arrow_forward11:14 ... worksheets.beyondlabz.com 3. To check your predictions, click this link for Interpreting NMR Spectra 1. You will see a list of all the - compounds in the spectra library in alphabetical order by IUPAC name. Hovering over a name in the list will show the structure on the chalkboard. The four buttons on the top of the Spectra tab in the tray are used to select the different spectroscopic techniques for the selected compound. Make sure the NMR button has been selected. 4. Scroll through the list of names to find the names for the two compounds you have been given and click on the name to display the NMR spectrum for each. In the NMR tables below, list the chemical shift, the splitting, and the number of hydrogens associated with each peak for each compound. Compare your answers to your predictions. **Not all slots must be filled** Peak Chemical Shift (d) Multiplicity 1 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardО δα HO- H -Br δα HO-- + + -Br [B] 8+ HO- -Br δα नarrow_forward
- 1/2 - 51% + » GAY Organic Reactions Assignment /26 Write the type of reaction that is occurring on the line provided then complete the reaction. Only include the major products and any byproducts (e.g. H₂O) but no minor products. Please use either full structural diagrams or the combination method shown in the lesson. Skeletal/line diagrams will not be accepted. H3C 1. 2. CH3 A Acid OH Type of Reaction: NH Type of Reaction: + H₂O Catalyst + HBr 3. Type of Reaction: H3C 4. Type Reaction: 5. H3C CH2 + H2O OH + [0] CH3 Type of Reaction: 6. OH CH3 HO CH3 + Type of Reaction: 7. Type of Reaction: + [H]arrow_forwardhumbnai Concentration Terms[1].pdf ox + New Home Edit Sign in Comment Convert Page Fill & Sign Protect Tools Batch +WPS A Free Trial Share Inter Concreting Concentration forms. Hydrogen peroxide is a powerful oxidizing agent wed in concentrated solution in rocket fuels and in dilute solution as a hair bleach. An aqueous sulation of H2O2 is 30% by mass and has density of #liligime calculat the Ⓒmolality ⑥mole fraction of molarity. 20 9. B. A sample of Commercial Concentrated hydrochloric ETarrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forward
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward(a) Sketch the 'H NMR of the following chemical including the approximate chemical shifts, the multiplicity (splitting) of all signals and the integration (b) How many signals would you expect in the 13C NMR? CH3arrow_forwardDraw the Show the major and minor product(s) for the following reaction mechanisms for both reactions and show all resonance structures for any Explain why the major product is favoured? intermediates H-Brarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


