
a.
Construct the frequency distribution with approximately 5classes.
a.
Answer to Problem 31E
The frequency distribution is,
| Number of Words | Frequency |
| 0-1,999 | 26 |
| 2,000-3,999 | 25 |
| 4,000-5,999 | 5 |
| 6,000-7,999 | 0 |
| 8,000-9,999 | 1 |
| Total | 57 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that a table representing the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
Frequency:
The frequencies are calculated by using the tally mark and the
- Based on the given information, the class intervals are 0-1,999, 2,000-3,999, 4,000-5,999, 6,000-7,999, 8,000-9,999.
- Make a tally mark for each value in the corresponding number of words spoken and continue for all values in the data.
- The number of tally marks in each class represents the frequency, f of that class.
Similarly, the frequency of remaining classes for the number of words spoken is given below:
| Number of Words | Tally | Frequency |
| 0-1,999 | 26 | |
| 2,000-3,999 | 25 | |
| 4,000-5,999 | 5 | |
| 6,000-7,999 | 0 | |
| 8,000-9,999 | 1 | |
| Total | 57 |
b.
Construct the frequency histogram based on the frequency distribution.
b.
Answer to Problem 31E
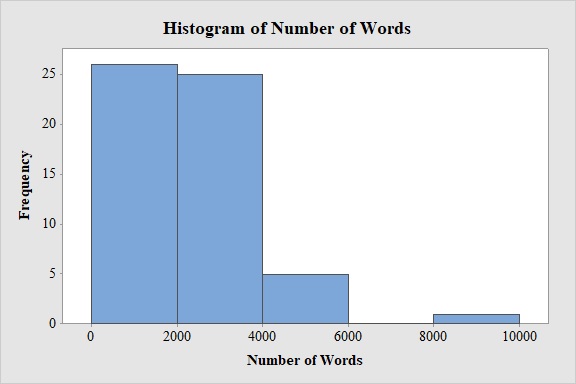
Output obtained from MINITAB software for the number of words spoken is:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Frequency Histogram:
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the relative frequency histogram for number of words spoken using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Histogram.
- Choose Simple.
- Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Number of Words.
- In Scale, Choose Y-scale Type as Frequency.
- Click OK.
- Select Edit Scale, Enter 0, 2,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000, 10,000 in Positions of ticks.
- In Binning, Under Interval Type select Cutpoint and under Interval Definition select Number of intervals as 5 and Cutpoint positions as 0, 2,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000, 10,000.
- In Labels, Enter 0, 2,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000, 10,000 in Specified.
- Click OK.
Observation:
From the bar graph, it can be seen that maximum number of words spoken are in the interval 0-2,000.
c.
Construct a relative frequency distribution for the data.
c.
Answer to Problem 31E
The relative frequency distribution for the data is:
| Number of Words | Relative frequency |
| 0-1,999 | 0.456 |
| 2,000-3,999 | 0.439 |
| 4,000-5,999 | 0.088 |
| 6,000-7,999 | 0.000 |
| 8,000-9,999 | 0.018 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Relative frequency:
The general formula for the relative frequency is,
Therefore,
Similarly, the relative frequencies for the remaining number of words spoken are obtained below:
| Number of Words | Frequency | Relative frequency |
| 0-1,999 | 26 | |
| 2,000-3,999 | 25 | |
| 4,000-5,999 | 5 | |
| 6,000-7,999 | 0 | |
| 8,000-9,999 | 1 |
d.
Construct the relative frequency histogram based on the frequency distribution.
d.
Answer to Problem 31E
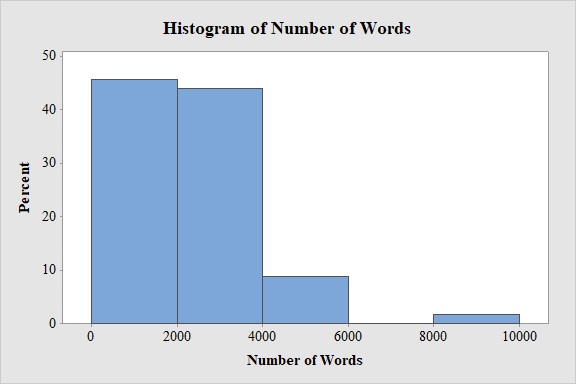
Output obtained from MINITAB software for the number of words spoken is:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Relative Frequency Histogram:
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the relative frequency histogram for the number of words spoken using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Histogram.
- Choose Simple.
- Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Number of Words.
- In Scale, Choose Y-scale Type as Percent.
- Click OK.
- Select Edit Scale, Enter 0, 2,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000, 10,000 in Positions of ticks.
- In Binning, Under Interval Type select Cutpoint and under Interval Definition select Number of intervals as 5 and Cutpoint positions as 0, 2,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000, 10,000.
- In Labels, Enter 0, 2,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000, 10,000 in Specified.
- Click OK.
Observation:
From the bar graph, it can be seen that maximum number of words spoken is in the interval 0-2,000.
e.
Check whether the histograms are skewed to the left, skewed to the right or approximately symmetric.
e.
Answer to Problem 31E
The histogram is skewed to the right.
Explanation of Solution
From the given histogram, the right hand tail is larger than the left hand tail from the maximum frequency value. Hence, the shape of the distribution is right skewed.
f.
Construct the frequency distribution with approximately 9classes.
f.
Answer to Problem 31E
The frequency distribution is,
| Number of Words | Frequency |
| 0-999 | 4 |
| 1,000-1,999 | 22 |
| 2,000-2,999 | 18 |
| 3,000-3,999 | 7 |
| 4,000-4,999 | 4 |
| 5,000-5,999 | 1 |
| 6,000-6,999 | 0 |
| 7,000-7,999 | 0 |
| 8,000-8,999 | 1 |
| Total | 57 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Frequency:
The frequencies are calculated by using the tally mark and the range of the data is from 0 to 8,999.
- Based on the given information, the class intervals are 0-999, 1,000-1,999, 2,000-2,999, 3,000-3,999, 4,000-4,999, 5,000-5,999, 6,000-6,999, 7,000-7,999, 8,000-8,999.
- Make a tally mark for each value in the corresponding number of words spoken and continue for all values in the data.
- The number of tally marks in each class represents the frequency, f of that class.
Similarly, the frequency of remaining classes for the number of words spoken is given below:
| Number of Words | Tally | Frequency |
| 0-999 | 4 | |
| 1,000-1,999 | 22 | |
| 2,000-2,999 | 18 | |
| 3,000-3,999 | 7 | |
| 4,000-4,999 | 4 | |
| 5,000-5,999 | 1 | |
| 6,000-6,999 | 0 | |
| 7,000-7,999 | 0 | |
| 8,000-8,999 | 1 | |
| Total | 57 |
g.
Repeat parts (b) to (d), using the frequency distribution constructed in part (f).
g.
Answer to Problem 31E
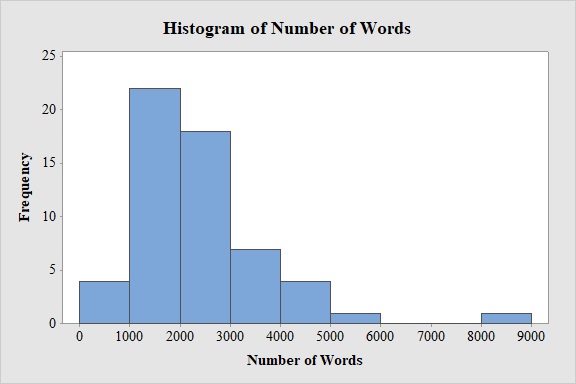
Output obtained from MINITAB software for the number of words spoken is:
The relative frequency distribution for the data is:
| Number of Words | Relative frequency |
| 0-999 | 0.070 |
| 1,000-1,999 | 0.386 |
| 2,000-2,999 | 0.316 |
| 3,000-3,999 | 0.123 |
| 4,000-4,999 | 0.070 |
| 5,000-5,999 | 0.018 |
| 6,000-6,999 | 0.000 |
| 7,000-7,999 | 0.000 |
| 8,000-8,999 | 0.018 |
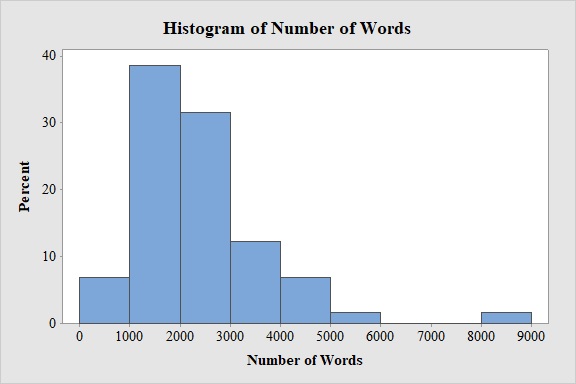
Output obtained from MINITAB software for the number of words spoken is:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Frequency Histogram:
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the relative frequency histogram for the number of words spoken using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Histogram.
- Choose Simple.
- Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Number of Words.
- In Scale, Choose Y-scale Type as Frequency.
- Click OK.
- Select Edit Scale, Enter 0, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, 8,000, 90,00 in Positions of ticks.
- In Binning, Under Interval Type select Cutpoint and under Interval Definition select Number of intervals as 9 and Cutpoint positions as 0, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, 8,000, 9,000.
- In Labels, Enter 0, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, 8,000, 9,000 in Specified.
- Click OK.
Observation:
From the bar graph, it can be seen that maximum number of words spoken is in the interval 1,000-2,000.
Relative frequency:
Similarly, the relative frequencies for the remaining number of words spoken are obtained below:
| Number of Words | Frequency | Relative frequency |
| 0-999 | 4 | |
| 1,000-1,999 | 22 | |
| 2,000-2,999 | 18 | |
| 3,000-3,999 | 7 | |
| 4,000-4,999 | 4 | |
| 5,000-5,999 | 1 | |
| 6,000-6,999 | 0 | |
| 7,000-7,999 | 0 | |
| 8,000-8,999 | 1 | |
| Total | 57 |
Relative Frequency Histogram:
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the relative frequency histogram for the number of words spoken using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Histogram.
- Choose Simple.
- Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Number of Words.
- In Scale, Choose Y-scale Type as Percent.
- Click OK.
- Select Edit Scale, Enter 0, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, 8,000 and 9,000 in Positions of ticks.
- In Binning, Under Interval Type select Cutpoint and under Interval Definition select Number of intervals as 9 and Cutpoint positions as 0, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, 8,000 and 9,000.
- In Labels, Enter 0, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, 8,000 and 9,000in Specified.
- Click OK.
Observation:
From the bar graph, it can be seen that maximum number of words spoken is in the interval 1,000-2,000.
h.
Check whether the 9 and 5 classes are reasonable or one choice is much better than the other and explain the reason.
h.
Answer to Problem 31E
Both the 5 and 9 classes are reasonable.
Explanation of Solution
Answer will vary.
The number of classes can be obtained by the following two points:
- The number of classes should be between 5 and 20.
- A larger number of classes will be appropriate for a very large data set.
Here number of classes for the histograms are 5 and 9 respectively. Thus, the number of classes are lies between 5 and 20.
Hence, the both 5 and 9 classes are reasonable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ESSENT. STAT ACCESS CARD
- The accompanying data represent the weights (in grams) of a simple random sample of 10 M&M plain candies. Determine the shape of the distribution of weights of M&Ms by drawing a frequency histogram. Find the mean and median. Which measure of central tendency better describes the weight of a plain M&M? Click the icon to view the candy weight data. Draw a frequency histogram. Choose the correct graph below. ○ A. ○ C. Frequency Weight of Plain M and Ms 0.78 0.84 Frequency OONAG 0.78 B. 0.9 0.96 Weight (grams) Weight of Plain M and Ms 0.84 0.9 0.96 Weight (grams) ○ D. Candy Weights 0.85 0.79 0.85 0.89 0.94 0.86 0.91 0.86 0.87 0.87 - Frequency ☑ Frequency 67200 0.78 → Weight of Plain M and Ms 0.9 0.96 0.84 Weight (grams) Weight of Plain M and Ms 0.78 0.84 Weight (grams) 0.9 0.96 →arrow_forwardThe acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured using pH. A pH less than 7 is acidic; a pH greater than 7 is alkaline. The accompanying data represent the pH in samples of bottled water and tap water. Complete parts (a) and (b). Click the icon to view the data table. (a) Determine the mean, median, and mode pH for each type of water. Comment on the differences between the two water types. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. A. For tap water, the mean pH is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) B. The mean does not exist. Data table Тар 7.64 7.45 7.45 7.10 7.46 7.50 7.68 7.69 7.56 7.46 7.52 7.46 5.15 5.09 5.31 5.20 4.78 5.23 Bottled 5.52 5.31 5.13 5.31 5.21 5.24 - ☑arrow_forwardく Chapter 5-Section 1 Homework X MindTap - Cengage Learning x + C webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?pos=3&dep=36701632&tags=autosave #question3874894_3 M Gmail 品 YouTube Maps 5. [-/20 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES BBUNDERSTAT12 5.1.020. ☆ B Verify it's you Finish update: All Bookmarks PRACTICE ANOTHER A computer repair shop has two work centers. The first center examines the computer to see what is wrong, and the second center repairs the computer. Let x₁ and x2 be random variables representing the lengths of time in minutes to examine a computer (✗₁) and to repair a computer (x2). Assume x and x, are independent random variables. Long-term history has shown the following times. 01 Examine computer, x₁₁ = 29.6 minutes; σ₁ = 8.1 minutes Repair computer, X2: μ₂ = 92.5 minutes; σ2 = 14.5 minutes (a) Let W = x₁ + x2 be a random variable representing the total time to examine and repair the computer. Compute the mean, variance, and standard deviation of W. (Round your answers…arrow_forward
- The acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured using pH. A pH less than 7 is acidic; a pH greater than 7 is alkaline. The accompanying data represent the pH in samples of bottled water and tap water. Complete parts (a) and (b). Click the icon to view the data table. (a) Determine the mean, median, and mode pH for each type of water. Comment on the differences between the two water types. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. A. For tap water, the mean pH is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) B. The mean does not exist. Data table Тар Bottled 7.64 7.45 7.46 7.50 7.68 7.45 7.10 7.56 7.46 7.52 5.15 5.09 5.31 5.20 4.78 5.52 5.31 5.13 5.31 5.21 7.69 7.46 5.23 5.24 Print Done - ☑arrow_forwardThe median for the given set of six ordered data values is 29.5. 9 12 23 41 49 What is the missing value? The missing value is ☐.arrow_forwardFind the population mean or sample mean as indicated. Sample: 22, 18, 9, 6, 15 □ Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. O A. x= B. μεarrow_forward
- Why the correct answer is letter A? Students in an online course are each randomly assigned to receive either standard practice exercises or adaptivepractice exercises. For the adaptive practice exercises, the next question asked is determined by whether the studentgot the previous question correct. The teacher of the course wants to determine whether there is a differencebetween the two practice exercise types by comparing the proportion of students who pass the course from eachgroup. The teacher plans to test the null hypothesis that versus the alternative hypothesis , whererepresents the proportion of students who would pass the course using standard practice exercises andrepresents the proportion of students who would pass the course using adaptive practice exercises.The teacher knows that the percent confidence interval for the difference in proportion of students passing thecourse for the two practice exercise types (standard minus adaptive) is and the percent…arrow_forwardCarpetland salespersons average $8,000 per week in sales. Steve Contois, the firm's vice president, proposes a compensation plan with new selling incentives. Steve hopes that the results of a trial selling period will enable him to conclude that the compensation plan increases the average sales per salesperson. a. Develop the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses.H 0: H a:arrow_forwardتوليد تمرين شامل حول الانحدار الخطي المتعدد بطريقة المربعات الصغرىarrow_forward
- The U.S. Postal Service will ship a Priority Mail® Large Flat Rate Box (12" 3 12" 3 5½") any where in the United States for a fixed price, regardless of weight. The weights (ounces) of 20 ran domly chosen boxes are shown below. (a) Make a stem-and-leaf diagram. (b) Make a histogram. (c) Describe the shape of the distribution. Weights 72 86 28 67 64 65 45 86 31 32 39 92 90 91 84 62 80 74 63 86arrow_forward(a) What is a bimodal histogram? (b) Explain the difference between left-skewed, symmetric, and right-skewed histograms. (c) What is an outlierarrow_forward(a) Test the hypothesis. Consider the hypothesis test Ho = : against H₁o < 02. Suppose that the sample sizes aren₁ = 7 and n₂ = 13 and that $² = 22.4 and $22 = 28.2. Use α = 0.05. Ho is not ✓ rejected. 9-9 IV (b) Find a 95% confidence interval on of 102. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


