
Concept explainers
a.
Construct a frequency bar graph.
a.
Answer to Problem 28E
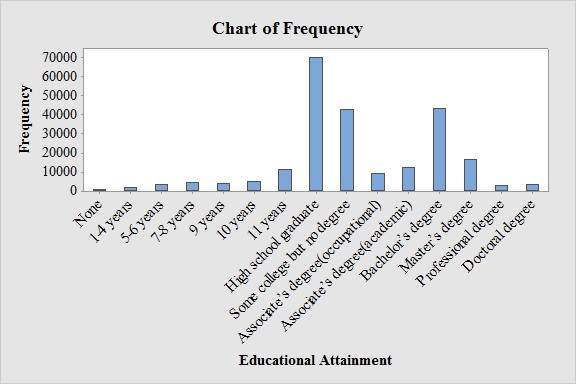
Output obtained from MINITAB software for the educational attainment is:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is a table representing the frequency distribution categorizes U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a year.
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the bar chart for educational attainment using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Bar Chart.
- From Bars represent, choose unique values from table.
- Choose Simple.
- Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Frequency.
- In Categorical variables, enter the column of Educational Attainment.
- Click OK
Observation:
From the bar graph, it can be seen that the most frequent educational attainment is High school graduate.
b.
Construct a relative frequency distribution for the data.
b.
Answer to Problem 28E
The relative frequency distribution for the data is:
| Educational Attainment | Relative Frequency |
| None | 0.004 |
| 1-4 years | 0.008 |
| 5-6 years | 0.015 |
| 7-8 years | 0.019 |
| 9 years | 0.017 |
| 10 years | 0.020 |
| 11 years | 0.049 |
| High school graduate | 0.300 |
| Some college but no degree | 0.194 |
| Associate’s degree(occupational) | 0.040 |
| Associate’s degree(academic) | 0.052 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 0.184 |
| Master’s degree | 0.071 |
| Professional degree | 0.013 |
| Doctoral degree | 0.014 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Relative frequency:
The general formula for the relative frequency is,
Therefore,
Similarly, the relative frequencies for the response are obtained below:
| Educational Attainment | Frequency | Relative Frequency |
| None | 834 | |
| 1-4 years | 1,764 | |
| 5-6 years | 3,618 | |
| 7-8 years | 4,575 | |
| 9 years | 4,068 | |
| 10 years | 4,814 | |
| 11 years | 11,429 | |
| High school graduate | 70,441 | |
| Some college but no degree | 42,685 | |
| Associate’s degree(occupational) | 9,380 | |
| Associate’s degree(academic) | 12,100 | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 43,277 | |
| Master’s degree | 16,625 | |
| Professional degree | 3,099 | |
| Doctoral degree | 3,191 |
c.
Construct a relative frequency bar graph for these data.
c.
Answer to Problem 28E
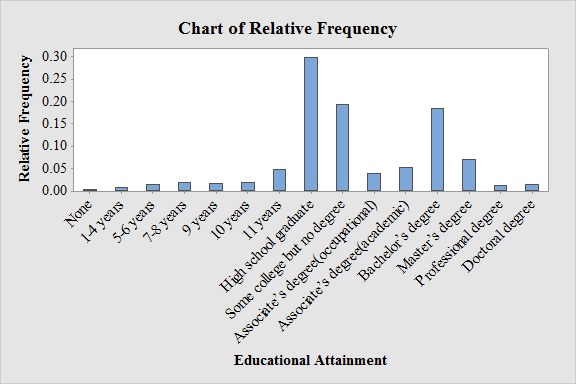
Output obtained from MINITAB software for the educational attainment is:
Explanation of Solution
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the Bar chart for the response using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Bar Chart.
- From Bars represent, choose unique values from table.
- Choose Simple.
- Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Relative Frequency.
- In Categorical variables, enter the column of Educational Attainment.
- Click OK
Observation:
From the graph, it can be seen that most probable educational attainment is High school graduate.
d.
Construct a frequency distribution for the categories 8 years or less, 9-11 years, High school graduate, Some college but no degree, College degree( Associate’s or Bachelor’s), Graduate degree ( Master’s Professional, or Doctoral).
d.
Answer to Problem 28E
The frequency distribution for the data is:
| Educational Attainment | Frequency |
| 8 years or less | 10,791 |
| 9-11 years | 20,311 |
| High school graduate | 70,441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45,685 |
| College degree | 64,757 |
| Graduate degree | 22,915 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The frequencies for the specified categories are obtained below:
| Educational Attainment | Frequency |
| 8 years or less | |
| 9-11 years | |
| High school graduate | 70,441 |
| Some college but no degree | 42,685 |
| College degree | |
| Graduate degree |
e.
Construct a pie chart for the frequency distribution in part (d).
e.
Answer to Problem 28E
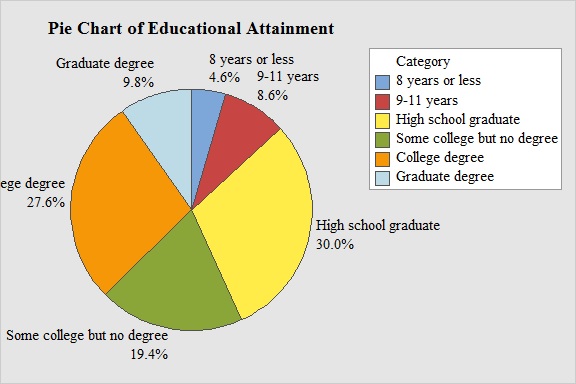
Output obtained from MINITAB software for frequency distribution in part (d) is:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the bar chart for frequency distribution in part (d) using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Pie Chart.
- Choose Chart values from table.
- Under categorical variable, select Educational Attainment.
- Under Summary variables, select Frequency.
- Click OK.
Observation:
There is about 30.0% of the adults are High school graduate and 4.6% of adults are 8 years or less.
f.
Find the proportion of people did not graduate from high school.
f.
Answer to Problem 28E
The proportion of people did not graduate from high school is 0.132.
Explanation of Solution
From the pie chart, it can be seen that there is about 4.6% of the adults are 8 years or less, 8.6% of adults are 9-11 years and all others are graduate from high school. Then the total proportion of people did not graduate from high school is
Hence, the proportion of people did not graduate from high school is 0.132.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ESSENT. STAT ACCESS CARD
- This is the information about the actors who won the Best Actor Oscar: Best actors 44 41 62 52 41 34 34 52 41 37 38 34 32 40 43 56 41 39 49 57 35 30 39 41 44 41 38 42 52 51 49 35 47 31 47 37 57 42 45 42 44 62 43 42 48 49 56 38 60 30 40 42 36 76 39 53 45 36 62 43 51 32 42 54 52 37 38 32 45 60 46 40 36 47 29 43 a. What is the variable? What type? b. Construct an interval-frequency table, with columns containing: class mark, absolute frequency, relative frequency, cumulative frequency, cumulative relative frequency, and percentage frequency.arrow_forwardans c plsarrow_forwardCritically analyze the following graph and, based on statistical information, indicate the type of error it presents IN NO MORE THAN 3 LINES SCOTCEN POLL OF POLLS SHOULD SCOTLAND BE INDEPENDENT? NO 52% YES 58% LIVE CAW NAS & 28.30 HAS KILLED MORE THAN 2,600 IN WEST AFRICA, WORLD HEALTH ORG. BROOKEBCNNarrow_forward
- Critically analyze the following graph and, based on statistical information, indicate the type of error it presents IN NO MORE THAN 3 LINES PRESIDENTIAL PREFERENCES RODOLFO CARTER 3% (+2pts) EVELYN MATTHEI 22% (+6pts) With the exception of President Boric, could you tell me who you would like to be the next president of Chile? CAMILA VALLEJO 4% (+2pts) JOSÉ ANTONIO KAST 19% (+5pts) MICHELLE BACHELET 6% (+1pts)arrow_forwardCritically analyze the following graph and, based on statistical information, indicate the type of error it presents IN NO MORE THAN 3 LINES 13% APPROVE 4% DOESN'T KNOW DOESN'T RESPOND 5% NEITHER APPROVES NOR DISAPPROVES 78% DISAPPROVES SURVEY PRESIDENTIAL APPROVAL DROPS TO 13%arrow_forwardPlease help with this following question I'm not too sure if question (a) and (b) are correct and not sure how to calculate (c) The csv data is below "","New","Current" "1","67",66 "2","77",73 "3","76",73 "4","76",76 "5","77",79 "6","84",76 "7","71",78 "8","84",72 "9","73",76 "10","71",73 "11","72",77 "12","70",72 "13","75",72 "14","84",71 "15","77",73 "16","65",72 "17","69",73 "18","71",73 "19","79",71 "20","75",78 "21","76",69 "22","73",74 "23","76",71 "24","64",74 "25","81",78 "26","79",76 "27","70",77 "28","79",71 "29","84",73 "30","79",69 "31","69",72 "32","81",76 "33","77",70 "34","77",71 "35","71",69 "36","67",72 "37","70",76 "38","77",73 "39","82",73 "40","72",73arrow_forward
- Please help me answer the following question(c) A previous study found that 15% of nurses reported participating in mental health support programs.From the 96% found in (b) , can you conclude that proportion of nurses reported participating in mental health support programs p(current), has changed from the previous study?(Yes/No) because the confidence interval in (b) (captures/does not capture) 15%.(d) Refer to your answer in (b) : The Alberta Nurses Association expects that not more than 23 % of nurses will participate in the survey on mental health support programs. Given the result in part (b) can we conclude that this expectation is reasonable?(Yes/No) because the (upper bound/lower bound) of the 96% confidence interval is (less than/not less than/greater than) 23%. The Alberta Nursing Association conducts an annual survey to estimate the proportion of nurses who participate in mental health support programs. The most recent application of this survey involved a random sample of…arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this questionThis is what was in the csv file:"","Diabetic","Heart Disease""1",32644,30646"2",789,1670"3",12802,36274"4",2177,5011"5",1910,3300"6",3320,4256"7",61425,39053"8",19768,28635"9",19502,39546"10",5642,12182"11",107864,152098"12",29918,60433"13",2397,3550"14",41559,34705"15",49169,57948"16",72853,83100"17",2155,2873"18",140220,134517"19",28181,26212"20",18850,38637"21",69564,68582"22",13897,12613"23",6868,9138"24",9735,4767"25",12102,13447"26",36571,50010"27",44665,55141"28",26620,33970"29",25525,29766"30",14167,20206Q(b) From this, the relationship between these two variables is (non-existent/positive/negative) . I can categorize this relationship as being (strong/weak/moderate).Q(c) Drop down is (+/-)Q(d) Drop downs in order are __% of the (average/median/variation/standard deviation) in the (the number of people diagnosed with heart disease/the number of people diagnosed with diabetes)−variable can be explained by its (linear relationship/relationship)…arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following question The drop down for question (e, f, and g) is (YES/NO) Based on the P-value above, the assumption of equal variances among the four machines (Is Met/Is Not Met) Based on the data, the average fill for machine 3 is (statistically lower than/statistically higher than/the same as/not statistically different than/statistically different than/Hard to say then when comparing to/Refuse to say when comparing to) machine 1.arrow_forward
- Business Discussarrow_forward1 for all k, and set o (ii) Let X1, X2, that P(Xkb) = x > 0. Xn be independent random variables with mean 0, suppose = and Var Xk. Then, for 0x) ≤2 exp-tx+121 Στ k=1arrow_forwardLemma 1.1 Suppose that g is a non-negative, non-decreasing function such that E g(X) 0. Then, E g(|X|) P(|X|> x) ≤ g(x)arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





