
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
To locate the two nonmetals form more than four bonds on the periodic table
Concept introduction:
A table in which the chemical elements are arranged in order by their
Nonmetals have a low melting point and boiling points. The nonmetals are dividing into two parts. They are reactive nonmetals and noble gases. The nonmetals present in the periodic table: hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, sulfur, selenium, and the noble gases.
Interpretation:
To locate the nonmetals form maximum four bonds on the periodic table
Concept introduction:
Nonmetals have a low melting point and boiling points. The nonmetals are dividing into two parts. They are reactive nonmetals and noble gases. The nonmetals present in the periodic table: hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, sulfur, selenium, and the noble gases. A table in which the chemical elements are arranged in order by their atomic number, an electronic configuration is said to be a periodic table. In general, the elements in a vertical column are said to be groups and rows are said to be periods. Elements in the same groups generally possess similar chemical properties.
Interpretation:
To locate the two nonmetals form oxides that are gases at
Concept introduction:
Nonmetals have a low melting point and boiling points. The nonmetals are dividing into two parts. They are reactive nonmetals and noble gases. The nonmetals present in the periodic table: hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, sulfur, selenium, and the noble gases. A table in which the chemical elements are arranged in order by their atomic number, an electronic configuration is said to be a periodic table. In general, the elements in a vertical column are said to be groups and rows are said to be periods. Elements in the same groups generally possess similar chemical properties.
Interpretation:
To locate the nonmetal that forms an oxide that is solid 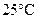
Concept introduction:
Nonmetals have a low melting point and boiling points. The nonmetals are dividing into two parts. They are reactive nonmetals and noble gases. The nonmetals present in the periodic table: hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, sulfur, selenium, and the noble gases. A table in which the chemical elements are arranged in order by their atomic number, an electronic configuration is said to be a periodic table. In general, the elements in a vertical column are said to be groups and rows are said to be periods. Elements in the same groups generally possess similar chemical properties.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry (7th Edition)
- Q7: Use compound A-D, design two different ways to synthesize E. Which way is preferred? Please explain. CH3I ONa NaOCH 3 A B C D E OCH3arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward(10 pts) The density of metallic copper is 8.92 g cm³. The structure of this metal is cubic close-packed. What is the atomic radius of copper in copper metal?arrow_forward
- Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardQ3: Rank the following compounds in increasing reactivity of E1 and E2 eliminations, respectively. Br ca. go do A CI CI B C CI Darrow_forward
- Q5: Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2). H₂O דיי "Br KN3 CH3CH2OH NaNH2 NH3 Page 3 of 6 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets CI Br excess NaOCH 3 CH3OH Br KOC(CH3)3 DuckDuckGarrow_forwardQ4: Circle the substrate that gives a single alkene product in a E2 elimination. CI CI Br Brarrow_forwardPlease calculate the chemical shift of each protonsarrow_forward
- Q1: Answer the questions for the reaction below: ..!! Br OH a) Predict the product(s) of the reaction. b) Is the substrate optically active? Are the product(s) optically active as a mix? c) Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction. d) What happens to the SN1 reaction rate in each of these instances: 1. Change the substrate to Br 'CI 2. Change the substrate to 3. Change the solvent from 100% CH3CH2OH to 10% CH3CH2OH + 90% DMF 4. Increase the substrate concentration by 3-fold.arrow_forwardQ6: Provide the reagents and conditions for the following reactions to make the product with a good yield. Br Br CI она CIarrow_forwardQ2: We would not expect the following primary alkyl halide to go through an SN1 reaction. However, it can go through an SN1 mechanism. Explain why. Hint: Think about what happens when the leaving group leaves. CI NaO EtOH H བྱིས་ Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





