
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
16th Edition
ISBN: 9780134475585
Author: Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 22.30P
Multinational transfer pricing, global tax minimization. Express Grow Inc., based in Ankeny, lowa, sells high-end fertilizers. Express Grow has two divisions:
- North Italy mining division, which mines potash in northern Italy
- U.S. processing division, which uses potash in manufacturing top-grade fertilizer
The processing division’s yield is 50%: It takes 2 tons of raw potash to produce 1 ton of top-grade fertilizer. Although all of the mining division’s output of 8,000 tons of potash is sent for processing in the United States, there is also an active market for potash in Italy. The foreign exchange rate is 0.80 Euro = $1 U.S. The following information is known about the two divisions:
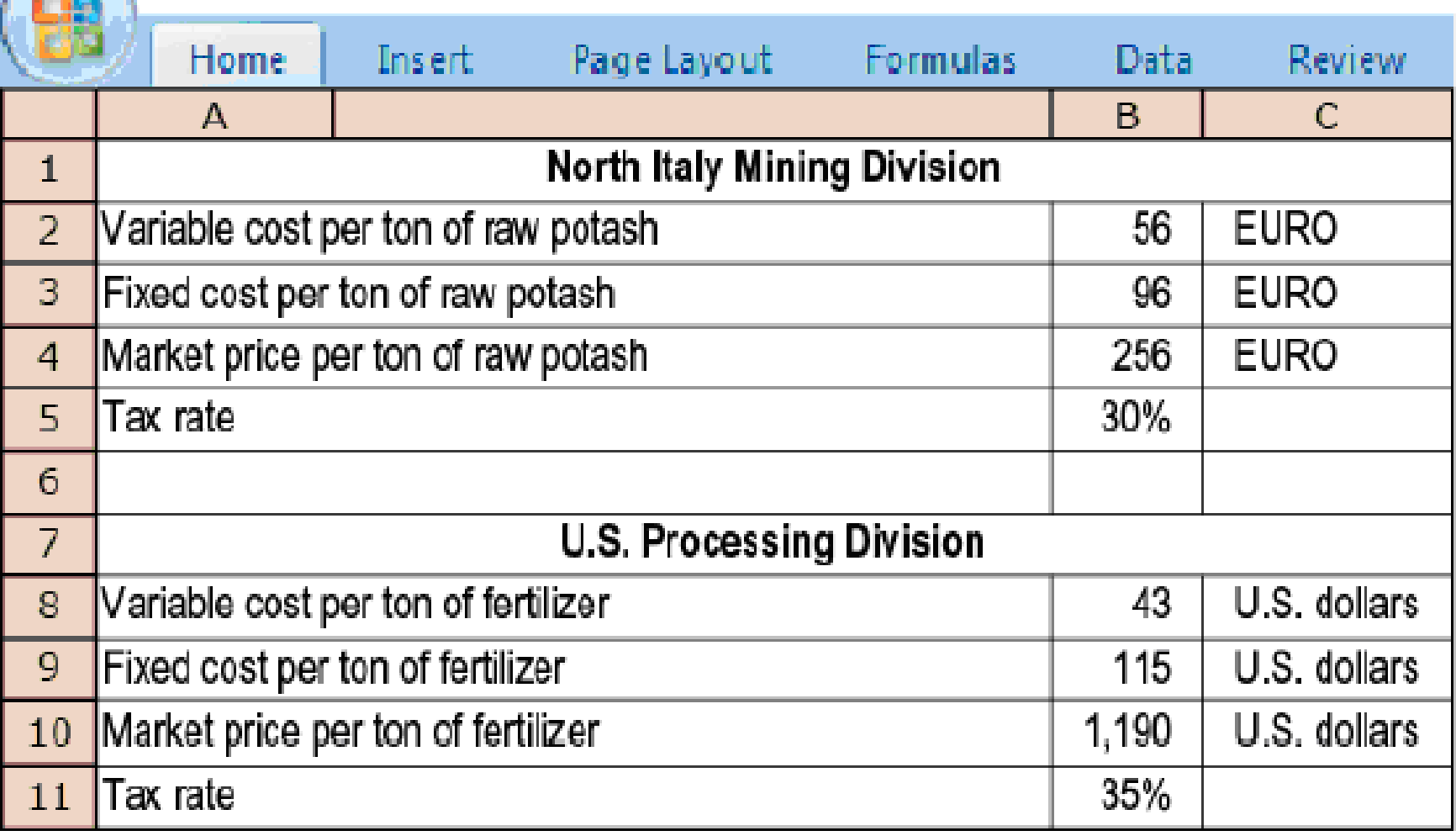
- A. Compute the annual pretax operating income, in U.S. dollars, of each division under the following transfer-pricing methods: (a) 150% of full cost and (b) market price.
- B. Compute the after-tax operating income, in U.S. dollars, for each division under the transfer-pricing methods in requirement 1. (Income taxes are not included in the computation of cost-based transfer price, and Express Grow does not pay U.S. income tax on income already taxed in Italy.)
- C. If the two division managers are compensated based on after-tax division operating income, which transfer-pricing method will each prefer? Which transfer-pricing method will maximize the total after-tax operating income of Express Grow?
- D. In addition to tax minimization, what other factors might Express Grow consider in choosing a transfer-pricing method?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
choose best answer for this questions carefully
subject- general accountant
I want answer
Chapter 22 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.1QCh. 22 - Describe three criteria you would use to evaluate...Ch. 22 - What is the relationship among motivation, goal...Ch. 22 - Name three benefits and two costs of...Ch. 22 - Organizations typically adopt a consistent...Ch. 22 - Transfer pricing is confined to profit centers. Do...Ch. 22 - What are the three methods for determining...Ch. 22 - What properties should transfer-pricing systems...Ch. 22 - All transfer-pricing methods give the same...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.10Q
Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.11QCh. 22 - Prob. 22.12QCh. 22 - Prob. 22.13QCh. 22 - Under the general guideline for transfer pricing,...Ch. 22 - How should managers consider income tax issues...Ch. 22 - Evaluating management control systems, balanced...Ch. 22 - Cost centers, profit centers, decentralization,...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.18ECh. 22 - Prob. 22.19ECh. 22 - Multinational transfer pricing, effect of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.21ECh. 22 - Multinational transfer pricing, global tax...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.23ECh. 22 - Prob. 22.24ECh. 22 - Transfer-pricing problem (continuation of 22-24)....Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.26PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.27PCh. 22 - Effect of alternative transfer-pricing methods on...Ch. 22 - Goal-congruence problems with cost-plus...Ch. 22 - Multinational transfer pricing, global tax...Ch. 22 - Transfer pricing, external market, goal...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.32PCh. 22 - Transfer pricing, goal congruence, ethics. Cocoa...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.34PCh. 22 - Transfer pricing, perfect and imperfect markets....Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.36PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.37P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
What is Transfer Pricing for Small Businesses?; Author: Nomad Capitalist;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Q6nN3s1Xjs;License: Standard Youtube License