
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 2.19P
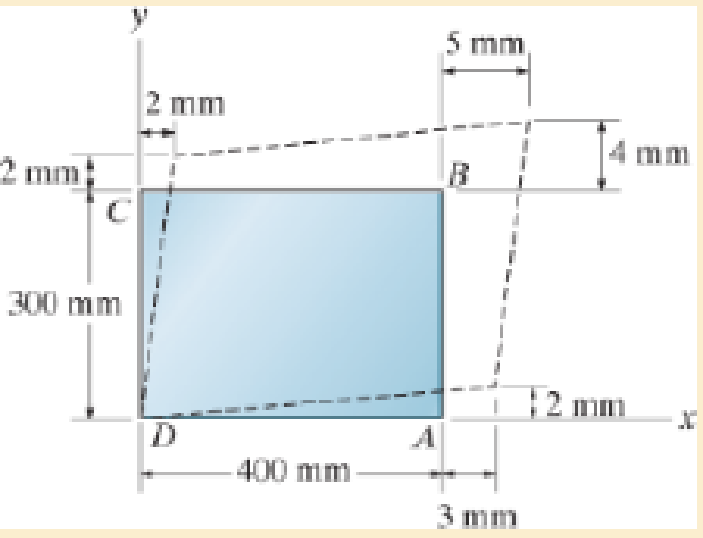
Determine the shear strain γxy at corners D and C if the plate distorts as shown by the dashed lines.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Both portions of the rod ABC are made of an aluminum for which E = 70 GPa.
Based on the given information find:
1- deformation at A
2- stress in BC
3- Total strain
4- If v (Poisson ratio is 0.25, find the
lateral deformation of AB
Last 3 student ID+ 300 mm=L2
724
A
P=Last 2 student ID+ 300 KN
24
24
Diameter Last 2 student ID+ 15 mm
Last 3 student ID+ 500 mm=L1
724
C
B
24
Q=Last 2 student ID+ 100 KN
24
Diameter Last 2 student ID+ 40 mm
Q2Two wooden members of uniform cross section are joined by the simple scarf splice shown. Knowing that the
maximum allowable tensile stress in the glued splice is 75 psi, determine (a) the largest load P that can be safely
supported, (b) the corresponding shearing stress in the splice.
น
Last 1 student ID+5 inch=W
=9
4
L=Last 1 student ID+8 inch
=12
60°
P'
Q4
The two solid shafts are connected by gears as shown and are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing
stress is 7000 psi. Knowing the diameters of the two shafts are, respectively, dBC
determine the largest torque Tc that can be applied at C.
4
and dEF
dBC=Last 1 student ID+3 inch
dEF=Last 1 student ID+1 inch
7
R=Last 1 Student ID+5 inch
9
R
B
Tc
2.5 in.
E
TF
H
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the member to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the mamber to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the wires to elongate into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...
Ch. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - The pin-connected rigid rods AB and BC are...Ch. 2.2 - The wire AB is unstretched when = 45. If a load...Ch. 2.2 - If a horizontal load applied to the bar AC causes...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - The nylon cord has an original length L and is...Ch. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the average normal strain that occurs...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The block is deformed into the position shown by...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate undergoes a deformation...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Experiment تكنولوجيا السيارات - Internal Forced convenction Heat transfer Air Flow through Rectangular Duct. objective: Study the convection heat transfer of air flow through rectangular duct. Valve Th Top Dead Centre Exhaust Valve Class CP. N; ~ RIVavg Ti K 2.11 Te To 18.8 21.3 45.8 Nath Ne Pre Calculations:. Q = m cp (Te-Ti) m: Varg Ac Acca*b Q=hexp As (Ts-Tm) 2 2.61 18.5 20.846.3 Tm = Te-Ti = 25 AS-PL = (a+b)*2*L Nu exp= Re-Vavy D heep Dh k 2ab a+b Nu Dh the- (TS-Tm) Ts. Tmy Name / Nu exp Naxe بب ارتدان العشريarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forward
- Procedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2D3D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D ∑Fx=0 ∑Fy=0 ∑Fz=0 ∑Mx=0 ∑My=0 ΣMz=0 2D ΣFx=0 ΣFy=0 ΣMz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forward
- Procedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forwardFor each system below with transfer function G(s), plot the pole(s) on the s-plane. and indicate whether the system is: (a) "stable" (i.e., a bounded input will always result in a bounded output), (b) "marginally stable," or (c) "unstable" Sketch a rough graph of the time response to a step input. 8 a) G(s) = 5-5 8 b) G(s) = c) G(s) = = s+5 3s + 8 s² - 2s +2 3s +8 d) G(s): = s²+2s+2 3s+8 e) G(s): = s² +9 f) G(s): 8 00 == Sarrow_forwardPlease answer the following question. Include all work and plase explain. Graphs are provided below. "Consider the Mg (Magnesium) - Ni (Nickel) phase diagram shown below. This phase diagram contains two eutectic reactions and two intermediate phases (Mg2Ni and MgNi2). At a temperature of 505oC, determine what the composition of an alloy would need to be to contain a mass fraction of 0.20 Mg and 0.80 Mg2Ni."arrow_forward
- The triangular plate, having a 90∘∘ angle at AA, supports the load PP = 370 lblb as shown in (Figure 1).arrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, ß2 = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. φ 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° 2.138 P1 Figure 1 Xarrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, B₂ = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° P1 Figure 1 2.138 Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Lec21, Part 5, Strain transformation; Author: Mechanics of Materials (Libre);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgJvz5j_ubM;License: Standard Youtube License