
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 2.26P
The corners of the square plate are given the displacements indicated. Determine the shear strain at A relative to axes that are directed along AB and AD, and the shear strain at B relative to axes that are directed along BC and BA.
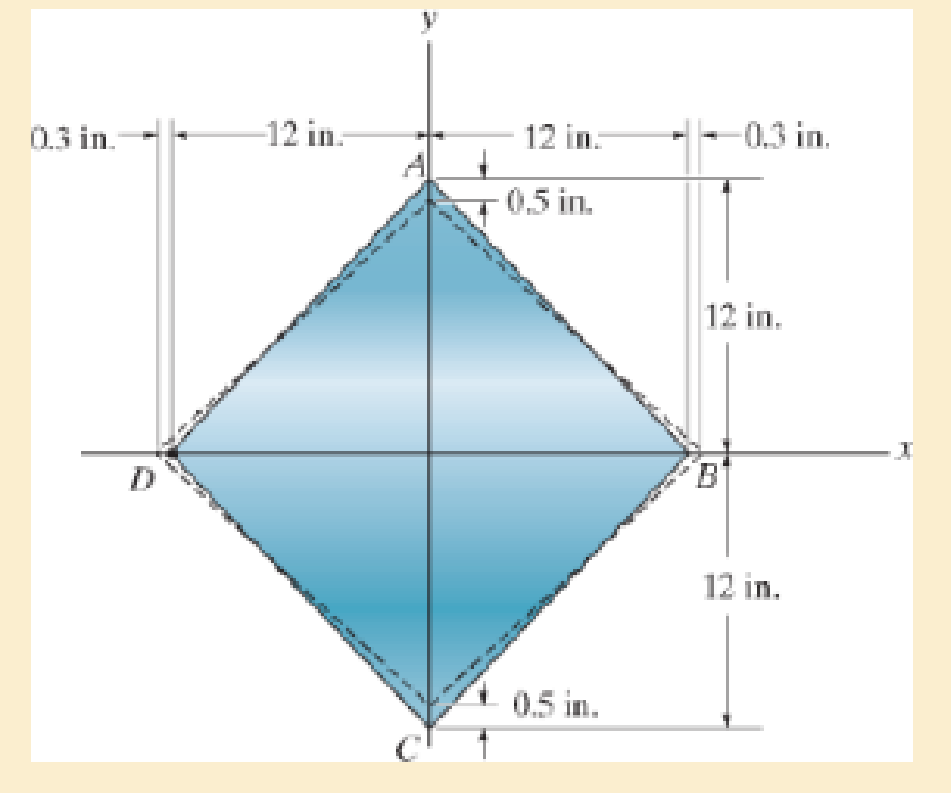
Prob. 2-26
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
handwritten-solutions, please!
handwritten-solutions, please!
Required information
An eccentric force P is applied as shown to a steel bar of 25 × 90-mm cross section. The strains at A and B have been
measured and found to be
εΑ = +490 μ
εB=-70 μ
Know that E = 200 GPa.
25 mm
30 mm
90 mm
45 mm
B
Determine the distance d.
The distance dis
15 mm
mm.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the member to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the mamber to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the wires to elongate into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...
Ch. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - The pin-connected rigid rods AB and BC are...Ch. 2.2 - The wire AB is unstretched when = 45. If a load...Ch. 2.2 - If a horizontal load applied to the bar AC causes...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - The nylon cord has an original length L and is...Ch. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the average normal strain that occurs...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The block is deformed into the position shown by...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate undergoes a deformation...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward! Required information Assume that the couple shown acts in a vertical plane. Take M = 25 kip.in. r = 0.75 in. A B 4.8 in. M 1.2 in. [1.2 in. Determine the stress at point B. The stress at point B is ksi.arrow_forward
- Problem 6 (Optional, extra 6 points) 150 mm 150 mm 120 mm 80 mm 60 mm PROBLEM 18.103 A 2.5 kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates with an angular velocity ₁ with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating as shown at the constant rate w212 rad/s. Friction in the bearing at A causes ₁ to decrease at the rate of 15 rad/s². Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E at a time when ₁ has decreased to 50 rad/s. Answer: 5=-22.01 +26.8} N E=-21.2-5.20Ĵ Narrow_forwardProblem 1. Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3 lb and length 2 ft, are welded to each other at their midpoints. Knowing that this assembly has an angular velocity of constant magnitude c = 12 rad/s, determine: (1). the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum HD of the assembly about D. (2). the dynamic reactions (ignore mg) at the bearings at A and B. 9 in. 3 in. 03 9 in. 3 in. Answers: HD = 0.162 i +0.184 j slug-ft²/s HG = 2.21 k Ay =-1.1 lb; Az = 0; By = 1.1 lb; B₂ = 0.arrow_forwardProblem 5 (Optional, extra 6 points) A 6-lb homogeneous disk of radius 3 in. spins as shown at the constant rate w₁ = 60 rad/s. The disk is supported by the fork-ended rod AB, which is welded to the vertical shaft CBD. The system is at rest when a couple Mo= (0.25ft-lb)j is applied to the shaft for 2 s and then removed. Determine the dynamic reactions at C and D before and after the couple has been removed at 2 s. 4 in. C B Mo 5 in 4 in. Note: 2 rotating around CD induced by Mo is NOT constant before Mo is removed. and ₂ (two unknowns) are related by the equation: ₂ =0+ w₂t 3 in. Partial Answer (after Mo has been removed): C-7.81+7.43k lb D -7.81 7.43 lbarrow_forward
- Problem 4. A homogeneous disk with radius and mass m is mounted on an axle OG with length L and a negligible mass. The axle is pivoted at the fixed-point O, and the disk is constrained to roll on a horizontal surface. The disk rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate o₁ about the axle. (mg must be included into your calculation) (a). Calculate the linear velocity of G and indicate it on the figure. (b). Calculate ₂ (constant), which is the angular velocity of the axle OG around the vertical axis. (c). Calculate the linear acceleration ā of G and indicate it on the figure. (d). Determine the force (assumed vertical) exerted by the floor on the disk (e). Determine the reaction at the pivot O. 1 Answers: N = mg +mr(r/L)² @² |j mr w IIG C R L i+ 2L =arrow_forwardProblem 2. The homogeneous disk of weight W = 6 lb rotates at the constant rate co₁ = 16 rad/s with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating at the constant rate 2 = 8 rad/s. Assume the rod weight is negligible compared to the disk. Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E (ignore mg). Answers: D=-7.12ĵ+4.47k lb r-8 in. 9 in. B D E=-1.822+4.47 lb 9 in. E 12 in. 12 in. xarrow_forwardProblem 3. Each of the right angle rods has a mass of 120 g and is welded to the shaft, which rotates at a steady speed of 3600 rpm. Ignore the weight of the shaft AB. Find the bearing dynamic reaction at A due to the dynamic imbalance of the shaft. (ignore mgs) 100 N A 100 100 100 100 100 (Dimensions in millimeters) Answer: A=-8521-426j N Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
An Introduction to Stress and Strain; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQf6Q8t1FQE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY