
Concept explainers
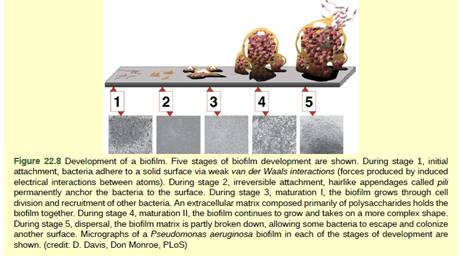
Figure 22.8 Compared to free-floating bacteria, bacteria in biofilms often show increased resistance to antibiotics and detergents. Why do you think this might be the case?
To write:
The bacteria of biofilms show increased resistance to antibiotics and detergents than free-floating bacteria.
Introduction:
The microbial mats or large biofilms may appear as a first prokaryotic life form on Earth, which originated around 3.5 billion years back. These mats are composed of multi-layered sheets of prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea). The primitive microbial mats typically reliant on chemicals from hydrothermal vents to acquire adequate energy and food.
Explanation of Solution
The microbial community is joined together by the extracellular matrix that is a gum-like sticky substance produced by them. The inner bacterial layer is protected by the extracellular matrix and outer layer of cells. The close proximity of cells usually enables the lateral gene transfer, that is, a mechanism of transfer of genes like detergent or antibiotic-resistance genes from one bacterial cell to another. Additionally, an exo-enzyme synthesized by a bacterial cell can destroy antibiotic or detergent and protect neighboring bacteria. This process helps bacterial cells present in the biofilms even if lateral gene transfer does not occur.
Therefore, bacteria present in the biofilms are more resistant to detergent and antibiotic as compared to the free-floating bacteria.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
BIOLOGY 2E
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- UARDIAN SIGNA Life Sciences/ Baseline Test Grade 10 ry must be written in point form. pot in full sentences using NO MORE than 70 words sentences from 1 to 7. only ONE point per sentence. words as far as possible. number of words you have used in brackets at the end GDE/2024 QUESTION 3 The table below shows the results of an investigation in which the effect of temperature and light on the yield of tomatoes in two greenhouses on a farm was investigated. TEMPERATURE (°C) AVERAGE YIELD OF TOMATOES PER 3.1 PLANT (kg) LOW LIGHT LEVELS HIGH LIGHT LEVELS 5 0,5 0,5 10 1,5 2,5 15 3,0 5,0 20 3,6 8,5 25 3,5 7,8 30 2,5 6,2 State TWO steps the investigator may have taken into consideration during the planning stage of the investigation. (2) 3.2 Identify the: a) Independent variables (2) b) Dependent variable (1) 3.3 Plot a line graph showing the results of the average yield of the tomatoes from 5°C to 30°C for low light levels. (6) 3.4 State ONE way in which the scientists could have improved the…arrow_forwardExplain why you chose this mutation. Begin by transcribing and translating BOTH the normal and abnormal DNA sequences. The genetic code below is for your reference. SECOND BASE OF CODON כ FIRST BASE OF CODON O THIRD BASE OF CODON SCAGUCAGUGAGUCAG UUU UUC UCU UAU UGU Phenylalanine (F) Tyrosine (Y) Cysteine (C) UCC UAC UGC Serine (S) UUA UUG Leucine (L) UCA UCG_ UAA UGA Stop codon -Stop codon UAG UGG -Tryptophan (W) CUU CUC CCU CAU CGU Histidine (H) CCC CAC CGC -Leucine (L) Proline (P) CUA CCA CAA CUG CCG CAG-Glutamine (Q) -Arginine (R) CGA CGG AUU ACU AAU AGU AUC Isoleucine (1) Asparagine (N) ACC AAC Threonine (T) AUA ACA AAA Methionine (M) Lysine (K) AUG ACG Start codon AAG AGC-Serine (S) -Arginine (R) AGA AGG GUU GCU GAU GUC GUA GUG GCC Valine (V) -Alanine (A) GCA GCG GAC GAA GAG Aspartic acid (D) GGU Glutamic acid (E) GGC GGA GGG Glycine (G) In order to provide a complete answer to the question stated above, fill in the mRNA bases and amino acid sequences by using the Genetic Code…arrow_forwardidentify the indicated cell in white arrowarrow_forward
- Gloeocaspa Genus - diagram a colony and label the sheath, cell wall, and cytoplasm. Oscillatoria Genus - Diagram a trichome, and label the shealth and individual cells Nostoc Genus- diagram a sketch of the colonoy microscopically from low power to the left of the drawing. Draw a filament showing intercalary heterocysts, and vegatative cells to the right of the drawing Merismopedia Genus- diagram a sketch of the colony. draw and label a filament showing the colony, cell wall, and sheath. Gloeotrichia Genus- diagram a habit sketch of the colony. draw a filament showing the heterocyst, akimetes and vegatative cells of the filamentarrow_forwardOf this list shown, which genus does the image belong toarrow_forwardidentify the cell shownarrow_forward
- identify the genusarrow_forwardWhat Genus is this?arrow_forwardAs a medical professional, it is important to be able to discuss how genetic processes such as translation regulation can directly affect patients. Think about some situations that might involve translation regulation. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: Why is translation regulation important? What are some examples of translation regulation in humans? Select one of the examples you provided and explain what happens when translation regulation goes wrong.arrow_forward
- The metabolic pathway below is used for the production of the purine nucleotides adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP) in eukaryotic cells. Assume each arrow represents a reaction catalyzed by a different enzyme. Using the principles of feedback inhibition, propose a regulatory scheme for this pathway that ensures an adequate supply of both AMP and GMP, and prevents the buildup of Intermediates A through G when supplies of both AMP and GMP are adequate.arrow_forwardQUESTION 27 Label the structures marked A, B, C and explain the role of structure A. W plasma membrane For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac). BIUS ☐ Paragraph Π " ΩΘΗ Β Open Sans, a... 10pt EEarrow_forwardexamples of synamptomorphyarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax CollegeBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:CengageEssentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:Cengage
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax CollegeBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:CengageEssentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:Cengage





