
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780132273244
Author: Doug Giancoli
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 12Q
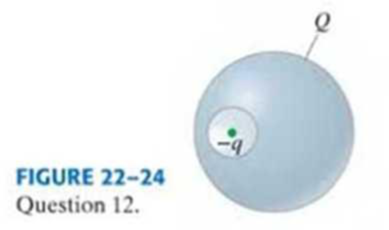
A solid conductor carries a net positive charge Q. There is a hollow cavity within the conductor, at whose center is a negative point charge –q (Fig. 22–24). What is the charge on (a) the outer surface of the conductor and (b) the inner surface of the conductor’s cavity?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A solid conducting sphere is surrounded by a thick, spheical conducting shell. Assume that a total charge +Q+Q is placed at the center of the sphere and released.
a) After equilibrium is reached, the inener surface of the shell will have
b) In terms of QQ, how much charge is on the interior, surface, inner surface, outer surface of the shell?
A point charge of 6.0 nC is placed at the center of a hollow spherical conductor (inner radius = 1.0 cm, outer radius = 2.0 cm) which has a net charge of -4.0 nC. Determine the resulting charge density on the inner surface of the conducting sphere.
7-) A conducting sphere, with an outer radius of 25 cm and an inner radius of 20 cm, has a surface charge density of 6.37 µC / m * 2. A charge of -0.50 µC is introduced into the internal cavity of the sphere. What is the new charge density just outside the sphere?
One of these answers:
-5.5 µC
-4.5 µC
5.5 µC
4.5 µC
Chapter 22 Solutions
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
Ch. 22.1 - Which of the following would cause a change in the...Ch. 22.2 - A point charge Q is at the center of a spherical...Ch. 22.2 - Three 2.95 C charges are in a small box. What is...Ch. 22.3 - A charge Q is placed on a hollow metal ball. We...Ch. 22.3 - CHAPTER-OPENING QUESTIONGuess now! A nonconducting...Ch. 22.3 - Which of the following statements about Gausss law...Ch. 22 - If the electric flux through a closed surface is...Ch. 22 - Is the electric field E in Gausss law....Ch. 22 - A point charge is surrounded by a spherical...Ch. 22 - What can you say about the flux through a closed...
Ch. 22 - The electric field E is zero at all points on a...Ch. 22 - Define gravitational flux in analogy to electric...Ch. 22 - Would Gausss law be helpful in determining the...Ch. 22 - A spherical basketball (a nonconductor) is given a...Ch. 22 - In Example 226, it may seem that the electric...Ch. 22 - Suppose the line of charge in Example 226 extended...Ch. 22 - A point charge Q is surrounded by a spherical...Ch. 22 - A solid conductor carries a net positive charge Q....Ch. 22 - A point charge q is placed at the center of the...Ch. 22 - A small charged ball is inserted into a balloon....Ch. 22 - (I) A uniform electric field of magnitude 5.8 102...Ch. 22 - (I) The Earth possesses an electric field of...Ch. 22 - (II) A cube of side l is placed in a uniform field...Ch. 22 - (II) A uniform field E is parallel to the axis of...Ch. 22 - (I) The total electric flux from a cubical box...Ch. 22 - (I) Figure 2226 shows five closed surfaces that...Ch. 22 - (II) In Fig. 2227, two objects, O1 and O2, have...Ch. 22 - (II) A ring of charge with uniform charge density...Ch. 22 - (II) In a certain region of space, the electric...Ch. 22 - (II) A point charge Q is placed at the center of a...Ch. 22 - (II) A 15.0-cm-long uniformly charged plastic rod...Ch. 22 - (I) Draw the electric field lines around a...Ch. 22 - (I) The field just outside a 3.50-cm-radius metal...Ch. 22 - (I) Starting from the result of Example 223, show...Ch. 22 - (I) A long thin wire, hundreds of meters long,...Ch. 22 - (I) A metal globe has l.50 mC of charge put on it...Ch. 22 - (II) A nonconducting sphere is made of two layers....Ch. 22 - (II) A solid metal sphere of radius 3.00 m carries...Ch. 22 - (II) A 15.0-cm-diameter nonconducting sphere...Ch. 22 - (II) A flat square sheet of thin aluminum foil,...Ch. 22 - (II) A spherical cavity of radius 4.50 cm is at...Ch. 22 - (II) A point charge Q rests at the center of an...Ch. 22 - (II) A solid metal cube has a spherical cavity at...Ch. 22 - (II) Two large, flat metal plates are separated by...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose the two conducting plates in Problem...Ch. 22 - (II) The electric field between two square metal...Ch. 22 - (II) Two thin concentric spherical shells of radii...Ch. 22 - (II) A spherical rubber balloon carries a total...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose the nonconducting sphere of Example...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose in Fig. 2232, Problem 29, there is...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose the thick spherical shell of Problem...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose that at the center of the cavity...Ch. 22 - (II) A long cylindrical shell of radius R0 and...Ch. 22 - (II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of...Ch. 22 - (II) A thin cylindrical shell of radius R1 is...Ch. 22 - (II) A thin cylindrical shell of radius R1 = 6.5...Ch. 22 - (II) (a) If an electron (m = 9.1 1031 kg) escaped...Ch. 22 - (II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of...Ch. 22 - (II) A nonconducting sphere of radius r0 is...Ch. 22 - (II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of...Ch. 22 - (II) A flat ring (inner radius R0, outer radius...Ch. 22 - (II) An uncharged solid conducting sphere of...Ch. 22 - (III) A very large (i.e., assume infinite) flat...Ch. 22 - (III) Suppose the density of charge between r1 and...Ch. 22 - (III) Suppose two thin flat plates measure 1.0 m ...Ch. 22 - (III) A flat slab of nonconducting material (Fig....Ch. 22 - (III) A flat slab of nonconducting material has...Ch. 22 - (III) An extremely long, solid nonconducting...Ch. 22 - (III) Charge is distributed within a solid sphere...Ch. 22 - A point charge Q is on the axis of a short...Ch. 22 - Prob. 51GPCh. 22 - The Earth is surrounded by an electric field,...Ch. 22 - A cube of side has one corner at the origin of...Ch. 22 - A solid nonconducting sphere of radius r0 has a...Ch. 22 - A point charge of 9.20 nC is located at the origin...Ch. 22 - A point charge produces an electric flux of +235 N...Ch. 22 - A point charge Q is placed a distance r0/2 above...Ch. 22 - Three large but thin charged sheets are parallel...Ch. 22 - Neutral hydrogen can be modeled as a positive...Ch. 22 - A very large thin plane has uniform surface charge...Ch. 22 - A sphere of radius r0 carries a volume charge...Ch. 22 - Dry air will break down and generate a spark if...Ch. 22 - Three very large sheets are separated by equal...Ch. 22 - In a cubical volume, 0.70 m on a side, the...Ch. 22 - A conducting spherical shell (Fig. 2249) has inner...Ch. 22 - A hemisphere of radius R is placed in a...Ch. 22 - (III) An electric field is given by...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Johnny was vigorously exercising the only joints in the skull that are freely movable. What would you guess he ...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
A Slice of pizza has 500 kcal. If we could burn the pizza and use all the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
WHAT IF? A chicken has 78 chromosomes in its somatic cells. How many chromosomes did the chicken inherit from ...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Body, Heal Thyself The precision of mitotic cell division is essential for repairing damaged tissues like those...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
16. Explain some of the reasons why the human species has been able to expand in number and distribution to a g...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
1.14 Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture. If a mixture, indicate whether it is homo...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) Determine the magnitude and sign of the point charge at the center of the shell. (b) Determine the charge on the spherical shell.arrow_forwardA point charge of 40 nC is placed at the center of a hollow spherical conductor (inner radius = 1.0 cm, outer radius = 5 cm) which has a net charge of -70nC. Determine the resulting charge density on the outer surface of the conducting sphere.arrow_forwardimagearrow_forward
- 1) In figure (top view of the cylinders), a solid conducting cylinder with radius a =3 cm is given, whose rotation axis is z-axis, and center is at the origin. It is concentric with a hollow cylindrical conductor of inner radius b = 5 cm and outer radius c = 6 cm. Both cylinders have L = 5 m length which can be assumed to be infinitely long. The solid cylinder has total net charge of Qi = 5 nC. The hollow cylinder has net charge Q2 = 10 nC. The reference voltage at the radial distance of p = 8 cm is given as V = -10 Volts. The medium except conductors is free-space. a) What are the voltage values at p= 2, 4 and 5.5 cm? b) What is the total stored electrostatic potential energy due to the charges in the figure? Hint: For surface charge densities, W, =Je.v ds where V is voltage on the source points.arrow_forwardA long copper cylindrical shell of inner radius 2 cm and outer radius 3 cm surrounds concentrically a charged long aluminum rod of radius 1 cm with a charge density of 4 pC/m. All charges on the aluminum rod reside at its surface. The inner surface of the copper shell has exactly charge to that of the aluminum rod while the outer surface of the copper shell has the same charge as the aluminum rod. Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at points that are at the following distances from the center of the aluminum rod: (a) 0.5 cm, (b) 1.5 cm, (c) 2.5 cm, (d) 3.5 cm, and (e) 7 cm.arrow_forwardplease help mearrow_forward
- A spherical conducting shell has a charge of-14 mC on its outer surface and a charged particle in its hollow. If the net charge on the shell is -10 mC, what is the charge (a) on the inner surface of the shell and (b) of the particle?arrow_forwardAn infinite uniform line charge with a linear charge of -11 n C/m presented in x=-3, y=-4 and an infinite uniform sheet with a charge density of 8 n C/m2 presented in z=3, Determines the total charge enclosed with a spherical surface of r=5 centred at the origin?arrow_forward(8) A conducting spherical shell of inner radius a and outer radius b carries a net charge +Q. A point charge +Q is placed at the center of the shell. The charge on the outer surface of radius b of the shell is (a) -Q (b) + Q (c) +3Q (d) + 2Q Conductor barrow_forward
- A neutral conductor contains a hollow cavity in which there is a +100 nC point charge. A charged rod then transfers -50 nC to the conductor. Afterward, what is the charge on (a) the inner wall of the cavity and (b) on the exterior surface of the conductor?arrow_forwardA solid spherical conductor encloses 3 cavities, a cross-section of which are as shown in the figure. A net charge +q resides on the outer surface ofthe conductor. Cavities A and C contain point charges +q and –q, respectively. (TIFR 2015] The net charges on the surfaces ofthese cavities are (a) A=-q, B= q, C = 0 (c) A=+q, B= 0, C = q (b) A==q, B= 0, C==q (d) A=-q, B = 0, C = +qarrow_forward(12-15) Consider two concentric conducting spherical shells. Inner shell carries an excess charge of +2 µC and outer shell carries +2 µC. In the figure, the inner shell has an inner radius of 0.1 m and an outer radius of 0.2 m, and the outer shell has an inner radius of 0.38 m and an outer radius of 0.5 m. darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY