
a.
Construct the percent frequency distribution of field of study for each degree.
a.
Answer to Problem 9E
The percent frequency distribution for bachelor’s degree is given below:
| Bachelor’s degree | Relative frequency | Percent frequency |
| B | 0.21 | 21% |
| CSE | 0.09 | 9% |
| E | 0.06 | 6% |
| H | 0.16 | 16% |
| NSM | 0.08 | 8% |
| O | 0.24 | 24% |
| SBS | 0.16 | 16% |
| Total | 1.00 | 100 |
The percent frequency distribution for Master’s degree is given below:
| Master’s degree | Relative Frequency | Percent frequency |
| B | 0.27 | 27% |
| CSE | 0.09 | 9% |
| E | 0.24 | 24% |
| H | 0.08 | 8% |
| NSM | 0.02 | 2% |
| O | 0.24 | 24% |
| SBS | 0.06 | 6% |
| Total | 1.00 | 100 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The Country U provided 1.8 million bachelor’s degree and 750,000 master’s degree and a sample of 100 graduates is considered. The field of studies of graduates are, Business (B), Computer science and Engineering (CSE), Education (E), Natural sciences and Mathematics (NSM), Social and Behavioral sciences (SBS), and other (O).
For Bachelor’s degree:
Frequency:
The frequencies are calculated using the tally mark. Here, the number of times each class repeats is the frequency of that particular class.
Here, “B (business)” is the department type data that is repeated 21 times in the data set and thus, 21 is the frequency for the category business (B).
Similarly, the frequency of remaining types of network is given below:
| Bachelor’s degree | Tally | Frequency |
| B | 21 | |
| CSE | 9 | |
| E | 6 | |
| H | 16 | |
| NSM | 8 | |
| O | 24 | |
| SBS | 16 | |
| Total | 100 |
Relative frequency:
The general formula for the relative frequency is as follows:
Therefore,
Similarly, the relative frequencies for the remaining types of classes (PPG) are obtained below:
| Bachelor’s degree | Frequency | Relative frequency |
| B | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| CSE | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| E | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| H | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| NSM | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| O | 0.24 | 0.24 |
| SBS | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Total | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Percentage frequency distribution:
The general formula for the percent frequency is as follows:
Therefore,
The percent frequencies for the remaining types of categories of education fields for bachelor degree are obtained below:
| Bachelor’s degree | Relative frequency | Percent frequency |
| B | 0.21 | 21% |
| CSE | 0.09 | 9% |
| E | 0.06 | 6% |
| H | 0.16 | 16% |
| NSM | 0.08 | 8% |
| O | 0.24 | 24% |
| SBS | 0.16 | 16% |
| Total | 1.00 | 100 |
For Master’s degree:
Here, “B (business)” is the department type data that is repeated for 27 times in the data set and thus, 27 is the frequency for the category business (B).
Similarly, the frequency of remaining types of department fields is given below:
| Master’s degree | Tally | Frequency |
| B | 27 | |
| CSE | 9 | |
| E | 24 | |
| H | 8 | |
| NSM | 2 | |
| O | 24 | |
| SBS | 6 | |
| Total | 100 |
Relative frequency:
Similarly, the relative frequencies for the remaining types of classes (PPG) are obtained below:
| Master’s degree | Frequency | Relative frequency |
| B | 27 | 0.27 |
| CSE | 9 | 0.09 |
| E | 24 | 0.24 |
| H | 8 | 0.08 |
| NSM | 2 | 0.02 |
| O | 24 | 0.24 |
| SBS | 6 | 0.06 |
| Total | 100 | 1.00 |
Percentage frequency distribution:
The percent frequencies for the remaining types of categories of education fields for master degree are obtained below:
| Master’s degree | Relative Frequency | Percent frequency |
| B | 0.27 | 27% |
| CSE | 0.09 | 9% |
| E | 0.24 | 24% |
| H | 0.08 | 8% |
| NSM | 0.02 | 2% |
| O | 0.24 | 24% |
| SBS | 0.06 | 6% |
| Total | 1.00 | 100 |
b.
Construct the bar chart for each degree.
b.
Answer to Problem 9E
The bar chart for bachelor’s degree is given below:
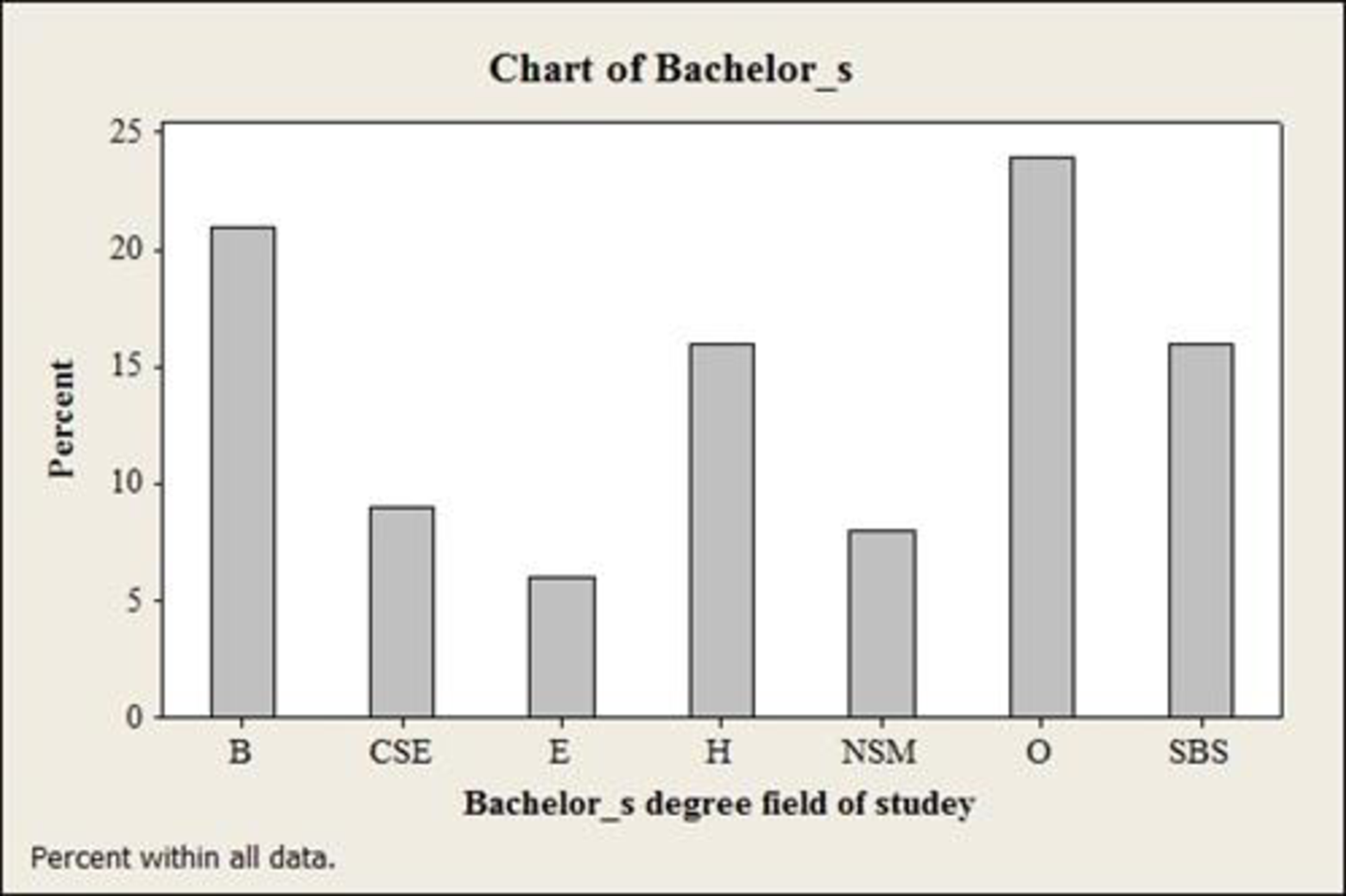
The bar chart for Master’s degree is given below:
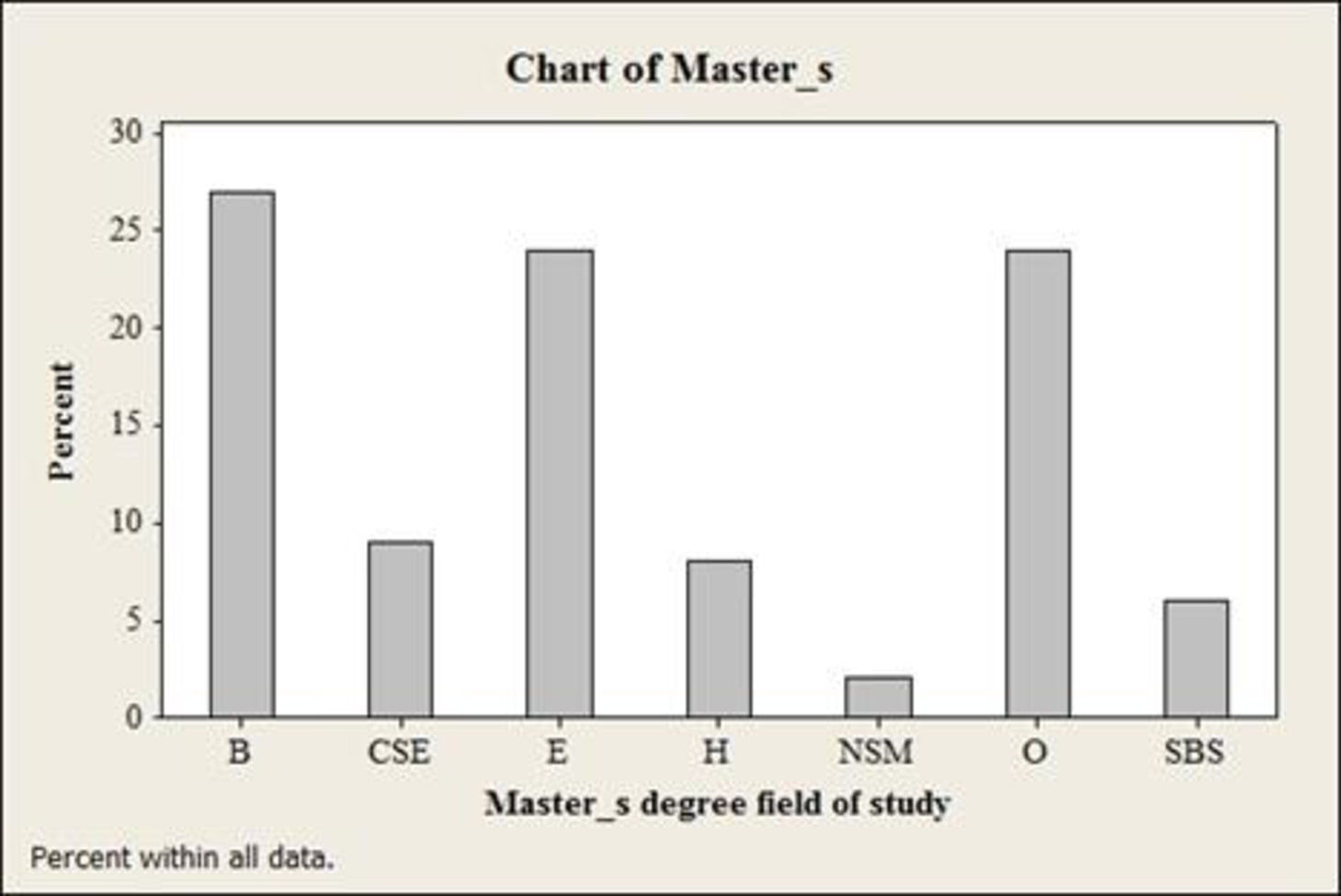
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For Bachelor’s degree:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to draw the bar chart for bachelor’s degree using MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Bar Chart.
- From Bars represent, choose unique values from table.
- Choose Simple. Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Bachelor’s degree.
- Click OK.
- For Master’s degree:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to draw the bar chart for Master’s degree using MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Bar Chart.
- From Bars represent, choose unique values from table.
- Choose Simple. Click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the column of Master’s degree.
- Click OK.
c.
Find the lowest percentage field of study for each degree.
c.
Answer to Problem 9E
The lowest percentage for a Bachelor’ degree is Education.
The lowest percentage for a Master’s degree is Natural science and Mathematics.
Explanation of Solution
For Bachelor’ degree, the percentage for education is 6%, which is low when compared to other categories.
For Master’s degree, the percentage for Natural science and Mathematics is 2%, which is low when compared to other categories.
d.
Find the highest percentage field of study for each degree.
d.
Answer to Problem 9E
The highest percentage for a Bachelor’ degree is Others.
The highest percentage for a Master’s degree is Business.
Explanation of Solution
For Bachelor’ degree, the percentage for others is 24%, which is high when compared to other categories.
For Master’s degree, the percentage for business is 27%, which is high when compared to other categories.
e.
Identify which field of study “Education” has the largest increase in percentage from bachelor’s to masters’.
e.
Answer to Problem 9E
The field of study “Education” has the largest increase in percentage from bachelor’s to masters’.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
In order to the obtain the study field that has the largest increase in percentage from bachelor’s to
Master, the difference between two respective percentages is calculated.
Therefore,
The differences between two fields are tabulated below:
| Field | Bachelor’s | Master’s | Difference |
| B | 21% | 21% | 6% |
| CSE | 9% | 9% | 0% |
| E | 6% | 6% | 18% |
| H | 16% | 16% | |
| NSM | 8% | 8% | |
| O | 24% | 24% | |
| SBS | 16% | 16% |
From the table, it is observed that the field of study “Education” has the largest increase in percentage from bachelor’s to masters’.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIALS OF STATISTICS FOR BUSINE
- TIP the aren't, the data are not sym 11 Suppose that the average salary at a certain company is $100,000, and the median salary is $40,000. a. What do these figures tell you about the shape of the histogram of salaries at this company? b. Which measure of center is more appro- priate here? c. Suppose that the company goes through a salary negotiation. How can people on each side use these summary statistics to their advantage? 6360 be 52 PART 1 Getting Off to a Statistically Significant Sarrow_forward12 Suppose that you know that a data set is skewed left, and you know that the two measures of center are 19 and 38. Which figure is the mean and which is the median?arrow_forwardy of 45 home- televisions u find that 010020 le own one, ee, and 1 owns y histogram of 4 Suppose that you have a loaded die. You roll it several times and record the outcomes, which are shown in the following figure. Histogram for Loaded Die 444% 34.00 48% 6% 2% Frequency 20 20 15 155 10 5- ம 0 1 2 3 4 Outcome 5 6 a. Make a relative frequency histogram of these results. b. You can make a relative frequency histo- gram from a frequency histogram; can you go the other direction?arrow_forward
- Calculate the mean for Study Hours and Test Scores. Compute the covariance between the two variables using the formula: Calculate the standard deviation for Study Hours (X) and Test Scores (Y). Determine the correlation coefficient Interpret the results: What does the calculated r-value indicate about the relationship between study hours and test scores?arrow_forwardFor unemployed persons in the United States, the average number of months of unemployment at the end of December 2009 was approximately seven months (Bureau of Labor Statistics, January 2010). Suppose the following data are for a particular region in upstate New York. The values in the first column show the number of months unemployed and the values in the second column show the corresponding number of unemployed persons. Months Unemployed Number Unemployed 1 1029 2 1686 3 2269 4 2675 5 3487 6 4652 7 4145 8 3587 9 2325 10 1120 Let x be a random variable indicating the number of months a person is unemployed. a. Use the data to develop an empirical discrete probability distribution for x (to 4 decimals). (x) f(x) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 b. Show that your probability distribution satisfies the conditions for a valid discrete probability distribution. The input in the box below will not be graded, but may be reviewed and considered by your instructor. blank c. What is the probability that a…arrow_forwardWest Virginia has one of the highest divorce rates in the nation, with an annual rate of approximately 5 divorces per 1000 people (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website, January 12, 2012). The Marital Counseling Center, Inc. (MCC) thinks that the high divorce rate in the state may require them to hire additional staff. Working with a consultant, the management of MCC has developed the following probability distribution for x = the number of new clients for marriage counseling for the next year. Excel File: data05-19.xls x 10 f(x) .05 20 30 .10 .10 40 .20 50 60 .35 .20 a. Is this probability distribution valid? - Select your answer- Explain. f(x) Σf(x) Select your answer Select your answer b. What is the probability MCC will obtain more than 30 new clients (to 2 decimals)? c. What is the probability MCC will obtain fewer than 20 new clients (to 2 decimals)? d. Compute the expected value and variance of x. Expected value Variance clients per year squared clients per yeararrow_forward
- For unemployed persons in the United States, the average number of months of unemployment at the end of December 2009 was approximately seven months (Bureau of Labor Statistics, January 2010). Suppose the following data are for a particular region in upstate New York. The values in the first column show the number of months unemployed and the values in the second column show the corresponding number of unemployed persons. Months Unemployed Number Unemployed 1 1029 2 1686 3 2269 4 2675 5 3487 6 4652 7 4145 8 3587 9 2325 10 1120 Let x be a random variable indicating the number of months a person is unemployed. a. Use the data to develop an empirical discrete probability distribution for x (to 4 decimals). (x) f(x) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 b. Show that your probability distribution satisfies the conditions for a valid discrete probability distribution. The input in the box below will not be graded, but may be reviewed and considered by your instructor. c. What is the probability that a person…arrow_forwardIn Gallup's Annual Consumption Habits Poll, telephone interviews were conducted for a random sample of 1014 adults aged 18 and over. One of the questions was "How many cups of coffee, if any, do you drink on an average day?" The following table shows the results obtained (Gallup website, August 6, 2012). Excel File: data05-23.xls Number of Cups per Day Number of Responses 0 365 264 193 3 4 or more 91 101 Define a random variable x = number of cups of coffee consumed on an average day. Let x = 4 represent four or more cups. Round your answers to four decimal places. a. Develop a probability distribution for x. x 0 1 2 3 4 f(x) b. Compute the expected value of x. cups of coffee c. Compute the variance of x. cups of coffee squared d. Suppose we are only interested in adults that drink at least one cup of coffee on an average day. For this group, let y = the number of cups of coffee consumed on an average day. Compute the expected value of y. Compare it to the expected value of x. The…arrow_forwardIn Gallup's Annual Consumption Habits Poll, telephone interviews were conducted for a random sample of 1014 adults aged 18 and over. One of the questions was "How many cups of coffee, if any, do you drink on an average day?" The following table shows the results obtained (Gallup website, August 6, 2012). Excel File: data05-23.xls Number of Cups per Day Number of Responses 0 365 264 193 2 3 4 or more 91 101 Define a random variable x = number of cups of coffee consumed on an average day. Let x = 4 represent four or more cups. Round your answers to four decimal places. a. Develop a probability distribution for x. x 0 1 2 3 f(x) b. Compute the expected value of x. cups of coffee c. Compute the variance of x. cups of coffee squared d. Suppose we are only interested in adults that drink at least one cup of coffee on an average day. For this group, let y = the number of cups of coffee consumed on an average day. Compute the expected value of y. Compare it to the expected value of x. The…arrow_forward
- A technician services mailing machines at companies in the Phoenix area. Depending on the type of malfunction, the service call can take 1, 2, 3, or 4 hours. The different types of malfunctions occur at about the same frequency. Develop a probability distribution for the duration of a service call. Duration of Call x f(x) 1 2 3 4 Which of the following probability distribution graphs accurately represents the data set? Consider the required conditions for a discrete probability function, shown below.Does this probability distribution satisfy equation (5.1)?Does this probability distribution satisfy equation (5.2)? What is the probability a service call will take three hours? A service call has just come in, but the type of malfunction is unknown. It is 3:00 P.M. and service technicians usually get off at 5:00 P.M. What is the probability the service technician will have to work overtime to fix the machine today?arrow_forwardA psychologist determined that the number of sessions required to obtain the trust of a new patient is either 1, 2, or 3. Let x be a random variable indicating the number of sessions required to gain the patient's trust. The following probability function has been proposed. x f(x) for x = 1, 2, or 3 a. Consider the required conditions for a discrete probability function, shown below. f(x) ≥0 Σf(x) = 1 (5.1) (5.2) Does this probability distribution satisfy equation (5.1)? Select Does this probability distribution satisfy equation (5.2)? Select b. What is the probability that it takes exactly 2 sessions to gain the patient's trust (to 3 decimals)? c. What is the probability that it takes at least 2 sessions to gain the patient's trust (to 3 decimals)?arrow_forwardA technician services mailing machines at companies in the Phoenix area. Depending on the type of malfunction, the service call can take 1, 2, 3, or 4 hours. The different types of malfunctions occur at about the same frequency. Develop a probability distribution for the duration of a service call. Which of the following probability distribution graphs accurately represents the data set? Consider the required conditions for a discrete probability function, shown below.Does this probability distribution satisfy equation (5.1)?Does this probability distribution satisfy equation (5.2)? What is the probability a service call will take three hours? A service call has just come in, but the type of malfunction is unknown. It is 3:00 P.M. and service technicians usually get off at 5:00 P.M. What is the probability the service technician will have to work overtime to fix the machine today?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

