
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119472780
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 21, Problem 62P
SSM In Fig. 21-44, what are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the net electrostatic force on particle 4 due to the other three particles? All four particles are fixed in the xy plane, and q1 = −3.20 × 10−19 C, q2 = +3.20 × 10−19 C, q3 = +6.40 × 10−19 C, q4 = +3.20 × 10−19 C, θ1 = 35.0°, d1 = 3.00 cm, and d2 = d3 = 2.00 cm.
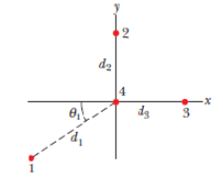
Figure 21-44 Problem 62.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X.
904
80-
70-
60-
50-
I/MA
40-
30-
20-
10-
0+
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
VIV
Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit.
A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA.
4.0V
4.0V
Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit.
(a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1]
(b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3]
(b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1]
(c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider
is moved from Q to P. [1]
(c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider
arrangement over the arrangement in (b).
1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A.
The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N.
(a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2]
(b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2]
(c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown.
wire P
wire R
wire Q
0.05 m
0.05 m
The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero.
(c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1]
(c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]
2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal.
V
A
50.00
(a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell.
The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor.
V
A
50.00
R
(b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m²,
resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation
R = KL
where k is a constant.
(b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2]
(b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2]
(c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3]
[2]
Chapter 21 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-11 shows 1 four situations in which five...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-12 shows three pairs of identical...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-13 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-14 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-15, a central particle of charge q is...Ch. 21 - A positively charged ball is brought close to an...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-16 shows three situations involving a...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-17 shows four arrangements of charged...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-18 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-19, a central particle of charge 2q is...
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-20 shows three identical conducting...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-21 shows four situations in which a...Ch. 21 - SSM ILW Of the charge Q initially on a tiny...Ch. 21 - Identical isolated conducting spheres 1 and 2 have...Ch. 21 - SSM What must be the distance between point charge...Ch. 21 - In the return stroke of a typical lightning bolt,...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge 3.00 106 C is 12.0 cm...Ch. 21 - ILW Two equally chained particles are held 3.2 ...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-23, three charged particles lie on an x...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-24, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square....Ch. 21 - ILW In Fig. 21-25, the particles have charges q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge l.0 C and...Ch. 21 - Three particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO The charges and coordinates of two charged...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-27a, particle l of charge q1 and...Ch. 21 - In Fig.21-28a, particles 1 and 2 have charge 20.0...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-29a, three positively charged particles...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge q and...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-30a shows an arrangement of three...Ch. 21 - GO A nonconducting spherical shell, with an inner...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-31 shows an arrangement of four...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-32, particles 1 and 2 of charge q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two tiny, spherical water drops, with identical...Ch. 21 - ILW How many electrons would have to be removed...Ch. 21 - Prob. 26PCh. 21 - SSM The magnitude of the electrostatic force...Ch. 21 - A current of 0.300 A through your chest can send...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-33, particles 2 and 4, of charge e,...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-26, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - ILW Earths atmosphere is constantly bombarded by...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-34a shows charged particles 1 and 2...Ch. 21 - Calculate the number of coulombs of positive...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-35 shows electrons 1 and 2 on an x...Ch. 21 - SSM In crystals of the salt cesium chloride,...Ch. 21 - Electrons and positrons are produced by the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 37PCh. 21 - GO Figure 21-37 shows four identical conducting...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-38, particle 1 of charge 4e is...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-23, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - a What equal positive charges would have to be...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-39, two tiny conducting balls of...Ch. 21 - a Explain what happens to the balls of Problem 42...Ch. 21 - SSM How far apart must two protons be if the...Ch. 21 - How many megacoulombs of positive charge are in...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-40, four particles are fixed along an x...Ch. 21 - GO Point charges of 6.0 C and 4.0 C are placed on...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-41, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - A neutron consists of ore up quark of charge 2e/3...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-42 shows a long, nonconducting, massless...Ch. 21 - A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 2.00...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge Q is Fixed at the origin of...Ch. 21 - What would be the magnitude of the electrostatic...Ch. 21 - A charge of 6.0 C is to be split into two parts...Ch. 21 - Of the charge Q on a tiny sphere, a fraction is...Ch. 21 - If a cat repeatedly rubs against your cotton...Ch. 21 - We know that the negative charge on the electron...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-26, particle 1 of charge 80.0C and...Ch. 21 - What is the total charge in coulombs of 75.0 kg of...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-43, six charged particles surround...Ch. 21 - Three charged particles form a triangle: particle...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-44, what are the a magnitude and b...Ch. 21 - Two point charges of 30 nC and 40 nC are held...Ch. 21 - Two small, positively charged spheres have a...Ch. 21 - The initial charges on the three identical metal...Ch. 21 - An electron is in a vacuum near Earths surface and...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge 5.00q and...Ch. 21 - Two engineering students, John with a mass of 90...Ch. 21 - In the radioactive decay of Eq. 21-13, a 238U...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square. The...Ch. 21 - In a spherical metal shell of radius R, an...Ch. 21 - An electron is projected with an initial speed vl...Ch. 21 - In an early model of the hydrogen atom the Bohr...Ch. 21 - A100 W lamp has a steady current of 0.83 A in its...Ch. 21 - The charges of an electron and a positron are e...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain why decomposition rates in a field in Nebraska would differ from the decomposition rates in a field in ...
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Name the components (including muscles) of the thoracic cage. List the contents of the thorax.
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
PRACTICE PROBLEM 15.9
Provide a mechanism for the following reaction and explain why it occurs faster than nitr...
Organic Chemistry
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. According to Keplers third law. (a) Me...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Your microbiology lab maintains reference bacterial cultures, which are regularly transferred to new nutrient a...
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
The number of moles of H+ in 15 mL of 0.025 M HCl solution needs to be determined. Concept Introduction: pH of ...
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forward
- A certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forward
- A 11.8 L gas tank containing 3.90 moles of ideal He gas at 26.0°C is placed inside a completely evacuated insulated bell jar of volume 39.0 L .A small hole in the tank allows the He to leak out into the jar until the gas reaches a final equilibrium state with no more leakage. Part A What is the change in entropy of this system due to the leaking of the gas? ■ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AS = ? J/K Submit Request Answer Part B Is the process reversible or irreversible?arrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forwardThree moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward
- 5.97 Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. Figure P5.97 B A S 36.9°arrow_forwardPlease take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardhelp me answer this with explanations! thanks so mucharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY