
Interpretation: The given
Concept Introduction: In an
Explanation of Solution
The given diagram is as follows:
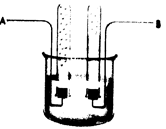
In the electrolysis of brine, electrolyte other than water is taken which can be more easily oxidized or reduced is taken. This will result in the formation of products of electrolysis other than hydrogen and oxygen. In the electrolysis of brine, the aqueous solution of sodium chloride is taken.
This results in the formation of three products that is chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and sodium hydroxide. In the electrolysis process, oxidation of chloride ions takes place at the anode to form chlorine gas. The reduction reaction of water takes place to form hydrogen gas at the cathode. Here, water molecules get easily reduced to hydrogen gas as compared to sodium ions; thus, sodium metal is not formed.
Here, the electrolyte solution becomes sodium hydroxide as the reduction of water also produces hydroxide ions.
The reactions at the cathode and anode are represented as follows:
Anode-Oxidation:
Cathode-Reduction:
Thus, the overall reaction will be:
Here, a spectator sodium ion is also introduced in the reaction. Thus, the overall reaction becomes:
Thus, the given diagram can be modified to show the electrolysis of brine as follows:
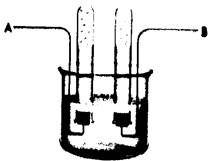
It shows the same amount of hydrogen and chlorine gas produced in the reaction as the number of moles are same.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. ? NH2 MgBr Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? ○ Yes ○ No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? O Yes O No Click and drag to start drawing a structure. :☐ G x c olo Ar HEarrow_forwardPredicting As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C - C bond as its major product: H₂N O H 1. ? 2. H3O+ If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. 0 If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. فا Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardHighlight the chirality (or stereogenic) center(s) in the given compound. A compound may have one or more stereogenic centers. OH OH OH OH OH OHarrow_forward
- Using wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration. NH H Br X टेarrow_forwardProvide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forward
- Given a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





