
Concept explainers
(a)
To check: Whether the statement
(a)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
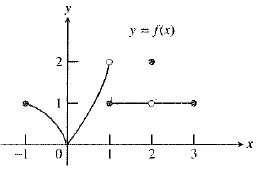
As observed from the graph, the function
Therefore, the statement
(b)
To check: Whether the statement
(b)
Answer to Problem 44E
The statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
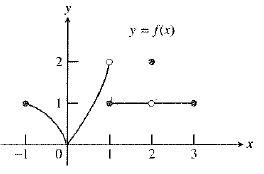
As observed from the graph, the function
So, the limit
Therefore, the statement
(c)
To check: Whether the statement
(c)
Answer to Problem 44E
The statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
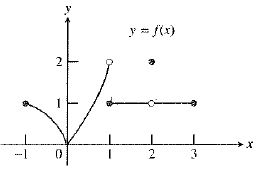
As calculated in part (b), the left hand limit and right hand limit is equal to
So, the value of
Therefore, the statement
(d)
To check: Whether the statement
(d)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
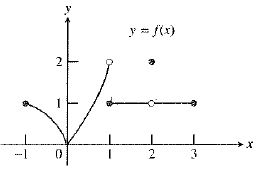
As observed from the graph, the function
Therefore, the statement
(e)
To check: Whether the statement
(e)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
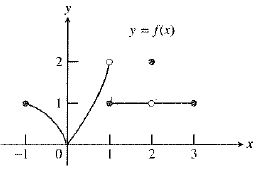
As observed from the graph, the function
Therefore, the statement
(f)
To check: Whether the statement
(f)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
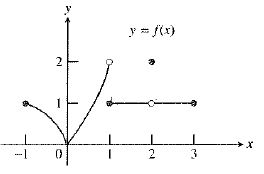
As calculated in part (d), the value
As calculated in part (e), the value
Both the left hand and right hand limits are not equal at
Therefore, the statement
(g)
To check: Whether the statement
(g)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
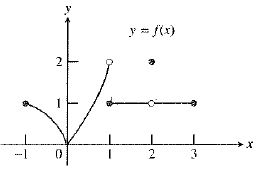
As observed from the graph, the function
So, the value of both
Therefore, the statement
(h)
To check: Whether the statement
(h)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
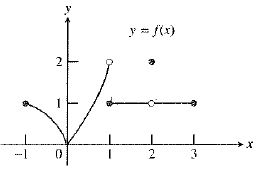
As observed from the graph, the function
So, the value
Therefore, the statement
(i)
To check: Whether the statement
(i)
Answer to Problem 44E
Yes, the statement
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function is:
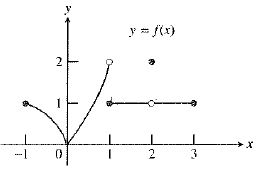
As observed from the graph, the function
So, the value
Therefore, the statement
Chapter 2 Solutions
Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra (7th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- explain of logical relationships of (11.1.1), (11.1.2), (11.3.4), (11.3.6)arrow_forwardProve 11.1.2arrow_forward39. (a) Show that Σeak converges for each α > 0. (b) Show that keak converges for each a > 0. k=0 (c) Show that, more generally, Σk"eak converges for each k=0 nonnegative integer n and each a > 0.arrow_forward
- #3 Find the derivative y' = of the following functions, using the derivative rules: dx a) y-Cos 6x b) y=x-Sin4x c) y=x-Cos3x d) y=x-R CD-X:-:TCH :D:D:D - Sin f) Sin(x²) (9) Tan (x³)arrow_forwardmate hat is the largest area that can be en 18 For the function y=x³-3x² - 1, use derivatives to: (a) determine the intervals of increase and decrease. (b) determine the local (relative) maxima and minima. (c) determine the intervals of concavity. (d) determine the points of inflection. b) (e) sketch the graph with the above information indicated on the graph.arrow_forwarduse L'Hopital Rule to evaluate the following. a) 4x3 +10x2 23009׳-9 943-9 b) hm 3-84 хто бу+2 < xan x-30650)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





