
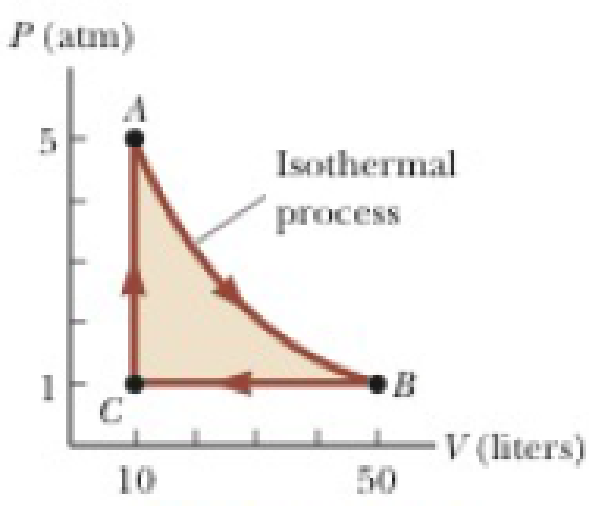
A 1.00-mol sample of an ideal monatomic gas is taken through the cycle shown in Figure P21.37. The process A → B is a reversible isothermal expansion. Calculate (a) the net work done by the gas, (b) the energy added to the gas by heat, (c) the energy exhausted from the gas by heat, and (d) the efficiency of the cycle. (e) Explain how the efficiency compares with that of a Carnot engine operating between the same temperature extremes.
Figure P21.37
(a)
The net work done by the gas.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The net work done by the gas is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
The formula for the net work done by the gas at
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the net work done by the gas at
The formula for the net work done by the gas at
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the net work done by the gas at BC is
The formula for the net work done by the gas at
As the change in the volume between processes
Thus, the net work done by the gas at
The formula for the total work done by the gas is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the total work done is
(b)
The energy added to the gas by heat.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The energy added to the gas by heat is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at
The formula for the energy added by the gas in process
Substitute
Thus, the energy added by the gas in process
The formula for temperature at
Substitute
Thus, the temperature at
The formula for temperature at
Substitute
Thus, the temperature at
The formula for the energy added by the gas in process
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the energy added in process
The formula for the total energy added is,
Substitute
Thus, the total energy added is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the total energy added is
(c)
The energy exhausted from the gas by heat.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The energy exhausted from the gas by heat is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
The formula for the energy added by the gas in process
Substitute
Thus, the energy exhausted in process
Conclusion:
Therefore, the energy exhausted in process
(d)
The efficiency of the cycle.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The efficiency of the cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
Formula to calculate the efficiency of the engine is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the efficiency of the engine is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the efficiency of the engine is
(e)
The comparison of efficiency to that of the Carnot engine.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The efficiency of Carnot engine is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
Formula to calculate the efficiency of the Carnot engine is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the efficiency of Carnot engine is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Serway/jewett's Physics For Scientists And Engineers, 10th, Single-term
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- Considering the cross-sectional area shown in Fig.2: 1. Determine the coordinate y of the centroid G (0, ỹ). 2. Determine the moment of inertia (I). 3. Determine the moment of inertia (Ir) (with r passing through G and r//x (// parallel). 4 cm 28 cm G3+ G 4 cm y 12 cm 4 cm 24 cm xarrow_forwardI need help understanding 7.arrow_forwardThe stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy is given in fig. 3. Determine the modulus of elasticity (E). σ (ksi) 40 30 20 10 0 0 0.0005 0.001 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 0.0030.0035 Earrow_forward
- A Van de Graff generator, if the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each other using Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force. Give your answer as the number of Coulombsarrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following question. I am having trouble understanding the directions of the things the question is asking for. Please include a detailed explanation and possibly drawings of the directions of Bsource, Binduced, and Iinduced.arrow_forward43. A mass må undergoes circular motion of radius R on a hori- zontal frictionless table, con- nected by a massless string through a hole in the table to a second mass m² (Fig. 5.33). If m₂ is stationary, find expres- sions for (a) the string tension and (b) the period of the circu- lar motion. m2 R m₁ FIGURE 5.33 Problem 43arrow_forward
- CH 70. A block is projected up an incline at angle 0. It returns to its initial position with half its initial speed. Show that the coefficient of ki- netic friction is μk = tano.arrow_forwardPassage Problems A spiral is an ice-skating position in which the skater glides on one foot with the other foot held above hip level. It's a required element in women's singles figure-skating competition and is related to the arabesque performed in ballet. Figure 5.40 shows Canadian skater Kaetlyn Osmond executing a spiral during her medal-winning perfor- mance at the 2018 Winter Olympics in Gangneung, South Korea. 77. From the photo, you can conclude that the skater is a. executing a turn to her left. b. executing a turn to her right. c. moving in a straight line out of the page. 78. The net force on the skater a. points to her left. b. points to her right. c. is zero. 79. If the skater were to execute the same maneuver but at higher speed, the tilt evident in the photo would be a. less. b. greater. c. unchanged. FIGURE 5.40 Passage Problems 77-80 80. The tilt angle 0 that the skater's body makes with the vertical is given ap- proximately by 0 = tan¯¹(0.5). From this you can conclude…arrow_forwardFrictionless surfarrow_forward
- 71. A 2.1-kg mass is connected to a spring with spring constant 72 k = 150 N/m and unstretched length 18 cm. The two are mounted on a frictionless air table, with the free end of the spring attached to a frictionless pivot. The mass is set into circular mo- tion at 1.4 m/s. Find the radius of its path. cor moving at 77 km/h negotiat CH —what's the minimum icient of frictioarrow_forward12. Two forces act on a 3.1-kg mass that undergoes acceleration = 0.91 0.27 m/s². If one force is -1.2î – 2.5ĵ N, what's the other?arrow_forward36. Example 5.7: You whirl a bucket of water around in a vertical circle of radius 1.22 m. What minimum speed at the top of the circle will keep the water in the bucket?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





