
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 32P
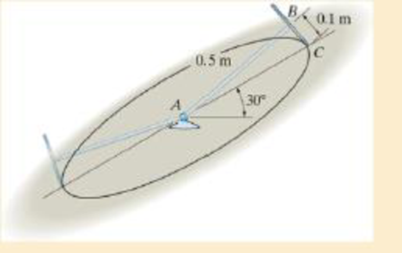
The 2-kg thin disk is connected to the slender rod which is fixed to the ball-and-socket joint at A. If it is released from rest in the position shown, determine the spin of the disk about the rod when the disk reaches its lowest position. Neglect the mass of the rod. The disk rolls without slipping.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Solve the following problem by hand and without the use of AI. Thank You!
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Chapter 21 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 21 - Show that the sum of the moments of inertia of a...Ch. 21 - Prob. 2PCh. 21 - Prob. 3PCh. 21 - Determine the moments of inertia Ix and Iy of the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 5PCh. 21 - Determine by direct integration the product of...Ch. 21 - Prob. 9PCh. 21 - Prob. 10PCh. 21 - Determine the moment of inertia Ixx of the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 21 - Prob. 14PCh. 21 - Prob. 15PCh. 21 - The bent rod has a weight of 1.5 lb/ft. Locate the...Ch. 21 - If a body contains no planes of symmetry, the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 23PCh. 21 - Prob. 25PCh. 21 - Prob. 28PCh. 21 - Prob. 29PCh. 21 - Prob. 30PCh. 21 - The 2-kg thin disk is connected to the slender rod...Ch. 21 - Prob. 33PCh. 21 - Prob. 36PCh. 21 - Prob. 37PCh. 21 - Prob. 40PCh. 21 - Prob. 41PCh. 21 - Prob. 42PCh. 21 - Prob. 48PCh. 21 - Prob. 51PCh. 21 - Prob. 54PCh. 21 - Show that the angular velocity of a body, in terms...Ch. 21 - A thin rod is initially coincident with the Z axis...Ch. 21 - The top consists of a thin disk that has a weight...Ch. 21 - Prob. 66PCh. 21 - Prob. 69PCh. 21 - Prob. 70PCh. 21 - Prob. 73PCh. 21 - Prob. 74PCh. 21 - Prob. 77P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward(B) A ductile solid rod, of initial area (25mm) and initial gauge length (8cm), show this tabular data during simple tension process Tensile load in (N) Elongation (mm) 4220.0310 17.7122 4317.3340 33.5254 4225.6478 45.465 Determine the Ludwik model coefficients of this rod numerically. (12.5M) 3957.9528 67.6031arrow_forward### Fluid-Mechanical Circuits Develop the circuit of a drill in the FluidSim, observing the following requirements: 1. The design and assembly of the Hydraulic Circuit drive (clamping and working), with the following characteristics: a. Sequential operation, put pressure, for the advance and return of the cylinders (according to the proper operation for the device) controlled by a directional 4x3 electric drive way; 2. The circuit must provide for different speed ranges for drilling work in order to allow different materials to be processed. Note: Set the safety valve to 55 bar. *The drill is attached in a figurearrow_forward
- Solve the following question by hand and without the use of AI. Thank You!arrow_forwardthe answers you provided is very blury to this homework equation can you resendarrow_forwardQ100 The following data refers to a test on a single-cylinder four-stroke oil engine Cylinder bore 220 mm; stroke 360 mm; area of indicator diagram 360mm ²; length of diagram 40mm; indicator spring rating = 1.25 mm/bar; Speed 300 rev/min brake load 441.3 N at 0.9m radius; fuel consumption 3.8 Kg/hr; Calorific value of fuel 43124 kj/kg; Cooling water flow 3.8kg/hr; rise in temperature of cooling water 48K; and specific heat capacity of water 4.1868 kj lkg. k. god valamily Calculate: @the mechanical efficiency the indicated thermal efficiency lo The heat balance sheet expressed as kj/min andas percentage of the heat supplied to the engine.arrow_forward
- Q In a test on a two.. strok, heavy oil, marine engine, the following observations were made: Oil consumption, 4.05 kg/h; Calorific value of oil, 43000kj/kg; het brake load 579N; Mean brake diameter, 1m; mean effective pressure 275 kN/m²; cylinder diameter 0.20m; stroke, 0.250m; speed, 360 rpm. Calculate the mechanical efficiency the indicated thermal efficiency Y The brake thermal efficiency and the quantity of jacket water required per مسموح به امتصت minute if 30% of the energy supplied by the fuel is absorbed by this water. Permissible rise in temperature is 20k and specific heat capacity of water-4.1868 kj Answers [84.2%, 26-8%, 22.6%, 8.33 kg/min] kg.k عماد داود عبودarrow_forwardQ78 A four cylinder, four-stroke Petrol engine has a compression ratio of 6 to 1. A test on this engine gave the following results; Net brake load = 20 kg, effective brake arm = 0.5 m, indicated mep=6*105 N/m², engine speed 2400 rpm, fuel consumption = 10 kg/h, Calorific value of the fuel = 44000kj/kg, Cylinder bore 86 mm, engine stroke-100mm. ข่าวล Calculate: the mechanical efficiency, ⑥the brake thermal efficiency the relative efficiency assuming the engine works on the Constant volume cycle and that 8-1.4 forair ⑧The brake mean effective pressure. Answers 1 88.4%, 48/5-35 × 105 N/m² 1 و وarrow_forwardHom Work عماد داود عبور (35) Q18 The Fiat car has a four strok engine of 1089 C.C capacity.It develops maximum power 32kw at 5000 r.p.m. The volumetric efficiency at this speed is 75% and the air-fuel ratio 13:1, At peak power the theoretical air speed at the choke is 120 m/sec. The coefficient of discharge for the venturi is 0.85 and that of the main petrol jet is 0.66. An allowance should be made for the emulsion tube, the diameter of which can be taken as (1/2.5) of the choke diameter. the Petrol surface is 6 mm blow the choke at this engine condition. Calculate the size of a suitable choke (D) and main jet (d).The specific gravity of Petrol is 0.75 andthe Latmospheric pressure 1.03 bar and temperature 27°c. [D=23.2mm,d=1.296mm]arrow_forward
- Q8: A test carried out on a single cylinder, two. Stroke oil engine gave the following data: Cylinder bore = 200 mm, stroke 250mm, engine speed = 300 rpm, net brake torque 500N.m indicated mean effective Pressure = 4.9*105 N/m², fuel consumption = 5kg/min, Cooling water. rate of flow = 0.0666 kg/sec, temperature rise of cooling water-55k, specific heat capacity of water =4.1868 kj/kg.k. calculate the mechanical efficiency, the specific fuel consumption, and draw up an energy balance in kw. Answers [@ 81.6, 0.318 kg/kW.hr, © Qtotal = 61.1kw,- Qb.p = 15.7 Kw₂ & Cooling water = 15.35kw,Q Exhaust = 30.05 kw]arrow_forwardQ6: A single cylinder oil engine has a compression ratio of 1081. The specific fuel cons umption is 0.6 kg/kw.h, the calorific value of the fuel oil is 44000kj/kg.199 calculate the thermal efficiency and the relative efficiency, assuming the engine operates on the constant volume cycle. Take 8=1.4 for air Answers [13.6% 22.6%] 2199arrow_forwardQ7: An amount of a perfect gas has initial conditions of volume (1 m³), pressure (1 bar) and temperature (18 °C). It undergoes ideal Diesel cycle operation, the pressure after isentropic compression being (50 bar) and the volume after constant pressure expansion being (0.1 m³). Calculate the temperature at the major points of the cycle and evaluate the thermal efficiency of the cycle. Assume y=1.4 for the gas Answers T2-890 K, T3 1455 K, T4-579 K, 63.59%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Column buckling; Author: Amber Book;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AvvaCi_Nn94;License: Standard Youtube License